Acute Respiratory Failure

Acute Respiratory Failure
David Aymond, PGY-II
4/16/2013
Disclaimer
• This lecture is evidence based description/explanation of Acute Respiratory
Failure. My compartmentalizing of things are my own from textbooks I read. Also, this lecture is no where near all inclusive and doesn’t replace a text book.
Objectives
• Define and discuss equations that will be used in the lecture
• Define and Discuss the A-a gradient
• Define and discuss shunts, dead space ventilation, and V/Q mismatch
• Discuss hypoxemia vs. hypoxia
• Discuss the 3 major sources of hypoxemia and how to differentiate clinically
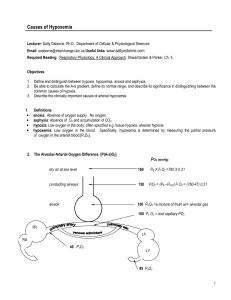
The A – a Gradient in Pictures
Respiratory Equation: The A-a Gradient
• Alveolar Gas Equation: the following is simplified for a patient breathing room air (21%):
PAO2= 150 – 1.2(PaCO2)
Remember, if an ABG is checked while the pt is on oxygen, this no longer holds true. This is only while breathing room air. If the ABG is checked while on oxygen, just simply google
“MD-Calc=A-a gradient” and fill in the numbers.
• A – a gradient: the difference between the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli (A= PAO2) and that seen in arterial blood (a= PaO2; this is from the ABG)
– Normally there is a small difference and this is called the A – a gradient. This represents the small fraction of blood that doesn’t participate in gas exchange b/c of bronchopulmonary anastamosis. The normal is < 10 mmHg.
– 3 Factors can falsely alter the A-a gradient:
• This number increases with age
• The A-a gradient increases by 5-7 mmHg for every 10% increase in FiO2
• Also, part of the PAO2 equation is the Barometric pressure. This is a constant 760mmHg in
Alexandria, LA. However, if the pt is intubated we need to add the mean airway pressure
(roughly) to the barometric pressure. The mean airway pressure can be automatically calculated by the ventilator.
Why is the A – a Gradient Important?
• In one answer: It is in the beginning of every algorithm for the work up of acute respiratory failure. This is the backbone of Acute
Respiratory Failure
• “Normal A – a gradient means that there is no problem with the lungs or the pulmonary circulation. The hypoxemia is a result of inadequate ventilation alone”
Acute Respiratory Failure
• Acute Respiratory Failure is classified into 2 broad categories:
Hypoxemic and Hypercapnic. But, there is significant etiological overlap in the two.
• There are 3 major sources of Hypoxemia:
1.
V/Q Abnormality
2.
Alveolar Hypoventilation
3.
DO2/VO2 Imbalance
• There are 2 major sources of Hypercapnia:
1.
V/Q Abnormality
2.
Alveolar Hypoventilation
• There is also another way to separate: Type I and Type II but these are confusing and not prudent to learn as they have no utility in clinical practice (in my opinion)
• Before we move on, lets define hypoxemia and hypoxia.
Hypoxia vs. Hypoxemia
• Hypoxia refers to inadequate delivery of oxygen to tissues or ineffective cellular utilization of oxygen, leading to anaerobic metabolism
• Hypoxemia refers to a PaO2 less than 60 mmHg
• To get a really clear understanding of the difference, we have to consider how oxygen is delivered to the tissues in an equation. Oxygen delivery is equal to the oxygen content times the cardiac output:
– Oxygen Content Eqn
• CaO2= 1.34 (Hgb)(SaO2) + 0.003 (PaO2)
Therefore its easy to see that the most important factors causing hypoxia are low Hgb and low SaO2. Therefore hypoxemia can cause hypoxia.
• There are 4 types of hypoxia (CASH)
– Cytopathic: heart pumps enough O2, but something inhibits oxidative phosphorylation (septic shock, cyanide, salicylate od)
– Anemic: not enough RBC to carry oxygen to the tissues
– Stagnant: low CO, which leads to tissue hypoxia even if the pt is breathing
100% O2
– Hypoxemic: low SaO2 leading to low delivery of O2 to tissues
3 Major Sources of Hypoxemia
1. V/Q Abnormality: Shunts, Dead Space, and Mismatch
2.
