Chapter 8 Section 2
advertisement
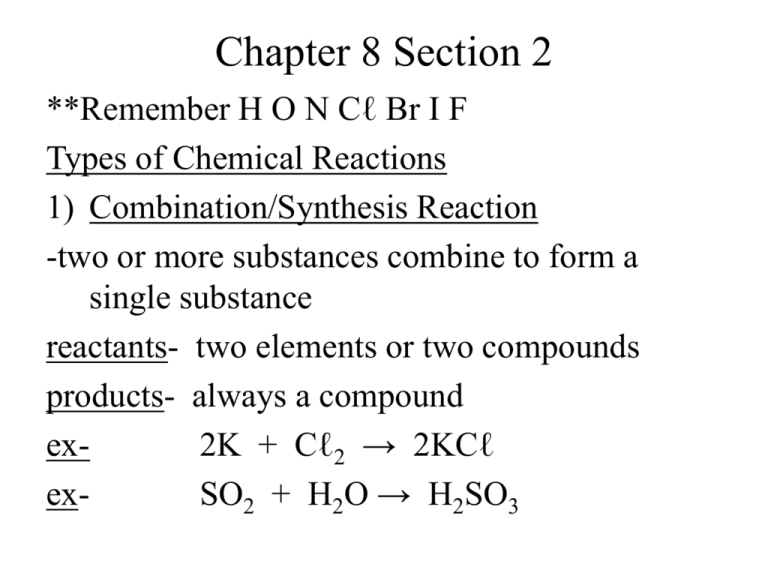
Chapter 8 Section 2 **Remember H O N Cℓ Br I F Types of Chemical Reactions 1) Combination/Synthesis Reaction -two or more substances combine to form a single substance reactants- two elements or two compounds products- always a compound ex2K + Cℓ2 → 2KCℓ exSO2 + H2O → H2SO3 Try these!! Don’t forget to balance!! a) aluminum + oxygen → Aℓ + O2 → Aℓ + O2 → Aℓ2O3 b) beryllium + oxygen → Be + O2 → Be + O2 → BeO c) strontium + iodine → Sr + I2 → Sr + I2 → SrI2 d) magnesium + nitrogen → Mg + N2 → Mg + N2 → Mg3N2 2) Decomposition Reaction -one compound breaks down or decomposes into two simpler compounds -the reverse of synthesis ex- 2H2O → 2H2 + O2 Try these!! a) lead(IV) oxide → PbO2 → PbO2 → Pb + O2 b) hydrogen iodide → HI → HI → H2 + I2 c) hydrogen bromide → HBr → HBr → H2 + Br2 d) sodium chloride → NaCℓ → NaCℓ → Na + Cℓ2 3) Single-Replacement Reactions -one element replaces a second element in a compound ex- 2K + CaO → K2O + Ca -whether one metal will replace another metal is determined by reactivity of the metal activity series of metals- lists metals in order of decreasing reactivity **Page 217 -a metal will replace another metal listed below it in the table ex- Mg + Zn(NO3)2 → *is Mg above Zn on the reactivity series? Mg + Zn(NO3)2 → Mg(NO3)2 + Zn ex- Mg + Ag2SO4 → Mg + Ag2SO4 → MgSO4 + Ag ex- Mg + LiNO3 → -lithium is above magnesium Mg + LiNO3 → no reaction (NR) -Halogens can replace each other in singlereplacement reactions -Reactivity decreases as you go down the halogen group Try These!! a) zinc + hydrogen sulfate → Zn + H2SO4 → Zn + H2SO4 → H2 + ZnSO4 b) chlorine + sodium bromide → Cℓ2 + NaBr → Cℓ2 + NaBr → Br2 + NaCℓ c) zinc + sodium nitrate → Zn + NaNO3 → no reaction d) iron(II) + lead(II) nitrate → Fe + Pb(NO3)2 → Fe + Pb(NO3)2 → Pb + Fe(NO3)2 e) chlorine + sodium iodide → Cℓ2 + NaI → Cℓ2 + NaI → I2 + NaCℓ 4) Double-Replacement Reactions -involve an exchange of cations between two reacting compounds ex- BaCℓ2 + K2CO3 → BaCO3 + 2KCℓ ex- FeS + 2HCℓ → H2S + FeCℓ2 Try These!! a) sodium hydroxide + iron(III) nitrate → NaOH + Fe(NO3) 3 → NaOH + Fe(NO3) 3 → NaNO3 + Fe(OH)3 b) barium nitrate + hydrogen phosphate → Ba(NO3) 2 + H3PO 4 → Ba(NO3) 2 + H3PO 4 → Ba3(PO4) 2 + HNO3 c) potassium hydroxide+hydrogen phosphate → KOH + H3PO4 → KOH + H3PO4 → K3PO4 + H2O d) hydrogen sulfate + aluminum hydroxide → H2SO4 + Aℓ(OH)3 → H2SO4 + Aℓ(OH)3 → Aℓ2(SO4)3 + H2O 5) Combustion Reaction -hydrocarbon combined with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water ex- C6H6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O -to balance: *always begin with a 2 in front of hydrocarbon *when done, if can divide by 2 do so 2C6H6 + 15O2 → 12CO2 + 6H2O Try These!! a) C14H26 + O2 → 2C14H26 + 41O2 → 28CO2 + 26H2O b) C8H12 + O2 → 2C8H12 + 22O2 → 16CO2 + 12H2O C8H12 + 11O2 → 8CO2 + 6H2O Summary of Reactions 1) Combination/Synthesis R + S → RS 2) Decomposition Reaction RS → R + S 3) Single-Replacement Reaction T + RS → R + TS 4) Double-Replacement Reaction RS + TU → RU + TS 5) Combustion Reaction CxHy + O2 → CO2 + H2O