America and the WOrld
advertisement

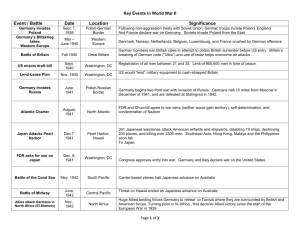
AMERICA AND THE WORLD Danielle Garceau Unit 10; Chapters 27 & 28 1920-1945 OLITICAL Retreat from Progressivism The Harding Administration (1921-1923): laissez faire government; return to “normalcy” The “Ohio Gang”: group of men loyal to Harding appointed to powerful government positions; abused power Teapot Dome Scandal (1922): accepted bribes to lease out petroleum reserves at Teapot Dome to large, private oil companies Bonus Bill Veto (1922): Harding claimed balancing the budget takes precedence over the nation's debt to veterans of WW1 The Coolidge Administration (1923-1929): laissez faire and isolation from foreign conflicts; felt he was unfit to run the country The Hoover Administration (1929-1933): isolationism; worked towards bettering the people during the Depression Hawley-Smoot Tariff (1930): raised tariffs on imported goods to a record high; cut American imports and exports by more than a half Franklin D. Roosevelt (1933-1945): brought faith, courage, and confidence through his terms (showed personal adversity by his polio) DEOLOGICAL/INTELLECTUAL Urbanism v. Suburbanism Garveyism: black nationalism Urbanism: consumerism and modernization in cities Suburbanism: resisted annexation to the cities Materialism and Consumerism: people using money more for pleasure rather than for need; due to technological breakthroughs (commercial travel, radio, adverstisments) (Urbanism) African-Americans should take pride in their own achievements and to develop an awareness of their African heritage – reject white assimilation Red Scare: fear of communism in the United States due to the growing Soviet Union and communism in the world Led to violence and arrests of innocents – Palmer Raids Convicted and arrested (possibly killed) if suspected of communism ELIGION Retreat from formal religion – began going out and expanding boundaries of values (Flappers) KKK: terrorized all non-Protestants Great Migration: African-Americans moved into cities due to lack of jobs and discrimination RTISTIC The Harlem Renaissance: black culture of literature and art Langston Hughes Coming of the Jazz Age: new carefree, primarily black popular culture ECHNOLOGY New home appliances to reduce servants and women can take care of the household on their own New military technology by the National Defense Research Committee: Development of sonar and radar capabilities (the centimetric radar) 4-engine bombers that could last longer that German ones Gee navigation system: helped plot exact locations – doubled bombing accuracy rate Enigma machine: constantly changed coding systems to prevent information from being deciphered. American Magic Operation (1941): device called “Purple” that would break Japanese coding system Ultra project: intelligence gathering The Manhattan Project (1942-46): developed the atomic bomb OCIAL African-Americans gained new job opportunities and could enlist in the army; still endured heavy discrimination (Detroit Race Riots of 1943) Native Americans assimilated to white culture Zoo-Suit Riots (LA 1943): white servicemen attacked Mexican-American servicemen (grew to growing tensions) because of their unpatriotic “zoo-suits” Women gained more job opportunities Left reservations to work in factories or become “code talkers” for the military (Navajo code) Mexican-Americans moved to work in factories where there was a labor shortage; tensions Fair Employment Practices Commission created to investigate and make right labor discrimination Rosie the Riveter: cultural icon that represented the American women who worked in factories during World War II Became romanticized by men at war – pinups (Betty Grable) Teens began dropping out of school to get jobs or enroll in the military (1/3) Increased prosperity led to more attendance at movies, dance halls, and casinos and more circulation of magazines and newspapers UPREME COURT CASES Coronado Coal Co. v. United Mine Workers (1922): striking unions were deemed in restraint of trade More to promote the economy than the workers’ rights Maple Floor Association v. US (1929): Anti-union groups were ruled not to be in restraint of trade *Government returned to pro-business EOPLE Increase in African-Americans’ and women’s rights activity Women began becoming more individualized Flappers: individual and assertive women who were more scandelous than tradition (in cities); short hair, short skirts, smoked, drank, more open about sex, etc. OREIGN (TIMELINE) 1922: The Washington Conference: goal was naval disarmament and to