Law of Superposition Lecture
advertisement

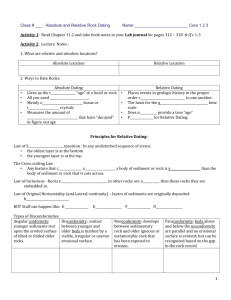
Dating Differences Defined Absolute vs. Relative Dating Relative Dating • A method of determining the age of a fossil by comparing its placement with that of fossils in other layers of rock Absolute Dating • Any method of measuring the age of an event or object in years Activity – Model • List 5 important events in your life (the one at the bottom should be the oldest!! ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Started working at Wendell Middle December 2014 Started working at Southwest Middle August 2013 Graduated from Southeastern University May 2013 Started work at Lakeland High School January 2013 Graduated from high school June 2008 Got Braces September 2004 Born November 1990 Radioactive dating Measurement of the amount of radioactive material (usually carbon 14) that an object contains; a form of absolute dating Uranium A white, radioactive metallic chemical element that weighs more than any other element in nature; used in radioactive dating BrainPop • See how radioactive dating works by watching this brainpop: Carbon Dating Rock Layers 8th Grade Science Spring 2015 Rock Layer • The four rock columns were found at the places indicated by letters A, B, C, D. Different rock layers are found on the surface at these places. The problem is to find which layers match. • Color the matching sections from A, B, C, and D the same color. • Cut out the columns of rock layers. • Arrange the columns of rock layers side by side by matching layers. Do not write what is in purple or teal • Write the following notes on the BACK of your Rock Layers Activity • Title: The Law of Superposition The Law of Superposition 8th grade science Spring 2015 Law of Superposition States that the oldest rocks lie on the bottom and the youngest rocks are on top of any undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rocks. Correlation Matching rock layers in different locations to see if they formed at the same time and under the same conditions Unconformity • A gap in the rock record • What could cause an unconformity? ▫ Erosion could cause rock to be worn away and “disappear” ▫ When plates move together (convergent boundary) one plate “disappears” Rock Layers Analysis Questions • Flip back over to the Rock Layers side and answer the following questions on that side. ▫ 1. Which rock layer is the oldest? The youngest? ▫ 2. Which fossil is the oldest? The youngest? ▫ 3. What happened to the layer in rock strip C? (Where did it go?) Use your vocabulary words to describe what happened to layer in rock strip C. Sedimentary Rock • Most fossils are found in Sedimentary Rock ▫ Rock that forms when sediments are compacted and cemented together Index Fossil • A fossil of an organism that is known to have lived in a particular geologic age that can be used to date the rock layer in which it is found ▫ A key example of an organism used as an index fossil are TRILOBITES, a group of hard-shelled animals whose body had three sections, lived in shallow seas, and became extinct about 245 million years ago Other Clues to Relative Age Clues From Igneous Rock • Lava that cools at the surface is called an extrusion • Rock below an extrusion is always older. Extrusion Intrusion • Magma that cools beneath the surface is called an intrusion • An intrusion is always younger than the rock layers around and beneath it The Cross-Cutting Law • Faults (a break in the rock) are always younger than the rock it cuts through! • Fractures (a crack in • The arrow points to a the rock) are always fault – notice the younger than the rock layer of white rocks it cuts through do not line up with each other To Summarize • Generally, the top layer is the youngest – bottom layer is the oldest • The rocks below an extrusion (lava at the top) are always older than the extrusion • The intrusion (lava within the rocks) is always younger than the rocks around it • A fault is younger than the rocks around it Using your knowledge of the Law of Superposition, put the following layers in order from the youngest to the oldest. YOUNGEST OLDEST E _______ D _______ _______ A _______ B _______ C Practice • You have two other examples on your worksheet – try to put the rock layers in order from youngest to oldest Items to STUDY for Tomorrow’s Quiz • Examples of Mechanical and Chemical Weathering • Vocabulary Definitions: ▫ Relative Dating, Absolute Dating, Radioactive Dating, Uranium, Correlation, Unconformity, Sedimentary Rock, Index Fossil • Law of Superposition ▫ Where are the oldest/youngest rock layers? ▫ What are intrusions, extrusions, faults and fractures?