H.3 Absorption
advertisement
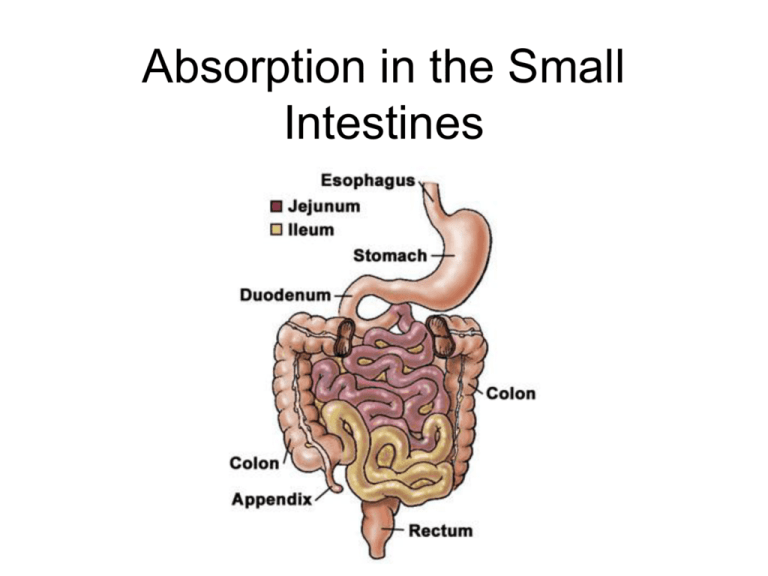
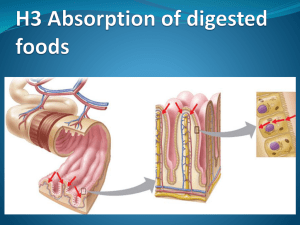
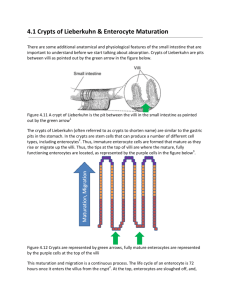
Absorption in the Small Intestines IB Assessment Statement • H.3.1 Draw and label a diagram showing a transverse section of the ileum as seen under a light microscope. Include mucosa and layers of longitudinal and circular muscle. Small Intestines • Most digested food is absorbed in the small intestines – Mainly in the latter part of the Intestines called the ileum. H.3.1: The ileum • The ileum is the main site for absorption of digested food, however, cellulose, lignin, bile pigments, bacteria and intestinal cells are not absorbed into the body. IB Assessment Statement • H.3.2 Explain the structural features of an epithelial cell of a villus as seen in electron micrographs, including microvilli, mitochondria, pinocytotic vesicles and tight junctions. Small Intestines – the ileum • The ileum is composed of small structures called villus. Small Intestines – Ileum -- Villus • The out layer of cells of the villus is where most absorption of digested food occurs. Outer layer of Cell on Villus • The outer layer of cells on the villus is called the villus epithelium cells. Villus Epithelium Cells • Vllius epithelium cells features – Tight junctions – Microvilli – Mitochondria – Pinocytic vessels Epithelium Cell of Villi IB LEARNING OBJECTIVE H.3.3 Explain the mechanisms used by the ileum to absorb and transport food, including facilitated diffusion, active transport and endocytosis. Animation for Absorption: http://nutrition.jbpub.com/resources/animatio ns.cfm Epithelium Cells of villi • Microvilli protrusions of plasma (cell membrane) - increase surface area of plasma membrane exposed to digested food. – Thus increase the rate of absorption of food by: • Simple diffusion – no energy required, moves with concentration gradient, permeable to plasma membrane • Facilitated diffusion – no energy required, moves with concentration gradient, can not pass through plasma membrane thus requires protein channel • Active Transport– requires energy, move against concentration gradient, require protein pump • Endocytosis -- pinocytosis Uptake of carbohydrates by villi • The Carbohydrates, (glucose & galactose) are actively transported into the epithelial cells • Frustose enters the epithelial cells via facilitated diffusion • All carbohydrates enter the blood stream via the capillary in the villus. Uptake of Proteins by the villi • Products of protein digestion (amino acids) are actively transported in to the epithelial cells • Amino acids then diffusion into the blood stream via the capillary in the villi Uptake of Lipids by the villi • The products of digested lipids ( fatty acid chains and glycerol enter the villi cells via simple diffusion. • Some are then transport into the blood stream via simple diffusion • Others enter the lacteals of the villi via endocytosis IB LEARNING OBJECTIVE H.3.3 Explain the mechanisms used by the ileum to absorb and transport food, including facilitated diffusion, active transport and endocytosis. Animation for Absorption: http://nutrition.jbpub.com/resources/animatio ns.cfm IB Assessment Statement • H.3.4 List the materials that are not absorbed and are egested – Limit this to cellulose, lignin, bile pigments, bacteria and intestinal cells •