File - integrated science 1a!
advertisement

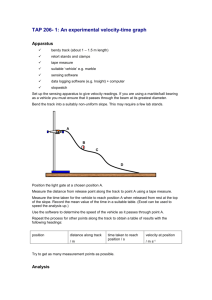
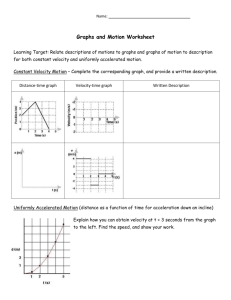
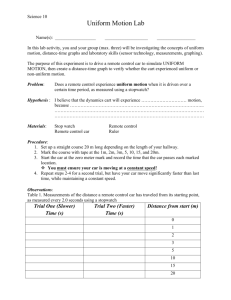
+ Acceleration Mr. Lambert Integrated Science 1A Trimester 1, 2014 + Bell Ringer Draw a distance-time graph of the following scenario: Martin gets in his car and speeds up to 60 mph. He then gets on the highway and maintains a constant speed until he reaches his exit. As he exits the highway, he slows down and stops at the red light. + Agenda 1. Bell Ringer 2. Learning Targets 3. Lab Activity 4. Velocity-time graphs 5. Exit Slip + Learning Targets On your Bell Ringer Sheet, write the following: We will analyze graphical representations of change in motion to explain acceleration. + Review Describe the motion of the object represented in the graph below. + A new graph! Before: Distance (m) Now: + Object not moving Object traveling at constant velocity + Constant velocity Constant acceleration + Object returns to starting point Deceleration + Challenge Negative Y-axis? What would this graph look like as a velocity-time graph? What would this graph look like as a distance-time graph? + Moving man simulation http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation /moving-man + What is the motion of this graph? + Graphing activity Follow my directions on how to make the pamphlet Make up a graph (Distance-Time OR Velocity-Time) with you group and draw it on the cover. Maximum of six changes in motion! When I signal that time is up, pass your pamphlet to the next group Example: Group 5 The it. next group must look at the graph and make up a story for When The Group 6 I signal time is up, pass the pamphlet next group must ONLY LOOK AT THE STORY and draw a graph. + Whiteboards + Practice #1 Draw a distance-time graph, and velocity-time graph showing an object with a constant acceleration. + Practice #2 Draw a distance-time graph, and velocity-time graph showing an object with a constant velocity. + Practice #3 Draw a distance-time graph, and velocity-time graph showing an object with a constant decelerating. + Practice #4 Describe below: the motion depicted by the velocity-time graph + Practice #5 Describe the motion depicted by the velocitytime graph below: + Practice #6 Describe the motion depicted by the velocitytime graph below: + Practice #7 Draw a distance-time graph and velocity-time graph of the following scenario: Jeremy is standing outside. He begins to run and reaches a speed of 10 mph. He keeps running at this speed for 1 hour and slows down to 5 mph. After another hour, he stops to catch his breath. + Practice #8 Draw a distance-time graph and velocity-time graph of the following scenario: Kiara steps out of her car and speeds up to a fast walking pace. She maintains this speed as she walks down the road. As she approaches a crosswalk, she slows down to a stop and waits for the light. Kira realizes that at this pace she will be late. She begins to run down the street and soon reaches her office building. + Practice #9 Bungee jumping https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zG22 qQydPVQ Skydiving (only until 0:35) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4VUe LDA27Mc Felix Baumgartner https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FHtvD A0W34I Supersonic flights https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHBe vPYVzaY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gWG LAAYdbbc ZR1 Corvette vs. Jet (start 8:00) Wingsuit skydive https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6m uw6pqzk_c https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TW fph3iNC-k Spiderman https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bm DnFqqp6Xk + + Group practice problems Groups Each group will work on a different problem. Once finished, all the groups will pass their problem clockwise to the next group. + Speed of Bowling Ball for Four Bowlers Speed of Bowling Ball (m/s) 25 Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from the data? 20 a) The bowling balls go faster if the size of the bowling ball is greater. b) The bowling balls slow down as they move down the lane. c) Bowler A bowled the fastest ball. d) None of the statements are true. 15 A 10 B C D 5 0 0 5 10 Distance Ball Travels (m) 15 + Speed of Bowling Ball for Four Bowlers Speed of Bowling Ball (m/s) 25 Which bowling ball was the slowest? 20 Were 15 A 10 B C D 5 0 0 5 10 Distance Ball Travels (m) 15 the bowling balls accelerating or decelerating? + Felix Baumgartner reading review What is terminal velocity? Why did he not keep accelerating? What caused Felix to heat up? + Learning Targets How did we do? We will analyze graphical representations of change in motion to explain acceleration. + Exit Slip Describe the motion depicted by the velocity-time graph below: + Exit Slip Describe the motion depicted by the velocity-time graph below: