Introduction to Classless Routing
advertisement

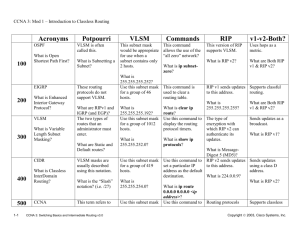
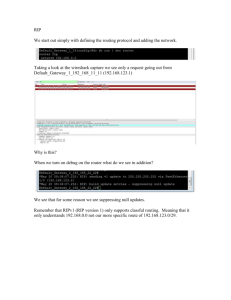
Ch. 1 – Introduction to Classless Routing CCNA 3 version 3.0 Overview of Information in Module 1 • • • • • • • • • Define VLSM and briefly describe the reasons for its use Divide a major network into subnets of different sizes using VLSM Define route aggregation and summarization as they relate to VLSM Configure a router using VLSM Identify the key features of RIP v1 and RIP v2 Identify the important differences between RIP v1 and RIP v2 Configure RIP v2 Verify and troubleshoot RIP v2 operation Configure default routes using the ip route and ip defaultnetwork commands Note • • Much of the information in this module is in addition to the online curriculum. The additional information was included to add clarity and make the topics more understandable. – Advanced IP Management • Subnetting • Classless interdomain routing (CIDR) • Variable length subnet masking (VLSM) • Route summarization • Network Address Translation (NAT) – Classless Routing Protocols • RIPv2 Advanced IP Management IPv4 Address Classes IPv4 Address Classes • No medium size host networks • In the early days of the Internet, IP addresses were allocated to organizations based on request rather than actual need. IPv4 Address Classes Class D Addresses • A Class D address begins with binary 1110 in the first octet. • First octet range 224 to 239. • Class D address can be used to represent a group of hosts called a host group, or multicast group. Class E Addresses First octet of an IP address begins with 1111 • Class E addresses are reserved for experimental purposes and should not be used for addressing hosts or multicast groups. IP addressing crisis • • Address Depletion Internet Routing Table Explosion IPv4 Addressing Subnet Mask • One solution to the IP address shortage was thought to be the subnet mask. • Formalized in 1985 (RFC 950), the subnet mask breaks a single class A, B or C network in to smaller pieces. Subnet Example Given the Class B address 190.52.0.0 Class B Using /24 subnet... Network Network Network Network Host Subnet Host Host Internet routers still “see” this net as 190.52.0.0 190.52.1.2 190.52.2.2 190.52.3.2 But internal routers think all these addresses are on different networks, called subnetworks Subnet Example Network Network Subnet Host Using the 3rd octet, 190.52.0.0 was divided into: 190.52.1.0 190.52.5.0 190.52.9.0 190.52.13.0 190.52.17.0 190.52.2.0 190.52.6.0 190.52.10.0 190.52.14.0 190.52.18.0 190.52.3.0 190.52.7.0 190.52.11.0 190.52.15.0 190.52.19.0 190.52.4.0 190.52.8.0 190.52.12.0 190.52.16.0 and so on ... Subnet Example Network address 190.52.0.0 with /16 network mask Using Subnets: subnet mask 255.255.255.0 or /24 Network Network Subnet Host 190 190 52 52 0 1 Host Host 190 190 190 190 52 52 52 52 2 3 Etc. 254 Host Host Host Host 190 52 255 Host Subnets 255 Subnets 28 - 1 Cannot use last subnet as it contains broadcast address Subnet Example Subnet 0 (all 0’s subnet) issue: The address of the subnet, 190.52.0.0/24 is the same address as the major network, 190.52.0.0/16. Network Network Subnet Host 190 190 52 52 0 1 Host Host 190 190 52 52 Etc. 254 Host Host Subnets 255 Subnets 28 - 1 190 52 255 Host Last subnet (all 1’s subnet) issue: The broadcast address for the subnet, 190.52.255.255 is the same as the broadcast address as the major network, 190.52.255.255. All Zeros and All Ones Subnets Using the All Ones and All Zeroes Subnet • There is no command to enable or disable the use of the all-ones subnet, it is enabled by default. Router(config)#ip subnet-zero • The use of the all-ones subnet has always been explicitly allowed and the use of subnet zero is explicitly allowed since Cisco IOS version 12.0. RFC 1878 states, "This practice (of excluding all-zeros and all-ones subnets) is obsolete! Modern software will be able to utilize all definable networks." Today, the use of subnet zero and the all-ones subnet is generally accepted and most vendors support their use, though, on certain networks, particularly the ones using legacy software, the use of subnet zero and the all-ones subnet can lead to problems. CCO: Subnet Zero and the All-Ones Subnet http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk648/tk361/technologies_tech_note09186a 0080093f18.shtml Need a Subnet Review? • If you need a Review of Subnets, please review the following links on my web site: – Subnet Review (PowerPoint) – Subnets Explained (Word Doc) Long Term Solution: IPv6 (coming) • • • • • • IPv6, or IPng (IP – the Next Generation) uses a 128-bit address space, yielding 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 possible addresses. IPv6 has been slow to arrive IPv4 revitalized by new features, making IPv6 a luxury, and not a desperately needed fix IPv6 requires new software; IT staffs must be retrained IPv6 will most likely coexist with IPv4 for years to come. Some experts believe IPv4 will remain for more than 10 years. Short Term Solutions: IPv4 Enhancements • • • • CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) – RFCs 1517, 1518, 1519, 1520 VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) – RFC 1009 Private Addressing - RFC 1918 NAT/PAT (Network