Gas Laws
advertisement

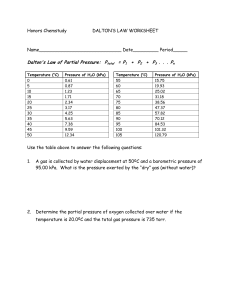
March 15, 2012 Quiz 1. According to Boyle’s Law, at constant temperature, pressure and volume are inversely related. As volume decreases the pressure increases. Explain WHY this is the case. 2. According to Charles’s Law, at constant pressure, temperature and volume are directly related. As temperature increases the volume increases as well. Explain WHY they are directly related. 3. According to Gay-Lussac’s Law, at constant volume, pressure and temperature are directly related. As temperature increases the pressure increases. Explain WHY. Today’s Objective Analyze and solve problems involving the Combined Gas Law and Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures Combined Gas Law Combination of each of the three basic gas laws: Boyle’s, Charles’s and GayLussac’s. Combined Gas Law Equation: P1V1 = P2V2 T1 T2 Combined Gas Law Example 1 A 2.30 L balloon is taken from the base of a mountain (15°C and 570mm Hg) to halfway up the mountain (-15°C and 425mm Hg) How big is the balloon? Combined Gas Law Example 2 A sealed metal container (250.0 mL, 1.0 atm, 25°C) is placed in a furnace that is at 500°C. What will be the final pressure? Combined Gas Law Example 3 A gas at 110 kPa and 30.0°C fills a flexible container with an initial volume of 2.00 L. If the temperature is raised to 80.0°C and pressure increased to 440 kPa, what is the new volume? Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures Developed by John Dalton in 1805. States that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases. Partial Pressure: Pressure of each gas in a mixture. Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures Equation: Ptotal = PA + PB + PC … Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures Example 1 A sealed container contains Hydrogen gas with a partial pressure of 80.0 kPa and Nitrogen with a partial pressure of 30.0 kPa. What is the total pressure in the container? Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures Example 2 A cylinder contains Helium and Argon. The total pressure is 5.00 atm. The partial pressure of Helium is 3.50 atm. What is the partial pressure of the Argon? Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures Example 3 A planet is discovered that contains 30.0% CO2 and 70.0% CH4 and has a total pressure of 60.0 kPa. What is the partial pressure of each gas in the atmosphere? Homework Combined Gas Law Worksheet Dalton’s Partial Pressure Worksheet Both are on the website!