The End of WWII & The Aftermath - Miami Beach Senior High School
advertisement

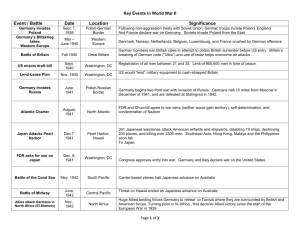
The End of WWII & The Aftermath SS.A.1.4.4; SS.A.3.4.9; SS.A.2.4.8 New European Order When Germans conquered eastern Europe they planned on killing Slavs and Jews and repopulating the area with Germans Plans set in motion soon after taking over Himmler plans on killing 30 million Slavs 1940: Germany uses 7 million slaves Einsatzgruppen: Death squads, kill Jews 6 million Jews also killed in death squads 13 million orphaned children in Europe New Asian Order Japan’s slogan: “Asia for the Asiatics” Resources used to benefit Japanese Puppet governments established 1944-45: over 1 million Vietnamese starve Japanese regularly kill, rape, rob locals Used captured people as slaves Rebels coordinate with American forces POWs forced into labor for Japanese “The Raping of Nanjing” 280,000 Chinese killed 80,000 women raped Mobilization of America WWII=more total war than WWI United States provides weapons to Allies African Americans move north and west looking for work, women go to work Even more women go to work in WWII Causes tension among established residents 110,000 Asian Americans moved to internment camps out east, take oath New place for women and minorities, leads to civil rights movement Camp Miami Beach The Allies Advance US, UK, USSR form Grand Alliance, stress military operations, not political differences 1942: War turns against Germany, Japan Agree to fight until all Axis Powers surrender Nov ’42: Allies invade N. Africa, defeat Germans May ’43 Feb ’43: German Sixth Army surrenders at Stalingrad June ’42: USA sinks 4 Japanese carriers at Midway Gen MacArthur begins offensive in Philippines Combined Army, Marine and Navy “island hopping” May 1943: Axis Tunisia surrenders September 1943: Allies invade Italy The European Theater After Allies take Sicily, King Victor Emanuel III arrests Mussolini, freed by Germans June 6, 1944: D-Day; Allies invade France June 1944: Allies take Rome Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower plans invasion of Normandy’s beaches, then on to Germany August ’44: Allies take Paris March ’45: Allies cross into Germany April ’45: Soviets enter Berlin, US not far away April 30, 1945: Hitler commits suicide May 7, 1945: Germany surrenders The Asian Theater April 1945: US President Franklin Delano Roosevelt, replaced by Harry S Truman Allied forces approach Japanese homeland Japanese refuse to surrender August 6, 1945: Atomic bomb dropped on Japanese city Hiroshima Truman must decide to use new atomic bomb Emperor refuses to surrender Aug 9, 1945: second atom bomb dropped on Nagasaki Japan Surrenders on August 14, 1945 Peace & A New War Allied victory brings tensions b/w powers Cold War: United States and Soviet Union enter period of ideological conflict Tehran Conference: Meeting of the “Big Three” Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin Outlines final attack on Germany (1943) Split Germany between, east and west, US-UK forces and Soviet forces Soviets would liberate eastern Europe The Yalta Conference The Big Three meet in February 1945 Roosevelt seeks Soviet help with Japan All three join new United Nations Promises Japanese land to Stalin in exchange First meeting set for April 1945 in San Francisco After war Germany to be split into four parts controlled by US, UK, USSR & France Sides divided over setting free elections Potsdam and New Struggles July 1945: Potsdam Conference, Germany President Truman replaces Roosevelt Truman demands elections for Europe Stalin refuses to allow them, knows better Soviets had lost more than other Allies Big Three agree to trials of Nazi war criminals in Nuremberg Germany(1945-1946) Churchill: “iron curtain has descended on the continent” splitting Europe east/west Chapter 24 Assessment On page 504, write and answer questions 1-11