National Assembly Background Started when Louis XVI's minister of
advertisement

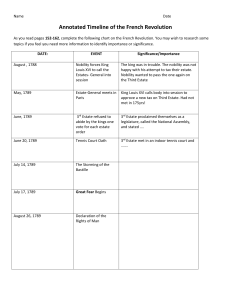
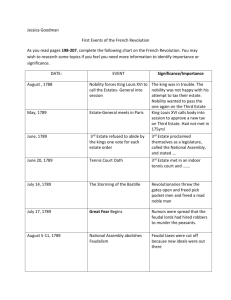
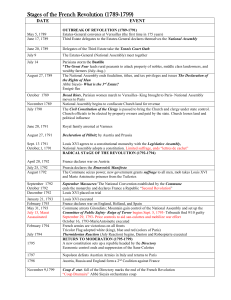
Enlightened Ideals : National Assembly Limited and Constitutional monarchy Declaration of the Rights of Man National Assembly Background Started when Louis XVI’s minister of finance convinced the king. The assembled notables demands Louis XVI trying to surpass the law Louis XVI beaten in 1788 Estates General spring session The three estates petition The third estate Oath of the Tennis Court Limited and Constitutional Monarchy August 27, 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man -Became popular throughout the world -Maintained mankind’s natural rights -Individual freedoms -Equality in the courts and law -Representative government for a sovereign people How much power should the king have? Women “We are going to cut off her head, tear out her heart, fry her liver, and that won’t be the end of it,” The National Assembly -Abolished the French Nobility -Constitutional monarchy The final constitution New laws - Women 1. Divorce 2. Property 3. No voting Women could now…. Put-out system Marie Antoinette The French Revolution Timeline • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • May 5, 1789: Estates General convene at Versailles June 17, 1789: Third estate declares itself the National Assembly June 20, 1789: Oath of the Tennis Court is sworn July 14, 1789: Storming of the Bastille occurs August 4, 1789: National Assembly abolishes feudal privileges August 27, 1789: National Assembly issues Declaration of the Rights of Man October 5, 1789: Women march on Versailles and force royal family to return to Paris. November 1789: National Assembly confiscates church lands. July 1790: Civil constitution of the clergy establishes a national church. Louis XVI reluctantly agrees to accept a constitutional monarchy. June 1791: Royal family is arrested while attempting to flee France. August 1791: Austria and Prussia issue the Declaration of Pillnitz. April 1792: France declares war on Austria. August 1792: Parisian mob attacks the palace and take Louis XVI prisoner September 1792: September Massacres occur National convention declares France a republic and abolishes monarchy. January 1793: Louis XVI is executed February 1793: France declares war on Britain, Holland and Spain. Revolts take place in some provincial cities. March 1793: Bitter struggle occurs in the National Convention between Girondists and the Mountain. • • • • • • • • • • April-June 1793 : Robespierre and the Mountain organize the Committee of public safety and arrest Girondist leaders September 1793: Price controls are instituted to aid the sans-culottes and mobilize the war effort. 1793-1794: Reign or Terror darkens Paris and the provinces. Spring 1794: French armies are victorious on all fronts. July 1794: Robespierre is executed. Thermidorian reaction begins 1795-1799: Directory rules 1795: Economic controls are abolished, and suppression of the san-culottes begins. 1797: Napoleon defeats Austrian armies in Italy and returns to Paris 1798: Austria, Great Britain, and Russia form the Second Coalition against France. 1799: Napoleon overthrows the Directory and seizes power. Girondist and the Mountain were the two groups who controlled the Natural Convention. - “I am innocent and shall die without fear. I would that my death might bring happiness to the French, and ward off the dangers which I foresee.” - The National Convention disagreed on the conviction of Louis XVI, the slim minority of the votes sentenced him to death.