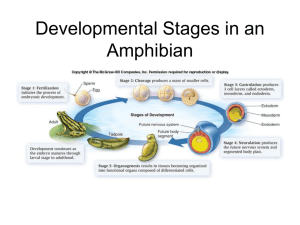
Lecture 22 Class: Early Development Starter: In the diagram to the
advertisement

Lecture 22 Class: Early Development Starter: In the diagram to the right, mark where you would find: a) nurse cell Nurse cells and oocyte b) unfertilized egg c) early embryo d) source of bicoid mRNA e) area of high bicoid mRNA f) area of high bicoid protein Fertilized egg Multicellular embryo Experiment by Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and Eric Wieschaus (1970’s): Used genetic screening: 1. Expose flies to mutagen, allow flies to __________ 2. Check offspring for __________________________ 3. Cross mother with flies with other phenotypes to map mutation on ____________________ The “bicoid” mutation looks like: If the bicoid mutant has two ________________, what does bicoid normally do? A. Turn on genes that code for a tail B. Turn on genes that code for a head A bicoid mutant has two tails. Where is the mutation? A. In the larvae B. In the mother Lecture 22 Page 1 Events of fertilization (Acrosome reaction and cortical reaction) http://youtu.be/3t8tg9iX9Cc Lecture 22 Page 2 More Problems: Binding of bicoid to an enhancer in an early Drosophila embryo: A. Causes binding of RNA polymerase B. Occurs in the posterior end of the embryo C. Turns off head genes In Drosophila, bicoid protein would most likely be found: A. In an egg prior to fertilization B. In the posterior end of an embryo C. In a bicoid mutant D. Binding to DNA E. Associated with abdomen development Which of the following is NOT a function of the acrosomal reaction during fertilization? A. Block polyspermy B. Propel the sperm toward the egg C. Digest the exterior coat of the egg Lecture 22 Page 3