ABSOLUTE AGE
advertisement
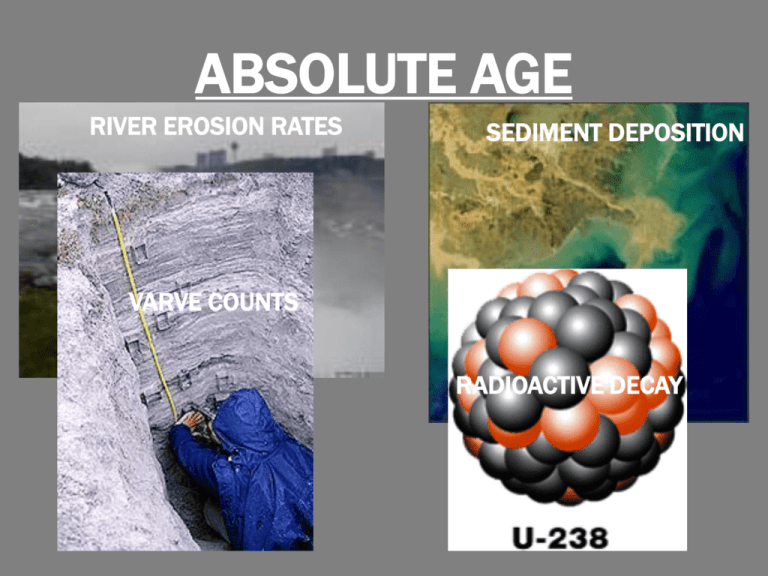
ABSOLUTE AGE RIVER EROSION RATES SEDIMENT DEPOSITION VARVE COUNTS RADIOACTIVE DECAY Absolute vs. Relative Age •Relative dating tells us which rocks are older by comparing position… •…it does not tell us age in actual years. •Absolute dating assigns an age in years; it gives rocks and fossils “birthdays!” Erosion Rates of Rivers •Niagara Falls erodes 1.3 meters per year. •…age is 9,900 years! •Only works with “younger” features. Deposition of Sediment •Rivers deposit sediment into oceans or lakes. •Rates of deposition can be inconsistent over time and thus inaccurate. Varve Count • Sediments are deposited yearly in glacial lakes. • Spring melt brings coarse (large) sediment first which settles on bottom; fine (small) material lands on top. • One year = one layer of big & small sediment. Varve Count …one band of dark & light = one year Radioactive Decay Radioactive Decay •Radioactive elements act as geologic clocks. •Radioactive decay: the loss of particles and energy from unstable (radioactive) elements. •Radioactive elements (such as uranium) decay at their own unique, constant rate to form new elements… Radioactive Decay •Once that rate is known, scientists compare the amount of original radioactive material (“parent”) in a rock sample to the amount of newly created element present (“daughter”)… •…and the age of the sample can be determined by plotting amount versus time on a logarithmic graph! Half-Life •Definition: the time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay to a different stable element. •Example: it takes 10 g of U-238 4.5 b.y. to “become” 5 g of Pb206 and 5 g of U-238. Half-Life Radioactive Parent Stable Daughter Half life Potassium-40 Argon-40 1.25 billion yrs Rubidium-87 Strontium-87 48.8 billion yrs Thorium-232 Lead-208 14 billion years Uranium-235 Lead-207 704 million years Uranium-238 Lead-206 4.47 billion years Good to Know… •The number that appears with the element name (U-238) is the atomic mass number of the element…the total of protons & neutrons found in the nucleus. •During decay, an element that loses neutrons becomes an ISOTOPE of that element (like U-236). •When that element loses protons, it becomes a different element! Good to Know… •Radioactive elements become concentrated in minerals found in igneous rocks (granite, gabbro) which make up continental crust. •So…radiometric dating is not useful for determining the ages of sedimentary rock (you would simply be finding the “birthday” of the igneous rock that got “changed” into the sedimentary rock…) Carbon Dating Problem… •Uranium, Potassium, & Rubidium work great with very old (more than 10 million year-old) ROCKS… •…but what about younger rocks and objects not containing radioactive elements (like onceliving things)? Carbon Dating •Carbon dating is used for younger samples that contain carbon such as organic material and some sedimentary rocks. •The half-life of C-14 is 5,730 years. •Works for wood, bone, shells, early humans up to 50,000 years old.