settle the Asia conflict 5-Power Pact: established limits on naval battleships by nation and power (US & GB:5, Japan:3, FR & Italy: 1.67), Japan got US and GB guarantee that they would stop fortifying their Far East territories 1924: Dawes/Young Plan: new financial system; US loans → Germany to pay debt from WW1→ GB & France to pay debt → US Loophole: no mention on small warships Also lowered payments and extended the amount of time they’ll have to pay back ($26.3 billion in 58.5 years) 1925: Locarno Pact: guaranteed Germany’s western boundaries as specified at Versailles 1919 1928: Clark Memorandum : US would not intervene in Latin American affairs to protect US property rights 1928: Kellogg-Briand Pact: outlawed war as an instrument of national policy – no way to enforce 1931: Hoover declares debt moratorium 1931: Japan attacks Manchuria, China and leaves the League of nations OREIGN (TIMELINE) 1932: Hoover-Stimson Doctrine: US would not recognize any territorial acquisitions gained by force 1933: FDR’s Good Neighbor Policy: attempt to create cooperation with Latin America non-violently and by non-intervention 1933: US recognizes the Soviet Union Led to Japanese 1932 bombing of Shanghai In order to gain Soviet Union on their side of the war against Japan 1934-36: Nye Committee Hearings: discovered that big businesses tricked Wilson into entering WW1 in order to protect their international interests 1935: Hitler denounced Versailles and League of Nations; Mussolini attacks Ethiopia 1936: Germany arms Rhineland, Fascists v. Communists in Spanish Civil War Neutrality Acts of 1935, 36, and 37 Prohibited sales of arms, loans, credit, and travel to belligerent nations Cash-and-Carry: nations not in war could trade with US but had to pay in cash and carry the goods on their own ships OREIGN (TIMELINE) 1937: Panay Incident: Japanese bombed USS Panay on the Yangtze R. to test US resolve 1938: AXIS created (Italy, Germany, Japan); Munich Agreement (GB, France, Hitler): Hitler can take the part of Czechoslovakia he wants, but it will be the very last land taken & no more aggression 1939: Germany takes all of Czechoslovakia; Sept. 1st march into Poland – Turning Point for US, start of WW1 1939: US begins the Manhattan Project Neutrality Act of 1939: Aggressors could not send ships to buy US munitions, but would supply other countries – made jobs Japanese apologized, gave US money, and promised no further attacks – US accepted due to isolationism US becomes “Arsenal of Democracy” 1940: “America First” Committee created (Charles Lindbergh): isolationism; put America first 1940: German ‘Blitzkrieg’ (lightning war – enormous power) in Belgium, Holland, and France 1940: British victory in Battle of Britain forces Hitler to postpone invasion plans 1st battle by German air; first major German defeat OREIGN (TIMELINE) 1941: Lend-Lease Act: will lend to countries in need of supplies; US would receive lease of land from countries it helped FDR restricted trade of goods and oil to Japan Japan had to either expand or give into US demands 1941: Atlantic Conference (GB & US): to decide postwar goals; started being called the United Nations 1941: Japan bombs Pearl Harbor; US enters the war 1942: Battle of Stalingrad begins(Russia, months without supplies and many casualties) and El Alamein (Egypt, first appearance by US – German victory) 1942: Battle of Midway; changing point in Pacific War – US begins Guadalcanal campaign and “Island Hopping” strategy 1942: Mass murdering of Jews at Auschwitz begins 1943: German surrender at Stalingrad – first major defeat 1943: Allied victory in North Africa (Patton and Montgomery) 1943: Tehran Conference (FDR, Churchill, Stalin): to finalize plans to open 2nd front in Europe 1943: US victory in Guadalcanal campaign and goes on offensive OREIGN (TIMELINE) June 6, 1944: D Day: Allied invasion of France – liberation of Paris 1944: Battle of the Bulge: Germans try to surprise Allies – failed 1944: Guam and Philippines liberated, US bombs Iwo Jima, decimates Japanese Navy at Leyte Gulf 1945: Yalta Conference: final plans to defeat Germany and plan post-war Europe 1945: Auschwitz liberated by Soviet Troops April 30, 1945: Hitler commits suicide May 8, 1945: V-E Day: German full surrender 1945: Potsdam Conference (Truman, Atlee, Stalin): plan action on Japan and post-war Germany August 6, 1945: atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima August 8, 1945: atomic bomb dropped on Nagasaki August 14, 1945: Japanese surrenders September 2, 1945: V-J Day: Japanese makes surrender official, end of WW2.