Do Now
● In your notebooks:
● Do you keep a small amount of cash somewhere
for incidental use?
● What kinds of things do you use that money for?
● How do you manage this money (what is the
maximum & minimum amount you would keep
any given time)?
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 1
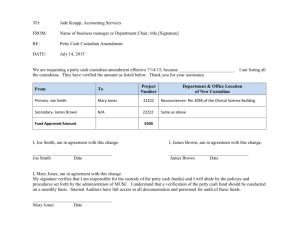
Petty Cash to You
● Look up the definition of petty cash
● Write down key words on front board
● Take money from pile that you would keep as
petty cash for your own hypothetical business
● For what purpose would you use this money?
● Use whiteboard to record journal entry you
would make to establish petty cash fund
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 2
Lesson 5-4
Establishing a Petty Cash Fund
LO9
● An amount of cash kept on hand and used for
making small payments is called petty cash.
● Amount needed by each business may differ
● Asset account
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 3
Lesson 5-4
Establishing a Petty Cash Fund
Petty Cash
June 8. January 19. Paid cash to establish
a petty cash fund, $100.00. Check No. 8.
1 Date
2
Debit
LO9
100.00
Cash
4 Source Document
100.00
3 Credit
1. Write the date in the Date column.
2. Write the title of the account to be debited in the Account Title column.
Record the amount debited in the Debit column.
3. On the next line, indented, write the title of the amount credited in the
Account Title column. Write the credit amount in the Credit column.
4. Write the source document number in the Doc. No. column.
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 4
Lesson 5-4
Making Payments from a Petty Cash Fund
with a Petty Cash Slip
LO9
● Information on a petty cash slip includes:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Petty cash slip number
Date of petty cash payment
To whom paid
Reason for payment
Amount paid
Account in which amount is recorded
Signature of person approving petty cash payment
● Petty cash slips kept in petty cash box until
replenished
● No entries made for individual petty cash payments
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 5
Lesson 5-4
Making Payments from a Petty Cash Fund
with a Petty Cash Slip
LO9
● A form showing proof of a petty cash payment
is called a petty cash slip.
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 6
Your Turn
● Create your own petty cash slip from a sheet
of paper in the front of the room
● Include a transaction you believe you’d engage
in based on the type of your business
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 7
Petty Cash Report
● Eventually, company will replenish petty cash
fund either when reduced to certain amount
or at end of month so that all expenses are
recorded in the month they are incurred
● Errors may be made when making payments
from petty cash fund
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 8
Lesson 5-4
Petty Cash Report
LO10
● A petty cash on hand amount that is less than
a recorded amount is called cash short.
● A petty cash on hand amount that is more
than a recorded amount is called cash over.
● The custodian prepares a petty cash report
when the petty cash fund is to be replenished.
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 9
Lesson 5-4
Petty Cash Report
LO10
1
Date and Custodian Name
2
Fund Total
3
Payments by
General Ledger
Account
4
Total
Payments
Amount to
8 Replenish
Recorded Amount on Hand
5
Subtract the actual cash on hand
6 Actual Cash on Hand
7 from the recorded amount on hand.
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 10
Lesson 5-4
Replenishing Petty Cash
LO11
● Account title—Cash Short and Over
● Debited when cash is short
● Credited when cash is over
● Account balance
● Either a debit or credit
● Usually a debit
● Petty cash fund more likely to be short than over
(operating expense of business, adds to cost)
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 11
Lesson 5-4
Replenishing Petty Cash
LO11
January 31. Paid cash to replenish the petty cash fund, $35.00: Miscellaneous
Expense, $20.00; Advertising, $14.00, Cash Short and Over, $1.00. Check No. 11.
Miscellaneous Expense
20.00
Advertising Expense
14.00
Cash Short and Over
1.00
Cash
35.00
1
Date
Debits
2
Credit
4
3
Cash Short (a Debit)
or Cash Over (a Credit)
5
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
Source Document
SLIDE 12
Lesson 5-4
Lesson 5-4 Audit Your Understanding
1. Why do businesses use petty cash funds?
ANSWER
For making small cash payments for which
writing a check is not time- or costeffective
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 13
Lesson 5-4
Lesson 5-4 Audit Your Understanding
2. Why is Cash rather than Petty Cash credited
when a petty cash fund is replenished?
ANSWER
The check issued to replenish petty cash is
a credit to Cash and does not affect Petty
Cash.
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 14
Working Papers
● As a class: 5-4 WT
● Individually: 5-4 OYO
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 15
Finish “King of the Hill”
● Everyone complete Application Problem 5-4
● However, only those students still remaining in
game from last class can advance to final two
● Those students who cannot advance can gain
points needed for review game on Wednesday
● Those out of contest create three questions to ask
final two contestants
● Best out of three wins
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 16
Closure
● What would be main differences between
petty cash for an individual and petty cash for
a business?
© 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
SLIDE 17