Labs 17 (cont.), 18, 21 - Biology102-104
advertisement

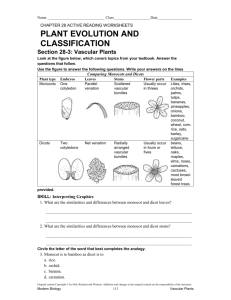
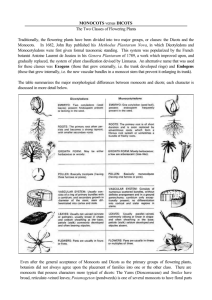
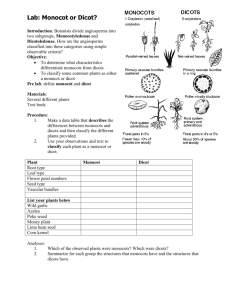
Biology 104 – Study Guide: Labs 17 (cont.), 18, 21 Lab 17: Seed Plants (cont.) Read. Know words in bold. See slides and specimens. Kingdom Plantae: Sporic life cycle (“meiosis produces spores) Be able to identify GAMETOPHYTE and SPOROPHYTE. o Gametophyte = “plant that produces gametes” (haploid) [gametes produced by mitosis] o Sporophyte = “plant that produces spores” (diploid) [spores produced by meiosis] Read introduction (pg. 221). 17. 1 Life Cycle of Seed Plants Sporophyte dominant, independent, vascular. Gametophyte GREATLY reduced (internal), dependent, nonvascular. 17. 3 Angiosperms = flowering plants (literally means = “covered seed”) Read introduction (pg. 230). Identify flower parts in Figure 17.8. Know Table 17.1 Monocots vs Eudicots (dicots) Observation: A Flower (FLOWER DISSECTION) o Directions will be given. o Find structures in #1. o Fill in blanks for questions 2-7. Read: Life Cycle of Flowering Plants and see Figure 17.9. The Male Gametophyte o Read introduction. o DEMO slide: find pollen grain, pollen tube, tube nucleus, 2 sperm o SKIP Experimental Procedure: Pollen Grains The Female Gametophyte o Read introduction. o See models and Figure 17.10. o Fill in blanks. 17.4 Comparison of Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Complete pg. 235. Know Answers to Laboratory Review *Go to Lab 21: Reproduction in Flowering Plants* 1 Lab 21: Reproduction in Flowering Plants Read introduction (pg. 277). Review Figure 21.1: Flowering plant life cycle. 21.1 Flowering Plant Life Cycle Read introduction (pg. 275). Read 21.1 Flowering Plant Life Cycle. Observation: Flowering Plant Life Cycle o Know. Fill in blanks. See Figure 21.2. Know Structure of a Flower: parts and function Observation: The Structure of a Flower o Fill in the blank. Read Plants and Their Pollinators o Read only. o SKIP Table 21.1. 21.2 Development of Eudicot Embryo o Read only. 21.3 Fruits o Read introduction (pg. 285). o Use dichotomous key to identify numbered fruits. Complete Table 21.2. Directions will be given. o Know fruits in key. Add: hesperidium, schizocarp, drupaceous nut. 21.4 Seeds Read introduction (pg. 287). Observation: Eudicot and Monocot Seeds o Do bean and corn seed dissection. o Be CAREFUL with bean: embryo is small, white, and easily lost. o Be CAREFUL with cutting corn kernel. Dry cut edge, place kernel into small Petri dish, add drop of iodine. o Know parts labeled in Figure 21.7 and Figure 21.8. o Seed Germination Read only. SKIP Experimental Procedure. Know Answers to Laboratory Review. 2 Lab 18: Organization of Flowering Plants Read. Know words in bold. See slides, specimens, lab charts, and hall posters. Know Tissues and Functions. Know Monocots and Dicots. Read introduction (pg 237). 18.1 and 18.2 Major Tissues of Vegetative Organs Read introduction. Know Table 18.1. Be able to identify those tissues in Fig. 18.2, 18.3, and on slides. Observation: Plant and Its Tissues o See DEMO slides: apical meristems in shoot, root. Compare to Fig. 18.2. Know monocots vs dicots, Fig. 18.4. Determine whether specimens are monocot or dicots (Eudicots). Know apical meristems, dermal tissue, ground tissue, vascular tissue, root, shoot (POXI: Phloem on the Outside, Xylem on the Inside). SKIP: Experimental Procedure and Table 18.2 (pg. 241). 18.3 Root System Only roots have and endodermis. Read introduction (pg. 242). See specimens, models, slides, charts, and posters. Know words in bold. Find parts and know functions of structures. Read Anatomy of a Root Tip. o Know primary and secondary growth, root cap, root hairs, zones of root tip Observation: Anatomy of a Root Tip o Answer questions 1-5 and compare to Fig. 18.5. o SLIDE: Branch root: Salix, lateral root CS. Compare to pg. 242 and to Hall Posters (Red Ring = Root). Anatomy of Eudicot and Monocot Roots o Fig. 18.6 and 18.7. Know labeled parts. o SLIDE: Monocot Root: Smilax (Look for endodermis and pattern of vascular tissue.) o SLIDE: Dicot Root: Ranunculus (Look for endodermis and pattern of vascular tissue.) Root Diversity: See specimens: taproots, fibrous roots, adventitious roots. o Compare roots of seedlings: monocots vs dicots (taproots??). 18.4 Stems Read introduction. 3 See specimens, models, slides, charts, posters. Find parts and know functions. Know words in bold type, and patterns of vascular bundles. SLIDES: Compare to text and to hall posters. o Know Monocot vs Dicot: o Dicot stem: Helianthus stem, cs (Identify sclerenchyma tissue outside vascular bundles.) o Monocot stem: Zea mays, CS only. Stem diversity: See specimens, stolons, rhizomes, tubers, corms, bulbs Anatomy of Woody Stems: o Know words in bold. Anatomy of Winter Twig o Read. Calculate age of sample twigs. Compare to Fig. 18.12. o SLIDES: Woody stems, cs. Compare to text. Calculate age of stem cs. 18.4 Leaves Read introduction. See specimens, models, slides, charts, and posters. Find parts and know functions. SLIDES: Compare to text and hall posters. o Syringa leaf, cs. Compare to Fig. 18.14 o Leaf epidermis, wm OR Tradescantia epidermis. Leaf Diversity: See specimens. Fill in blanks: Fig. 18.15. Know words in bold. o Know simple vs compound, patterns of venation. Know Answers to Laboratory Review. 4