ACTIVE TRANSPORT WORKSHEET Go to my website Go to
advertisement

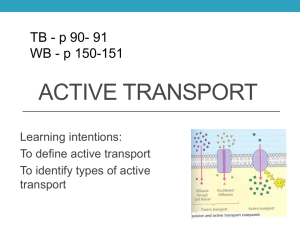
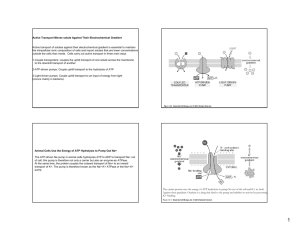
ACTIVE TRANSPORT WORKSHEET Go to my website Go to animations Click on McGraw Hill series of animations Click on sodium potassium pump animation Follow animation & answer the following questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Is sodium-potassium pump a form of active or passive transport? What is the energy source for the sodium-potassium pump? How much sodium ion attach to protein pump? Which direction is sodium ion pumped? How much potassium ion attach to the protein pump? Which direction is potassium ion pumped? Is this a uniport, symport, or antiport? Are both sodium ion and potassium ion moved against their concentration gradient? 9. What cell type is this type of transport extremely important? Click on co-transport animation and answer following questions: 1. What are some types of molecules that might be transported against a concentration gradient? 2. In co-transport where is the sugar concentration high and where is it low? 3. What is the energy source for the movement of sugar? 4. In co-transport where is the sodium ion concentration high and where is it low? 5. Is this a uniport, symport, or antiport? 6. What maintains sodium ion concentration for co-transport? Click on proton pump animation and answer following questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Describe the proton pump? Does it require energy? Does it move hydrogen ions against its concentration gradient? Does it create an electrochemical gradient? Do you think it (hydrogen ions) can be used to co-transport another substance into cell? Explain 6. Is this a uniport, symport, or antiport? Click on endocytosis & exocytosis animation and answer the following questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Define endocytosis What are three types of endocytosis? Describe phagocytosis Describe pinocytosis 5. Describe receptor mediated endocytosis 6. Describe exocytosis Go to my website Go to animations Click on active transport Follow animation & answer the following questions: 1. Read introduction and describe the difference between primary active transport & secondary active transport. 2. Describe how an electrochemical gradient is created 3. Can the electrochemical gradient be tapped for energy? 4. What maintains the electrochemical gradient? 5. Describe how glucose is transported by secondary active transport?