DO2/VO2 Imbalance
3.
Alveolar Hypoventilation
All of these can be separated based on the A-a gradient and Mixed
Venous PO2. Remember these 2 major rules:
1. The only time we have a normal A-a gradient is when there is
NO LUNG PATHOLOGY. Meaning the lungs have nothing to do with the respiratory failure. This is only the case in Alveolar
Hypoventilation!
2. DO2/VO2 imbalance is the only situation where we have a decrease in the mixed venous PO2.
*What is the mixed venous PO2 and where do we find it?
Hypoxemia: V/Q Abnormality
• The adequacy of gas exchange in the lungs is determined by the balance between pulmonary ventilation and capillary blood flow. This balance is expressed as the ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) ratio.
• The influence of V/Q ratios on pulmonary gas exchanged is described in slide using an alveolar-capillary schematic
Drawing Comparing Shunt and Dead
Space Ventilation
Shunt Dead Space
Blood
Blood is shunted from the right to the left side of the heart as it passes alveoli without gas exchange
Blood
Dead space is the opposite of a shunt-the alveoli are ventilated but there is no perfusion
Hypoxemia: V/Q Abnormality
Shunt
• A shunt describes the condition where blood flow passes from the right side of the heart to the left side of the heart through areas where there is no ventilation whatsoever.
The V/Q ratio is < 1 in a shunt.
• Shunts are termed “Intra-pulmonary Shunts”. They are termed True Shunt and Venous Admixture
– True Shunt
• Uncorrected ASDs and VSDs. The Eisenmenger Syndrome is a VSD with shunt reversal (begins Left to Right, but as the right ventricle hypertrophies the shunt becomes right to left and the pt becomes hypoxemia). This is our only situation where we have “true shunt”.
– Venous Admixture
• Venous Admixture: flow that does not equilibrate completely with alveolar gas. As the venous admixture increases, the V/Q ratio decreases until it reaches true shunt conditions (V/Q = 0)
Hypoxemia: V/Q Abnormality
Venous Admixture
• Patho-physiology:
– The intra-pulmonary shunt fraction increases when the small airways are occluded (asthma), alveoli are filled with fluid
(pneumonia, pulmonary edema), or when alveoli collapse
(ARDS, atelectasis).
• Arterial Blood Gases
– The typical manifestations of a shunt on an ABG are a decrease in the PaO2 with a normal or decreased PaCO2. The PaO2 falls progressively as shunt fraction increases, but the PaCO2 stays constant until the shunt fraction exceeds 50%. The PaCO2 is often low due to the hyperventilation triggered by the disease process (e.g., sepsis) or by the accompanying hypoxemia. See figure on next page.
Shunt Fraction on PaO2 and PaCO2
100
PaO2
Notice the PaCO2 doesn’t rise until there is 50% shunting mm HG
PaCO2
40
0 50
% Shunt
How to Calculate the Shunt Fraction
• This is a cumbersome calculation that is not realistic. The quick and dirty way is to calculate shunt fraction is the PaO2/FiO2 ratio. This is a broad definition:
PaO2/FiO2 % Shunt
<200
>200
>20%
<20%
The PaO2 is found on the ABG and the FiO2 is 21% on room air, increases by 5% with each liter of O2
(variable), or is set on the ventilator. Remember to turn the FiO2 into a decimal (21%=.21)
Is the PaO2/FiO2 ratio used in any other settings?
Shunt Fraction, FiO2, and PaO2
• The shunt fraction determines the influence of inhaled oxygen (FiO2) on the arterial PO2 (PaO2). As intrapulmonary shunt increases from 10-50%, an increase in the FiO2 produces less of an increment in the arterial PO2. When the shunt fraction exceeds 50%, the arterial PO2 is independent of changes in FiO2, and the condition behaves like a true shunt. This means, in conditions associated with a high shunt fraction (e.g.,
ARDS), the FiO2 can often be lowered to non-toxic levels (<50%) without further compromising arterial oxygenation. This prevents pulmonary oxygen toxicity.
