File
advertisement

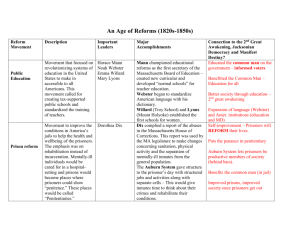
A Reforming Society The Reform Movement improve schools Improve prisons Stop alcohol abuse Stop slavery The Public School Movement What they wanted: • Tax-supported public schools • Laws requiring children to attend school Why they wanted it: • Education would give Americans the knowledge they needed to participate in government • Educated workers would promote economic growth • Educating all will keep the wealthy from oppressing the lower classes Horace Mann • Established and led the first Board of Education in Massachusetts • Argued for: • School oversight • Adequate funding for education • Abolition of corporal punishment in classrooms Worked to create well-trained teachers Women In the Reform Movement Catherine Beecher Emma Willard Elizabeth Blackwell Ann Preston Dorothea Dix Education Reform Education Reform Medical Training for women Medical Training for women Prison and Hospital Reform DorotHea Dix • Travelled around Massachusetts, noting the condition of prisons, almshouses and hospitals • Petitioned Massachusetts legislature to stop the abuses she saw • Advocated for the creation of mental hospitals • Leader of the penitentiary movement Penitentiary movement • Saw prisons as a place to instill penitence rather than punish criminals The Pennsylvania System • Prisoners lived and worked in complete solitary confinement • Eastern State Penitentiary • was expensive and thought to be cruel Auburn Prison, New York • prisoners work together by day in silence • at night prisoners slept in solitary cells • Most American prisons adopted this system Temperance Movement • Wanted to take control of alcohol abuse which they saw as the root of many social problems • Temperance = drinking alcohol in moderation • Some wanted prohibition • Used pamphlets, posters, rallies, and petitions to governments Temperance Victory • Leader of the movement Neal Dow became mayor of Portland, Maine (1851) • He passed the so-called “Maine Law” which restricted the sale of alcohol • Many states followed suit