Image Formation on a Concave Mirror Rules
advertisement
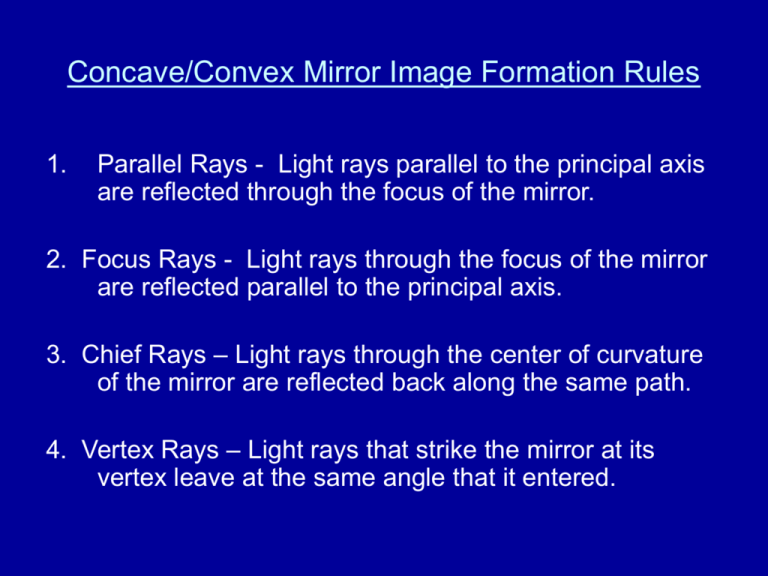
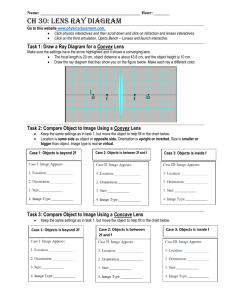
Concave/Convex Mirror Image Formation Rules 1. Parallel Rays - Light rays parallel to the principal axis are reflected through the focus of the mirror. 2. Focus Rays - Light rays through the focus of the mirror are reflected parallel to the principal axis. 3. Chief Rays – Light rays through the center of curvature of the mirror are reflected back along the same path. 4. Vertex Rays – Light rays that strike the mirror at its vertex leave at the same angle that it entered. Object Located Beyond f and C. 1 object 4 3 2 C f 2 image 4 1 3 Concave Mirror Image Formation for an Object Less than f 2 object C f 3 1 4 image Convex Mirror Image Formation 1 3 2 image f object 4 C Concave Mirror Image Formation • Concave Mirror Beyond C • Concave Mirror Between C and f • Concave Mirror Image Formation Less than f Lenses The focal length for a lens is dependent on both the curvature of the lens, and the lens material. Convex Lens (Converging Lens) f All light rays parallel to the principal axis converge to the focal point after passing through the convex lens. Image Properties Image Type: Real or Virtual Image Orientation: Inverted or Erect Image Height (Size): Smaller, Larger, Same Image Distance: Closer, Farther, Same •The image properties of a convex lens are the same as a concave mirror. Concave Lens (Diverging Lens) f Image Properties Image Type: Virtual Image Orientation: Erect Image Size: Smaller Image Distance: Closer The light rays parallel to the principal axis refract and diverge after going through the lens, such that if the refracted light rays are extended backwards, then the rays would converge at the focal point for the lens. • The image properties of a concave lens are the same as a convex mirror. Lens Ray Image Formation Rules 1. Parallel Ray – A light ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted towards the lens focus. 2. Focal Ray - A light ray passing through the focus refracts parallel to the principal axis. 3. Chief Ray – A light passing through the center of the lens continues traveling along its original path unaffected by the lens. Convex Lens Ray Diagram (Beyond f) 1 1 2 3 image object 2f f f 3 2 2f Convex Lens Ray Diagram (Less than f) 2 2 1 image 2f f object 1 f 2f 3 Concave Lens Ray Diagram 1 1 object 2 2 3 2f f image f 2f 3 Image Properties Graphic (Converging Instruments) object C>do>f, do>C, hi>ho, real do from ∞ When do=∞, di=f, hi<<ho, real C f do=f, di=∞, no image When do=C, di=C, hi=ho, real image When do<f, di>do, hi>ho, virtual Convex Mirror Image Formation do<∞, di<f, hi<ho, virtual object image f do=∞, di=f, hi<<ho, virtual C Concave Lens Ray Diagram object 2f do<∞, di<f, hi<ho, virtual f do=∞, di=f, hi<<ho, virtual image f 2f