The Influence of Shunt Fraction on the
Relationship Between FiO2 and the
Arterial PO2
120
100
Shunt
10% 20%
PaO2
(mm Hg)
80
60
30%
50%
This implies that PEEP should be used to enhance oxygenation in high shunt fraction diseases
40
20
FiO2 (%)
60 100
Hypoxemia: V/Q Abnormality
Dead Space Ventilation
• Ventilation is excessive relative to capillary blood flow. The excessive ventilation, known as dead space ventilation, does not participate in gas exchange with the blood. There are 2 types of dead space ventilation:
– Anatomic: the gas in the large conducting airways that does not come in contact with capillaries. Approx.
50% of the anatomic dead space is in the pharynx
– Physiologic: is the alveolar gas that doesn’t fully equilibrate with capillary blood.
• In normal pt’s, the dead space ventilation accounts for 20-
30% of the tidal volume
Hypoxemia: V/Q Abnormality
Dead Space Ventilation
• Pathophysiology
– Dead space ventilation occurs when the alveolarcapillary interface is destroyed (COPD), when blood flow is reduced (PE, CHF) or when the alveoli are over distended (PEEP ventilation).
• Arterial Blood Gases
– The typical manifestations of dead space ventilation on ABG is a decrease in PaO2 and increase in PaCO2.
The hyper-capnia usually appears when the dead space ventilation accounts for 50% of the tidal volume.
Hypoxemia: V/Q Abnormality
V/Q Mismatch
• Most cases of hypoxemia are the result of a V/Q mismatch in the lungs. Either shunt, dead space ventilation, or a combination of them both. This is the major etiology of acute respiratory failure: a V/Q mismatch
• Virtually any lung disease can be included in this category, but the common ones encountered in the ICU by us are pneumonia, ARDS, COPD, hydrostatic pulmonary edema, and PE
• Once again the A-a gradient is always elevated in these conditions
Hypoxemia: DO2/VO2 Imbalance
Definition
• DO2= systemic O2 delivery, controlled by cardiac output and hemoglobin
• VO2= systemic O2 uptake, controlled by numerous tissue factors
• A decrease in the DO2 is usually accompanied by an increase in O2 extraction from capillary blood, and this serves to maintain a constant rate of systemic O2 uptake (VO2) into the tissues. The increased O2 extraction from capillary blood results in a decrease in the PO2 of venous blood, and this can have a deleterious effect on arterial oxygenation.
Hypoxemia: DO2/VO2 Imbalance:
Mixed Venous PO2
• Sum of Oxygen in arterial blood is the sum oxygen in mixed venous blood (pulmonary artery, Internal
Jugular) + the oxygen added from alveolar gas. When gas exchange is normal, the major determinant is the oxygen from alveolar gas.
• However when gas exchange is faulty, the contribution from alveolar PO2 declines and the contribution of mixed venous PO2 rises. The greater the abnl in gas exchange, the greater the contribution from mixed venous PO2 to the arterial PO2.
• See graph on next page
The Influence of a V/Q Abnormality on the transition from arterial PO2 and the added effect of a low mixed venous PO2.
100
80
60
PO2
Mm Hg NL PvO2
40
20
Low PvO2
Normal
V/Q Abnormality
Venous blood
Arterial blood
Hypoxemia: DO2/VO2 Imbalance
Graph Explanation
• This graph demonstrated the influence of mixed venous PO2 on the arterial PO2 when gas exchange is impaired
• This graph illustrates how a decrease in mixed venous PO2 can aggravate the hypoxemia caused by a V/Q abnormality. It also indicates that, in the presence of a V/Q abnormality, the mixed venous PO2 is an important consideration in the evaluation of hypoxemia.
Hypoxemia: DO2/VO2 Imbalance
PvO2 Equation
• PvO2=Mixed Venous O2= k X (DO2/VO2)
• K= constant
• So any condition that reduces DO2 (low cardiac output, anemia) can decrease the
PvO2 and aggravate the hypoxemia caused by abnormal gas exchange in the lungs.
