Opening welcome from JINR
advertisement

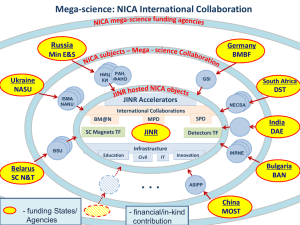
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research V.A.Matveev The 5th International Conference”Distributed Computing and GRID-technolodgies in Science and Education”GRID`2012` July 16-21, Dubna JINR is located in the city of Dubna in 120 km from Moscow 2 Science Bringing Nations Together The Convention on the establishment of JINR was signed on 26 March 1956 in Moscow Days of JINR in Czech Republic Science Bringing Nations Together REPUBLICS OF FORMER SOVIET UNION AMERICA BRAZIL BRAZIL CANADA CANADA CLAF CUBA UNITED STATES STATES UNITED ARMENIA AZERBAIJAN BELARUS GEORGIA KAZAKHSTAN MOLDOVA RUSSIA UKRAINE UZBEKISTAN DUBNA EUROPE AUSTRIA BELGIUM BULGARIA CERN CROATIA CZECH REPUBLIC DENMARK FINLAND FRANCE GERMANY GREECE HUNGARY IRELAND ITALY NETHERLANDS NORWAY POLAND PORTUGAL ROMANIA SLOVAKIA SERBIA SLOVENIA SPAIN SWEDEN SWITZERLAND UNITED KINGDOM AFRICA ASIA EGYPT SOUTH AFRICA CHINA AUSTRALIA AND OCEANIA AUSTRALIA DEMOCRATIC PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF KOREA INDIA ISRAEL JAPAN MONGOLIA SOUTH KOREA TURKEY VIETNAM JINR’s partners are about 700 institutions located in 60 countries, including about 300 institutions and universities from the JINR Member States JINR – Russia Agreement Federal Law 6 January, 2000 Synchrocyklotron 680 Mev (1949) M.Meshcheryakov Synchrophasotron 10 Gev (1957) V.Veksler 7 JINR comprises 7 Laboratories, each being comparable with a large institute in the scale and scope of investigations performed Dzhelepov Laboratory of Nuclear Problems Veksler and Baldin Laboratory of High Energy Physics Bogoliubov Laboratory of Theoretical Physics Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics Laboratory of Information Technologies Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions 8 Laboratory of Radiation Biology Czech days in JINR JINR’s Science Policy 7-Year Program: ‘2010 – 2016’ Basic Scientific Directions High Energy Physics Fundamental Science Innovative activities Special Economic Zone “Dubna” Public-Private-Partnership Nuclear Physics Condensed Matter Physics Education programme UC, DIAS-TH International Univ. “Dubna” Seven-Year Plan 2010-2016: Fundamental Science Particle Physics Nuclear Physics Condensed Matter Physics Closely interrelated with: IT, educational program, innovation activities MAIN GOALS Completion of the upgrade program of basic facilities: Nuclotron-M (completed in 2011) U400M (complete in 2011) IBR-2M (completed in 2011) Construction of new facilities: complex NICA (2017), DRIBs-III (2016), Spectrometer complex of IBR-2M (2016) 11 Discoveries • 46 prestigious academic and state awards, and prizes of Russia, Czech Republic, Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, and other countries. More than 40 discoveries, including: – 1959 – nonradiative transitions in mesoatoms – 1960 – antisigma-minus hyperon – 1963 – element 105 – 1972 – postradiative regeneration of cells – 1973 – quark counting rule – 1975 – phenomenon of slow neutron confinement – 1988 – regularity of resonant formation of muonic molecules in deuterium – 1999-2010 – super-heavy elements 113-118 and their chemical identification Recently 114 named Flerovium after Flerov CzechG. days in JINR D.I. Mendeleev 1834 - 1907 113 114 115 Discovered at JINR in 2003 Discovered at JINR in 1999 Discovered at JINR in 2003 116 117 Discovered Discovered at JINR in 2000 at JINR in 2009 118 Discovered at JINR in 2001 13 2011: Names and Symbols of the Elements with Atomic Numbers 114 and 116 A joint IUPAC/IUPAP Working Party (JWP) has confirmed the discovery of the elements with atomic numbers 114 and 116. In accord with IUPAC procedures, the discoverers proposed names as follows: Flerovium and symbol Fl for the element with Z = 114 and Livermorium and symbol Lv for the element with Z = 116. Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 83, No. 7, pp. 1485–1498, 2011 The Inorganic Chemistry Division recommended these proposals for acceptance. 14 FLEROV LAB ACCELERATORS views of set-ups U400M U400 IC-100 MT-25 U200 DRIBS Towards DRIBs-III (2016) SHE factory U400R Accelerator Complex 1500m2 2016 1000m2 U200 IC100 NanoLab 2012 1500m2 2015 U400R MT25 U400M+DECRIS-SC SHE experiments Nuclear Physics Exotic Nuclei E = 30 ÷ 60 MeV/n A < 60 16 1960: anti-sigma minus hyperon discovery 105 V.I. Veksler, Acad. JINR (March 1907) Synchrophasotron, leadership (1949-1950) 55 JINR Synchrophasotron April 1957, 10 GeV proton energy achieved. World wide record energy High Energy Ion Physics Nuclotron with Nuclotron is a superconducting synchrotron for heavy ions (has been operating since 1993). The main home facility today: Nuclotron complex of VBLHEP Future plan: NICA/MPD/SPD – Nuclotron-based Ion Collider fAcility with Multipurpose Detector and Spin Detector (start 2017) Complex NICA @ JINR (VBLEP) accelerator facility Collider FT experiment area New Linac Booster Nuclotron Lu 20 Days of JINR in Czech Republic Russia & JINR: Mega-science projects Dubna, 5 July 2011, Session of the Russian Governmental Commission for High Technology and Innovation, which was chaired by the Prime Minister of the Russian Federation, V. Putin. Note was taken that the NICA project has been included by the Commission in the list of six megaprojects that may receive substantial dedicated support from the Russian Government. 20 The IBR reactor idea: D. Blokhintsev (1955). Parameters D. Blokhintsev Reactor core Main movable reflector Additional movable reflector Fuel Active core volume22 dm3 Cooling Average power PuO2 Pulsed power Repetition rate Average flux Pulsed flux Pulse width 1500 MW 5 s-1 8·1012 n/cm2/s 5·1015 n/сm2/s (fast / therm.) Number of channels liquid Na 2 МW 215 / 320 μs 14 21 IBR-2M power start-up Peak power 1850 MW Average power 2 MW 200 μs On October 12 , 2011 the reactor reached the full designed aver. power of 2 MW. New experiments are in active preparation stage. IBR-2 applications Fe (3-5 нм) Сr (1-2 нм) Nanosystems and Nanotechnology Biomedical research New materials Diagnostics. Earth science. Physics of high-temperature superconductivity Geological texture research Nanotechnology Areas of scientific research Preparation for the user’s program at the IBR-2M Biology Chemistry 10.4% 16% Materials science 23.6% Other Applied science Geophysics 12.3% Medicine Biophysics 37.7% Physics Radiation Biology Lens and Retina UV-induced aggregation of bLcrystallin pre-irradiated with B11 Cataractogenesis cytoplasm micro-vacuolization, fiber cell swelling, nuclear fragmentation electroretinogram А Mutagen-induced functional retinal damage Control Б МНМ, 70 mg/kg, 2h Applied research: hadron therapy Phasotron operation time in 2011: 900 hours More than 100 patients were treated in 2011 on Phasotron proton medical beams. In total > 800 patients have been treated since 2000. JINR at leadership of the Russian Federal MedicoBiological Agency participated in the development of the Project of the Dimitrovgrad Proton Centre, which being implemented under Federal Program. New technological centre was constructed at JINR for assembling and testing medical proton cyclotrons. Assembling and beam tests of the proton cyclotron C235-V3 was started in 2011. Cyclotron C235-V3 will be delivered to Dimitrovgrad at the end of 2012. 26 JINR Educational Programs EDUCATIONAL FACILITIES AT JINR LABS It is foreseen at the JINR scientific laboratories to create elements of educational infrastructure, which allow students to get acquainted with modern equipment of physics experiments. An important task of the JINR UC is to renovate ties with leading universities of the Member States. These should lead to emergence of new training programs and to involvement of young scientists and engineers to Complex NICA, DRIBs, IBR-2M and other facilities of JINR. 27 Welcome to Dubna! 29