Dalton and Graham
advertisement

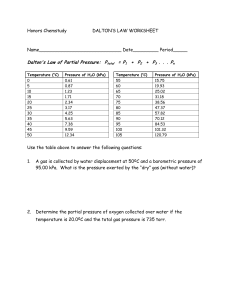
Quiz According to the kinetic theory of gases… What is the formula for Boyle’s Law? The student will be able to: Explore mixtures and movements of gases in order to relate total pressure to partial pressure and explain gas diffuses and effuses. An ideal gas is made up of gas particles that… Have a high mass b. Are in random motion c. Have volume d. Can be liquefied e. Attract each other a. Gases Mixtures and Movements Gases: Mixtures and Movements • A list of gear for an expedition to Mount Everest includes climbing equipment, ski goggles, a down parka with a hood, and most importantly compressed-gas cylinders of oxygen. You will find out why a supply of oxygen is essential at higher altitudes. Dalton’s Law The contribution each gas in a mixture makes to the total pressure is called the partial pressure exerted by that gas. Dalton’s Law In a mixture of gases, the total pressure is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases. Dalton’s Law Dalton’s law of partial pressures states that, at constant volume and temperature, the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases. Dalton’s Law Animation 17 Observe the behavior of a mixture of nonreacting gases. Three gases are combined in container T. Dalton’s Law The partial pressure of oxygen must be 10.67 kPa or higher to support respiration in humans. The climber below needs an oxygen mask and a cylinder of compressed oxygen to survive. Sample Problem Sample Problem Sample Problem You Try! Click Here for Stimulation Graham’s Law Diffusion is the tendency of. molecules to move toward areas of lower concentration until the concentration is uniform throughout. Bromine vapor is diffusing upward through the air in a graduated cylinder. Graham’s Law After several hours, the bromine has diffused almost to the top of the cylinder. Graham’s Law During effusion, a gas escapes through a tiny hole in its container. Gases of lower molar mass diffuse and effuse faster than gases of higher molar mass. Graham’s Law Thomas Graham’s Contribution Graham’s law of effusion states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the gas’s molar mass. This law can also be applied to the diffusion of gases. Graham’s Law Comparing Effusion Rates A helium filled balloon will deflate sooner than an air-filled balloon. Helium atoms are less massive than oxygen or nitrogen molecules. So the molecules in air move more slowly than helium atoms with the same kinetic energy. Graham’s Law Because the rate of effusion is related only to a particle’s speed, Graham’s law can be written as follows for two gases, A and B. Graham’s Law Helium effuses (and diffuses) nearly three times faster than nitrogen at the same temperature. Graham’s Law Animation 18 Observe the processes of gas effusion and diffusion. Practice! 1. What is the partial pressure of oxygen in a diving tank containing oxygen and helium if the total pressure is 800 kPa and the partial pressure of helium is 600 kPa? a. 200 kPa b. 0.75 kPa c. 1.40 104 kPa d. 1.33 kPa Practice! 2. A mixture of three gases exerts a pressure of 448 kPa, and the gases are present in the mole ratio 1 : 2 : 5. What are the individual gas pressures? a. 44 kPa, 88 kPa, and 316 kPa b. 52 kPa, 104 kPa, and 292 kPa c. 56 kPa, 112 kPa, and 280 kPa d. 84 kPa, 168 kPa, and 196 kPa Practice! 3. Choose the correct words for the spaces. Graham's Law says that the rate of diffusion of a gas is __________ proportional to the square root of its _________ mass. directly, atomic b. inversely, atomic c. inversely, molar d. directly, molar a. Small Scale-Lab Purpose: To infer diffuse of a gas by observing color changes during chemical reactions. Be sure to wear : Safety goggles Lab apron Gloves (20 min) Small Scale-Lab Analysis questions 1-4 (20 MIN) 1. Did we accomplish the objective? Explain. 2. Compare and Contrast Partial pressure to total pressure. 3. Compare and contrast Diffusion to Effusion. 4. Explain the purpose or objective of the Small ScaleLab 5. Was there anything from the lab that surprised you? Were you already aware that gases can turn certain chemical colors? Dalton’s Law and Graham’s Law worksheet Final Exam Review Packet Questions 16-18