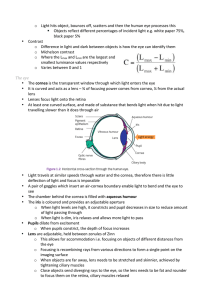
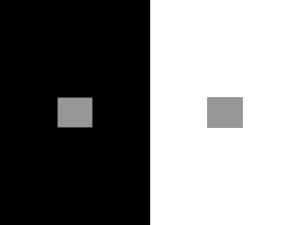Functional organization of the nervous system
advertisement

Sensory system: The eye & the central visual system 정성권 (schung@med.skku.ac.kr) http://www.physpharm.fmd.uwo.ca/undergrad/sensesweb/index.htm Structure of eye 1. Focusing carried by cornea, lens, and pupil 2. Organization of retina: functional roles of 5 different neuron types in the retina Signal transduction in photoreceptors 1. dark current 2. Photoisomerization of rhodopsin - http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/matthews/rhodopsin.html * signal amplification 3. Receptive field in retina: “on” and “off” center ganglion neurons * Lateral inhibition - http://cas.bellarmine.edu/tietjen/Animal%20Behavior/lateral_inhibition.htm ** What is the advantage to have antagonist surround? 4. M-, P-, nonM-nonP-type ganglion cells: very color sensitive Color vision 1. Color-opponent cells: color adaptation 2. Double-opponent cells: color sensitivity, explains color adaptation Targets of optic track 1. LGN → optic radiation → primary visual cortex 2. Transection in the optic track and the visual defects 3. Non-thalamic targets of the optic track - hypothalamus: biological rhythm (sleep/ wakefulness) - pretectum: control the size of pupil - superior colliculus: saccadic eye movements, quick jump in eye position 4. Input, output in LGN Primary visual cortex 1. Retinotopy: brain’s interpretation of distributed patterns of activity 2. Six cell layers in cortex: ocular dominance columns Layer IVC → layer IVB, III (binocular input) Patterns of outputs Assignments Q1. What are the reasons for the following eye disorders? Cataract Glaucoma Q2. What is the major reason for the presbyopia (old eye)? And how would you fix the problem? Q3. What is the function of pigmented epithelium in visual system? Q4. Illumination on photoreceptor induces hyperpolarization. Why? Q5. There are two reasons why the rod system has poor visual acuity. Explain them. Q6. The response of a bipolar cell’s membrane potential to light in the receptive field center is opposite to that of light in the surround. Explain the mechanism for this arrangement. Q7. How does the brain compute what it must using so few active neurons? Q8. Early visual scientist thought that a large bright light would best activate ganglion cells. Why were they wrong? Q9. Draw the stimulus that would maximally activate an off center ganglion cell. Q10. The prolonged exposure to red light produces a shade of green in white back ground. Why? Q11. What are the functions of some retinal ganglion cell’s projections to hypothalamus and pretectum? Q12. What are the dimension and the function of “cortical module (hypercolumn)”?