Franklin D. Roosevelt and the New Deal(s)
advertisement

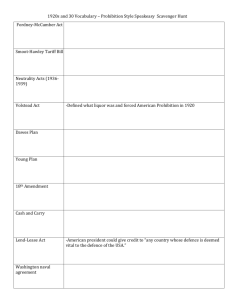
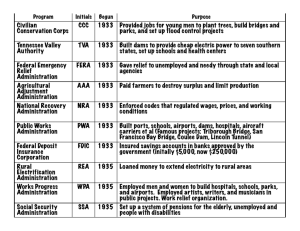
1933 – 1941 Introduction Listening to the “Fireside Chats” Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s No master blueprint contradictory hodgepodge of programs New Deal didn’t end Great Depression – only World War II did that F.D.R. possessed ability to inspire and restore confidence The Election of 1932 Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s Press Shoring Up the Financial State Emergency Banking Relief Act (March 9) allowed Treasury to reopen solvent banks & reorganize insolvent ones Federal Securities Act (May 27) mandated full disclosure on all new securities Home Owners’ Loan Corp. (June 13) created to refinance home mortgages Glass-Steagall Act (June 16): Separated commercial & investment banking Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. created to insure bank deposits up to $5,000.00 Securities Exchange Commission created in 1934 to monitor Wall Street Creating Jobs for the Unemployed Civilian Conservation Corps (March 31, 1933) put young, unmarried men to work planting trees & creating parks Almost 3 million men, aged 18-25, participated 2,650 segregated, military-style camps Paid nominal $30 a month, but point was to keep them out of the labor force Federal Emergency Relief Administration (May 12, 1933) gave grants to states to fund relief efforts Run by Harry Hopkins Set up some works programs Public Works Administration (June 12, 1933) hired private contractors for large infrastructure projects Run by Secretary of the Interior Harold Ickes Spent $3.3 billion on projects like Triborough Bridge Used private contractors who hired union members & did not discriminate FDR and the CCC Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s Press Helping the Farmers Agricultural Adjustment Administration (May 12, 1933) Run by George Peek Set crop quotas & prices based on 1909-14 Worked through state & local officials, so benefits went to middle & upper class Declared unconstitutional by Supreme Court in U.S. v. Butler (1936) Emergency Farm Mortgage Act (May 12, 1933) allowed refinancing of farm mortgages The Dust Bowl The Tennessee Valley Authority May 18, 1933 TVA created to bring economic Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s development to poor rural region Cheap electricity used as yardstick to measure private companies’ rates Government bought nitrates for military use Caused vast pollution Rural Electrification Administration created in 1935 to bring electricity to rural areas Norris Dam ELECTRICITY COMES TO RURAL AMERICA TVA workers at Norris Dam construction site REA customer admires her new electric meter National Recovery Administration June 16, 1933 N.R.A. meant to be centerpiece of New Deal – based on T.R.’s New Nationalism Run by Gen. Hugh Johnson Joint committees of labor, management & government created fair practice codes Section 7(a) guaranteed union recognition Declared unconstitutional by Supreme Court in Schecter Poultry Co. v. U.S. (1935) Critics on the Right Conservative Democrats formed the American Liberty League – opposed New Deal as corrupt patronage politics Hoover & Republicans labeled the New Deal “socialist” & warned of loss of personal liberty Supreme Court invalidated legislation: Schecter Poultry Co. v. U.S. - declared NRA restricted intrastate commerce & delegated legislative power to executive branch U.S. v. Butler - invalidated AAA as attempt to use taxing power to unconstitutionally regulate agriculture Justice Owen Roberts Critics on the Left Father Charles Coughlin created the National Union for Social Justice Father Coughlin Claimed New Deal really benefited wealthy, not poor charged that an international conspiracy of Jewish financiers was behind Roosevelt Dr. Francis Townshend suggested a revolving pension scheme for the elderly Sen. Huey Long (the Kingfish) wrote Every Man a King & created Share Our Wealth Clubs Sen. Huey Long Called for seizing incomes above $1 million & redistributing to all families Planned to run for president in 1936 The Second New Deal, 1935: Works Progress Administration Run by Harry Hopkins Spent $4.8 billion Employed 8.5 million put people to work using their existing talents Wagner National Labor Relations Act Guaranteed unions right to organize & bargain collectively Est. National Labor Relations Board to supervise elections & mediate disputes The W.P.A. at Work W.P.A. Projects The Second New Deal (cont.): Social Security Act Social Security Admin. Provides pensions to elderly & disabled Financed by flat payroll tax Aid to Dependent Children (later AFDC) was 1st federal direct welfare program “Soak the Rich” Tax Increased income, inheritance, gift & excess profits taxes Didn’t really redistribute Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s Press 1937 Recession Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s The Third New Deal, 1937-38: United States Housing Authority (1937) Long-term loans to local agencies & subsidized rents Redlining continued segregation Farm Security Administration (1937) gave loans to tenant farmers Second A.A.A. (1938) required a 2/3 vote in plebiscites to set quotas Food, Drug & Cosmetics Act (1938) forbade false or misleading ads – regulated by FTC Fair Labor Standards Act (1938) set min. wage & max. 40-hour work week New Deal Gains & Losses Growth of labor unions AFL grew from 2.3 million to 6.89 million, 1933-45 CIO had 3.7 million by 1938 More women working, but often excluded from relief Blacks benefited from some programs (esp. W.P.A.) Wheeler-Howard Act (1934) reversed Dawes Act & restored tribal land & self-government Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s