Anatomy LAB: Back Muscles

Knee joint and
Muscles of Leg
Dr. Sama ul Haque
Name and identify the bony features of the tibia and fibula.
Know the type and formation of knee joint.
Explain the stability factors of the knee joint.
Identify the muscles that act at the knee joint.
Know the locking and unlocking mechanism of the knee joint.
Understand the functions of the Popliteus and Iliotiabial tract.
Identify the neurovasculature behind the knee (popliteal fossa) and in the leg.
Enlist the contents of the muscular compartments of the leg.
Identify the muscles of the leg in terms of their origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions.
Enlist the muscles causing plantar flexion, dorsiflexion, eversion, inversion, flexion of digits and extension of digits.
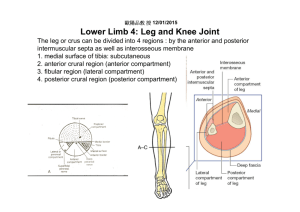
Anterior.
Head of
Fibula interosseous membrane
Tibia:
Condyles
Tibial tuberosity
Tibia and fibula are united by an interosseous
Membrane.
[Proximal and distal tibio-fibular joints]
The fibula is not part of the knee joint.
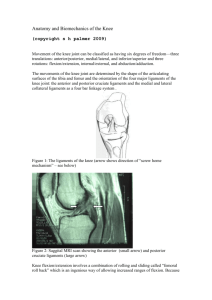
Sagittal section thru knee
Patella articulates with the femur.
During the entire range of knee flexion, the patella only articulates with the femur.
KNEE.
Modified hinge jt.
-flexion / extension
(some rotation)
Superior view of tibial surface.
Tibial Condyles lateral articular surface medial articular surface
Tibial Condyles
Medial and lateral articular surfaces, separated by an intercondylar eminence.
Medial and lateral Meniscii: intercondylar eminence lateral meniscus PCL medial meniscus
Fibrocartilage shock-absorbers that sit on surface of tibial condyles and deepen the articular surface.
Anterior and posterior
Cruciate ligaments (ACL, PCL):
-hold femur and tibia together
-stabilize knee joint
ACL
Femur
Medial and lateral femoral condyles have same shape as corresponding tibial condyles:
Medial – elongated
Lateral – circular
Meniscii:
Each is attached to tibia at their ends
(horns).
Anterior Cruciate
Ligament:
- Weaker of the two, slack when knee is flexed & tightens in extension.
- Prevents hyperextension.
Posterior Cruciate
Ligament:
- Tightens during flexion of knee joint
Joint capsule
Retinacular fibres
Stabilization of the medial knee:
Tibial collateral ligament.
tibial collateral ligament
A flat strap which is attached to the medial aspect of tibia and medial femoral epicondyle.
Its deeper fibres are attached to the medial meniscus.
Pes anserinus: Common insertion of
Sartorius, gracilis, semitendinosus
Ilio-tibial band fibular collateral ligament
Biceps femoris
Head of fibula
Stabilization of the lateral knee:
Fibular collateral ligament
- a cord which is attached to the head of the fibula and the lateral epicondyle of the femur.
*Its deep fibers are not attached to the meniscus.
» Remember the 3 C’s:
» -cartilage
» -cruciates
» -collaterals
Unhappy triad - common associated injury to:
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament)
MCL (Medial / tibial collateral ligament) medial meniscus
Anterior knee in extension
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis extensor retinacula
Patellar
Ligament
Fibrous capsule of the
KNEE (anterior):
Stabilized by:
Extensor Retinacula
- Derived from insertions of vastus lateralis and vastis medialis into patella and into sides of patellar ligament.
Posterior knee in extension
Tendon of
Semimembranosus oblique popliteal ligament
Fibrous capsule of the
KNEE (posterior): arcuate popliteal ligament
Thickened by ligaments:
-Arcuate popliteal ligament
(arching over popliteus muscle)
Popliteus
-Oblique popliteal ligament
(from tendon of insertion of semimembranosus m.)
Bursae of Knee Joint: suprapatellar bursa prepatellar bursa infrapatellar bursae
Sagittal section shows:
- Suprapatellar bursa
(extension of synovium under tendon of quadriceps femoris)
Subcutaneous bursae:
- Prepatellar,
- Infrapatellar (2):
(superficial & deep to patellar ligament).
Popliteal Fossa
Popliteal fossa
Diamond-shaped region
Posterior to knee
-semimembranosus / semitendinosus
-biceps femoris
-medial & lateral heads of gastrocnemius.
Contents:
-popliteal vessels (from femoral vessels)
-Tibial and Common fibular (peroneal) divisions of the sciatic nerve.