Hypoxemia: Alveolar Hypoventilation
• This term implies there is no underlying lung pathology. There is no V/Q imbalance in the lungs.
• Alveolar hypoventilation causes both hypoxemia and hypercapnia as a result of a decrease in the total volume of air inhaled and exhaled each minute.
• The etiology of alveolar hypoventilation can be broken down into 3 categories: Brainstem respiratory depression, peripheral neuropathy, and muscle weakness. See table on next page.
Alveolar Hypoventilation in the ICU
Brainstem respiratory depression
Drugs (opiates)
Obesity-Hypoventilation
Syndrome
Peripheral Neuropathy
Critical Illness
Polyneuropathy
Guillian-Barre Syndrome
Muscle Weakness
Critical Illness Myopathy
Hypophosphatemia,
Hypomagnesmia
Myasthenia gravis
Hypoxemia: Alveolar Hypoventilation
Respiratory Muscle Weakness
• Most cases of respiratory muscle weakness are a combination an idiopathic polyneuropathy (critical illness polyneuropathy) + myopathy (critical illnes myopathy). These 2 illness are specific to ICU patients, particularly those with sepsis, prolonged mechanical ventilation, and prolonged neuromuscular paralysis.
• How do we evaluate respiratory muscle strength?
– NIF: this is the maximum pressure recorded during a maximum inspiratory effort against a closed valve. Most healthy adults can generate a NIF of -80 cm H2O. A NIF that does not exceed -25 cm H2O is considered evidence of respiratory muscle failure. Do we discuss NIF anywhere else?
Putting It All Together:
Diagnostic Evaluation of Hypoxemia
Normal
A-a PO2
Increased
V/Q Abnormality
Alveolar
Hypoventilation
NIF?
PvO2 NL
Central
Hypoventialtion
Low
Neuromuscular
Disorder
>40mmHg <40mmHg
V/Q Abnl DO2/VO2 Imbalance
Hypercapnia
• Hypercapnia is defined as an arterial PCO2 above 46 mm Hg that does not represent compensation for a metabolic alkalosis.
• The causes of hypercapnia can be identified by considering the determinants of arterial PCO2. Those are the CO2 production, CO2 elimination by alveolar ventilation, and the dead space ventilation.
• These are put into an equation and that equation identifies the 3 major sources of hypercapnia:
1. Alveolar hypoventilation
2. Increased dead space ventilation
3. Increased CO2 production
Hypercapnic Predominant
Alveolar Hypoventilation
• Alveolar hypoventilation causes hypoxemia and hypercapnia. See table on slide 27 for the etiology of alveolar hypoventilation. The thing to keep in mind is if we have pure alveolar hypoventilation, there would be NO LUNG
PATHOLOGY (i.e. normal A-a gradient).
• We most commonly see this in our OSA/OHS patients.
Hypercapnic Predominant
V/Q Abnormality
• As I said earlier, hypercapnia is not a feature of increased intrapulmonary shunt until the shunt is >50%. This is why hypercapnia is not a feature of pulmonary edema or pneumonia until they are far advanced.
• Hypercapnia is more a feature of dead space ventilation. As in advanced emphysema
(where the alveolar capillary interface is destroyed) or a large PE.
Increased CO2 Production
• Normally, increases in CO2 production are matched by an increase in minute ventilation and therefore are inconsequential. However, if there is a lung pathology or weakness that impairs minute ventilation this can change CO2 levels.
The most common cause of increased CO2 production that the critically ill patient cant overcome is overfeeding. The major problem is overfeeding with carbohydrates due to the fact there is more CO2 produced from carbohydrate metabolism.
Just a few Random Thoughts
• ABG can vary spontaneously without a change in clinical condition of the patient. A study done showed large spontaneous variations in PaO2 and PCO2 over a one hour period in a group of stable pt’s. The arterial
PO2 could vary by as much as 36 mm Hg, while the arterial PCO2 varied by as much as 12 mm HG. Should we routinely monitor ABGs in stable patients?
• Over the course of an average ICU stay, about 125 lab measurements are performed on each pt, requiring an avg of 550 mL of blood. This is enough to drop the hemoglobin level by 3 g/dL.