Chapter 6: Photosynthesis
advertisement

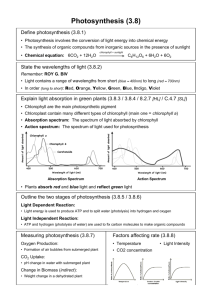
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Overview Objectives Explain the role of light and pigments in photosynthesis Explain the role of electron carrier molecules in photosynthesis State the overall equation for photosynthesis Think About It How would you design a system to capture the energy of sunlight and convert it into a useful form? Caution: solar panels are not very effective or cheap Photosynthesis Defined Is the process by which autotrophs use the energy of sunlight to produce highenergy carbohydrates (sugars and starches) that can be used as food From the Greek words “photo,” which means _____ and “synthesis,” meaning ____________ In other words, it is _____________ In the process of photosynthesis, plants convert the energy of sunlight into chemical energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates Light & Pigments Visible light from the sun is in a __________ but perceived as “white” When separated by a prism, it is red at one end and violet at the other When light strikes an object it can be _______, ________, or ________ Pigments are organic compounds within objects that absorb light Visible Light Spectrum Photosynthetic Pigments There are 3 main kinds of photosynthetic pigments in living things 1. Chlorophylls—green pigments Chlorophyll a is found in all plants, algae and cyanobacteria Chlorophyll b is found in all plants and green algae Chlorophyll c is found in diatoms and brown algae Chlorophyll d is found in red algae Photosynthetic Pigments 2. Carotenoids—red, orange, or yellow pigments Carotene is found in most plants and some algae Carotene gives carrots their color Fucoxanthin is found in brown algae and diatoms 3. Phycobilins—blue or red pigments Phycobilins are found only in red algae and cyanobacteria Some phycobilins are fluorescent Chlorophylls Chlorophylls are located in the chloroplasts Chlorophylls absorbs light very well in the _____ and _____ regions of the spectrum They do not absorb light in the _____ region of the spectrum The 2 most common types are chlorophyll a & chlorophyll b Chlorophyll a is the main pigment responsible for capturing light Chlorophyll b is an accessory pigment Carotenoids provide the yellow, orange and brown pigment colors seen during the fall Think About It So, why are plants green? Why do leaves turn colors in the fall? HINT: explain your answers in terms of light absorption and reflection Parts of the Chloroplast 1. Outer membrane 2. Inner membrane 3. Thylakoids: system of membranes arranged in flattened sacs 4. Grana: are stacks of thylakoids (Granum s.) 5. Stroma: is the aqueous solution surrounding the grana High-Energy Electrons Are produced by chlorophyll and are ____________ They require a special electron carrier molecule An electron carrier is a compound that can accept a pair high-energy electrons and transfer them, along with most of their energy, to another molecule The main carrier molecule in photosynthesis is ________ NADP+ Is also known as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate Its job is to accept and hold 2 high-energy electrons, along with a hydrogen ion (H+) Once it has done this, NADP+ coverts to _________ This conversion allows some of the energy of sunlight to be trapped in chemical form Overview of Photosynthesis Reactants Products Photosynthesis Equation Light Energy 6 CO2 6 H2O Carbon Dioxide Water C6H12O6 6 O2 Glucose Oxygen Two major steps 1. Light-dependent reactions AKA _____________ Use energy from sunlight to produce energy-rich compounds such as ATP Take place in the ________ of the _________ of the chloroplasts Water is a requirement as it is the source of electrons and hydrogen ions Oxygen is released as a __________ Two major steps 2. Light-independent reactions AKA The Calvin Cycle, the Calvin-Benson cycle, and the dark reactions ATP and NADPH molecules are used to produce high-energy sugars from carbon dioxide No light is required for this step and its takes place in the ________ of the chloroplasts Photosynthesis: An Overview Chloroplast Light CO2 NADP+ ADP + P Calvin Cycle Light Reactions ATP NADPH O2 Sugars 1. Where does ALL energy for life come from? TURNING LIGHT ENERGY INTO CHEMICAL ENERGY 2. In what cellular structure does it happen? The Importance of Chlorophyll 3. Explain the importance of chlorophyll. What color is it and why is that so? What is its role in photosynthesis? 4. Name the requirements of photosynthesis. 5. Name the products of photosynthesis.