Superficial:
-Small saphenous vein draining into popliteal vein
Muscles that act on the knee (modified hinge joint):
Main movement = flexion / extension
Flexion – mainly hamstrings (+ Sartorius, gracilis, gastrocnemius)
Extension – mainly quadriceps (+ tensor fascia lata)
Rotation (possible when the knee is partially flexed, or in the final stage of extension):
[here defined as rotation of tibia with respect to the femur]
Medial rotation – semitendinosus, semimembranosus popliteus (extended knee)
Lateral rotation – biceps femoris
Lateral malleolus interosseous membrane
Medial malleolus
LEG.
Tibia and fibula:
-held together by an interosseus membrane.
-anterior border of tibia is subcutaneus from the tibial condyles to its distal end.
[Shin]
only the distal ¼ of fibula is subcutaneus
The distal ends are held together to form the proximal articular surface of ankle.
Each ends subcutaneusly as a Malleolus
(medial – tibial and lateral - fibular).
Proximal and distal tibio-fibular joints
Mid-shaft cross-section of leg:
Functional compartments.
Fascial compartments:
-anterior
-lateral
-posterior (superficial & deep) anterior compartment (dorsiflexion, extension of digits) lateral
Compartment
(eversion) deep posterior compartment
(plantarflexion) superficial posterior compartment
(inversion, flexion of digits)
Plantarflexion / dorsiflexion: (ankle joint)
Flexion / extension: (digits)
Inversion / eversion: Complex twisting movement at transverse tarsal and subtalar joints. [inter-tarsal joints]
extensor digitorum longus extensor retinaculum tibialis anterior extensor hallucis longus
Anterior compartment of leg:
-tibialis anterior
-extensor hallucis longus
-extensor digitorum longus
(fibularis tertius)
All supplied by the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve.
Hallux = big toe [hallucis]
Tendons are bound down by extensor retinaculum as they cross the ankle jt.
Function: -dorsiflexion (ankle)
-extension (digits)
-inversion
Common
Fibular n.
Superficial
Fibular n.
extensor digitorum longus
Deep Fibular n.
Tibialis
Anterior
Deep dissection
Anterior view:
Note vulnerability of common fibular nerve as it winds around the neck of fibula.
extensor hallucis longus
DROP FOOT??????
peroneal retinaculum
Fibularis longus
Lateral compartment of leg:
- Fibularis (peroneus) longus
- Fibularis (peroneus) brevis
-both supplied by the superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve.
Tendons are bound down by fibular retinaculum as they pass behind the lateral malleolus.
Functions:
- eversion
Fibularis brevis
- plantarflexion
Fibularis tertius
FIBULARIS=PERONEUS
Posterior compartment of leg:
Superficial medial & lateral heads of gastrocnemius gastrocnemius
Insert into calcaneus
(heel)
Function –plantar flexion
Achilles tendon
(calcaneal tendon)
Innervated by Tibial nerve.
plantaris soleus
Deeper dissection of superficial posterior compartment:
- medial & lateral heads of gastrocnemius
- soleus
- (plantaris)
Common tendon:
Calcaneal (achilles) tendon
- insert into calcaneus (heel)
Function – plantar flexion
Innervated by Tibial nerve.
flexor digitorum longus tibialis posterior flexor retinaculum
Posterior (deep) compartment of leg:
-Tibialis posterior
-Flexor digitorum longus
-Flexor hallucis longus flexor hallucis longus
Tendons are bound down by flexor retinaculum as they pass into foot behind the medial malleolus.
Functions: -plantarflexion
-flexion
-inversion
Innervated by Tibial nerve .
posterior tibial a.
popliteal a.
Blood supply to the lower limb:
Thigh:
Femoral artery and branches:
(profunda, medial & lateral circumflex) anterior tibial a.
Behind knee:
Popliteal artery fibular artery Leg:
divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
to supply these compartments.
The posterior tibial artery gives off the fibular (peroneal) artery to supply the lateral compartment.
Anterior
Cutaneus innervation of thigh and leg:
Posterior
Anterior, lateral, medial thigh ( lumbar plexus).
- branches of femoral n.
- lateral femoral cutaneous n.)
Post. femoral
Posterior thigh
– from sacral plexus.
cutaneous n.
Anteromedial leg
– branch of femoral n.
(Saphenous nerve).
saphenous nerve
L4
Posterolateral leg
– from Sciatic n.
(Sural nerve).
Anterior leg:
- From Sciatic n.
(Superficial fibular n.)
S1 sural nerve
Superficial drainage of the lower limb
Varicose veins
Great
Saphenous vein:
Drains into femoral vein in femoral triangle
Small
Saphenous vein:
Drains into popliteal vein