Tropical Savanna - katlinvermeulen
advertisement

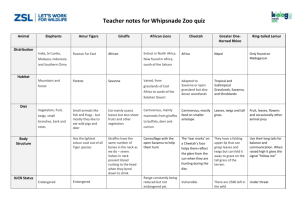
Tropical Savanna QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. By Katie Vermeulen The Climate • The annual precipitation of the tropical savanna is 20 - 40 inches. • The average temperature is 78F • Both the dry, and wet seasons last 5-6 months each. Abiotic Factors • The factors that can affect the tropical savanna and its organisms living in it are unseasonably warm temperatures, seasonal rainfall which can be too high or low which can cause floods or droughts, and fires that can be set by lightning can be harmful to the organisms. Dominant Plants • The dominant plants in the tropical savanna is fire resistant and drought tolerant shrubs, and highly elevated grass. The trees are isolated along with the shrubs. Since the trees are isolated, the tropical savanna is an open area filled with the tall grass. Dominant Wildlife • The dominant animals in the tropical savanna are the hoofed mammals which include antelope, buffalo, wildebeest, zebra, rhinos, giraffes, and elephants which are the herbivores. The dominant mammal carnivores are lions, cheetahs, leopards, and hyenas. Geographical Distribution • The tropical savanna is located in northern and east central South America, central and southern Africa, the Indian Peninsula in Asia, and scattered throughout Australia. Impact of human Activity Human had caused a lot of changes to the landscape of and the animals in grasslands since a long time ago. Large areas of grassland have been turned into farmlands for growing crops and for rearing cattle. Sometimes, fires are started by human and they spread quickly through grasses and damage the soils. Moreover, a large number of animals have been hunted for their valuable body parts. For example, elephants were shot for their tusks, lions were killed for their fur and bison were hunted for their meats. Sites Used • www.blueplanetbiomes.org/savanna.ht ml • Adtbma.tripod.com/idl.html • Library.thinkquest.org/26634/text/grass/i mpact.html