Adderall - Biology - University of New Mexico
advertisement

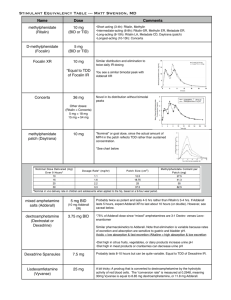
(Dextroamphetamine and Amphetamine) Javier Manriquez Travis Maestas Adderall is the brand name of any type of amphetamine salt-based medication used to control symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity and in some cases narcolepsy. It is a Central Nervous System Stimulant (CNS) that enhances the release and prevents the re-uptake of dopamine which in turn creates hyper-alertness and the ability to focus on something for extended period of times. We wanted to do further research on this popular drug that when used properly, can help those who suffer from ADD/ADHD and in some cases narcolepsy. We will briefly touch on the legal uses of Adderall and focus mostly on the abuse of this drug when it is not prescribed. We will analyze the effects on the long term neurochemical pathways of the brain so our readers get a deeper understanding of the dangers of abusing this drug. Originally, Adderall was used as a treatment for obesity known as Obertrol or Rexar Pharmacal. It was used throughout the 1960’s and in 1994 a new pharmaceutical company bought the formula and began marketing it as Adderall. It is used to treat cases of ADD/ADHD Allows for the person to concentrate for long periods of time. Adderall is the most commonly abused drug in the market right now and it is most used by college aged students as the “study” drug. Adderall is a phenylalkylamine, which contains a phenyl ring and a nitrogen group. It is molecularly similar to catecholamines such as norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, ect. This drug is intended for oral ingestion, but when it is abused it can also be insufflated. High acidic levels in the stomach and GI tract decrease the absorption and increase excretion via urine. When taken orally, it is metabolized in the liver and has a half life of about 10 hours in adults. Two kinds: Instant Release which takes 3 hours to reach its maximum concentration. Extended release from which takes 7 hours to reach its maximum concentration. Amphetamines in Adderall bind to receptors in place of the catecholamine's produced naturally. This stimulates the Central Nervous System by acting as a reuptake inhibitor and increases the levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain and in between neurons. AdderallPhenylacetoneBenzoic AcidHippuric Acid Since this drug increases the amount of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft this makes the user have: More energy Sexual desire Better focus Productivity Common Anorexia Dry mouth Chronic thirst Insomnia Migraines and headaches Stomach pain High blood pressure Mood swings Nausea Vomiting Dizziness Sudden spikes in heart rate Chest pain Slowing of growth in children Lethal Suicidal thoughts and ideations Depression It has a highly addictive nature Can result in: Seizures Heart attacks High blood pressure Stroke Death College is stressful most of the time. When something is not due in one class, it is due in the next. Most of our peers see Adderall as a way to gain time and make the most of the time that is allotted to them. Others like the “high” of Adderall and the hyper awareness of their environment. Here at the University of New Mexico, like in many other campuses across the U.S, can be attained easily at a cost of $3.00 to $5.00 a pill. We think that a combination of factors such as price, the length of the high, and the wide availability are what make this the most widely abused prescription in the country and on our campus. o o o o “If you are drinking, it helps you drink more and stay up for the whole party” “You can cram an entire tests material in one night” “You are Productive and feel on top of the world” “The most important meal of the day” Those who do not suffer from ADD/ADHD have a baseline of stimulation already there working normally. Adderall in an ADD/ADHD patient causes under stimulation for a few minutes until the brain reaches the normal baseline that allows them to concentrate Affects the nucleus accumbens in the mid brain known also as the “pleasure center” It affects dopamine which is an inhibitory transmitter that tries to stop any excitement from occurring. The nucleus accumbens releases another inhibitory transmitter called GABA and by virtue of inhibiting the inhibitor, dopamine acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter. In large doses, Adderall produces the same chemical effects in the brain as amphetamines. In the long run, more and more of the drug is needed to sustain the high, and this happens because the process where dopamine recycles itself is blocked and this “reuptake” is blocked. With constant doses, the amount of dopamine in each neuron decreases, even thought the drug tells the brain to release all it has, the abuser will take more and more of the drug to get the same rush but there is not enough dopamine left. It works similarly to cocaine therefore it has the potential to become highly addictive over a period of time. There is very little research about the use of Adderall in healthy populations. If it is used as a study aid in school, it is more likely to be used again and again, regardless of the physical dependence. Adderall when abused can be as dangerous and toxic as meth or cocaine and if you are caught using it without a prescription, it is a felony and can land you 3 years in jail and up to a $10,000.00 fine! It “fries” your neurotransmitter network and can lead to diseases such as Parkinson's with its extended use. The Drug: Adderall Uses: Commonly used to treat patients diagnosed with ADD/ADHD Abuse: Commonly used amongst college students as a study aid Effects: Users can become addicted to the drug Adderall has similar effects on humans as Cocaine Can lead to diseases such as Parkinson’s Disease Results: The brain can become dependant on Adderall and cause it to potentially stop producing Dopamine In conclusion, Adderall has its benefits to those who need it for medical reasons, but there is a large portion of our population that abuses the drug and are unaware of the potential dangerous and harmful long term effects that it can have on the brain. http://www.drugs.com/monograph/adderall.html https://online.epocrates.com/noFrame/showPage.do?method=drugs&MonographId=359&A ctiveSectionId=5 Behavioral and pharmacokinetic assesment of the components of Adderall, Slezak, J.M. Mueller, M, Ricuarte G.A. The perceptions of pharmacological cognitive enhancers on campus: A classroom exercise in neuroethics. Stuthers W.M. Non-Medical use of Prescription drugs and Sexual risk behavior in young adults. Benotsh, Koester, Luckman Nonmedical prescription stimulant use among college students: why we need to do something and what we need to do.