Address Translation / Port Address Translation) CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) • By 1992, members of the IETF were having serious concerns about the • • • • • exponential growth of the Internet and the scalability of Internet routing tables. The IETF was also concerned with the eventual exhaustion of 32-bit IPv4 address space. Projections were that this problem would reach its critical state by 1994 or 1995. IETF’s response was the concept of Supernetting or CIDR, “cider”. To CIDR-compliant routers, address class is meaningless. – The network portion of the address is determined by the network subnet mask or prefix-length (/8, /19, etc.) – The first octet (first two bits) of the network address (or networkprefix) is NOT used to determine the network and host portion of the network address. CIDR helped reduced the Internet routing table explosion with supernetting and reallocation of IPv4 address space. Active BGP entries Report last updated at Thu, 16 Jan 2003 http://bgp.potaroo.net/ CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) • First deployed in 1994, CIDR dramatically improves IPv4’s scalability • and efficiency by providing the following: – Eliminates traditional Class A, B, C addresses allowing for more efficient allocation of IPv4 address space. – Supporting route aggregation (summarization), also known as supernetting, where thousands of routes could be represented by a single route in the routing table. • Route aggregation also helps prevent route flapping on Internet routers using BGP. Flapping routes can be a serious concern with Internet core routers. CIDR allows routers to aggregate, or summarize, routing information and thus shrink the size of their routing tables. – Just one address and mask combination can represent the routes to multiple networks. – Used by IGP routers within an AS and EGP routers between AS. Without CIDR, a router must maintain individual routing table entries for these class B networks. With CIDR, a router can summarize these routes using a single network address by using a 13-bit prefix: 172.24.0.0 /13 Steps: 1. Count the number of left-most matching bits, /13 (255.248.0.0) 2. Add all zeros after the last matching bit: 172.24.0.0 = 10101100 00011000 00000000 00000000 CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) • By using a prefix address to summarizes routes, administrators can • • • • keep routing table entries manageable, which means the following – More efficient routing – A reduced number of CPU cycles when recalculating a routing table, or when sorting through the routing table entries to find a match – Reduced router memory requirements Route summarization is also known as: – Route aggregation – Supernetting Supernetting is essentially the inverse of subnetting. CIDR moves the responsibility of allocation addresses away from a centralized authority (InterNIC). Instead, ISPs can be assigned blocks of address space, which they can then parcel out to customers. ISP/NAP Hierarchy - “The Internet: Still hierarchical after all these years.” Jeff Doyle (Tries to be anyways!) NAP (Network Access Point) Network Service Provider Regional Service Provider ISP Subscribers ISP Subscribers ISP Subscribers Network Service Provider Regional Service Provider Regional Service Provider ISP ISP Subscribers Subscribers Regional Service Provider ISP Subscribers ISP Subscribers ISP Subscribers Supernetting Example • Company XYZ needs to address 400 hosts. • Its ISP gives them two contiguous Class C addresses: • • – 207.21.54.0/24 – 207.21.55.0/24 Company XYZ can use a prefix of 207.21.54.0 /23 to supernet these two contiguous networks. (Yielding 510 hosts) 207.21.54.0 /23 – 207.21.54.0/24 – 207.21.55.0/24 23 bits in common Supernetting Example • With the ISP acting as the addressing authority for a CIDR block of addresses, the ISP’s customer networks, which include XYZ, can be advertised among Internet routers as a single supernet. CIDR Restrictions • Dynamic routing protocols must send network address and mask • (prefix-length) information in their routing updates. In other words, CIDR requires classless routing protocols for dynamic routing. Example from online curriculum Number of Networks Aggregated = 2^(network bits borrowed) Are we over summarizing here? Summarized and Specific Routes: Longest-bit Match (more later) ISP Summarized Update Specific Route Update 172.16.0.0/16 172.16.1.0/24 172.16.5.0/24 172.16.5.0/24 Sub1 Sub2 172.16.2.0/24 172.16.10.0/24 • ISP receives a summarized /16 update from Sub1 and a more specific • • • /24 update from Sub2. ISP will include both routes in the routing table. ISP will forward all packets matching at least the first 24 bits of 172.16.5.0 to Sub2 (172/16/5/0/24), longest-bit match. ISP will forward all other packets matching at least the first 16 bits to Sub1 (172.16.0.0/16). Another example from online curriculum Route flapping • • • • • • Route flapping occurs when a router interface alternates rapidly between the up and down states. Route flapping can cripple a router with excessive updates and recalculations. However, the summarization configuration prevents the RTC route flapping from affecting any other routers. The loss of one network does not invalidate the route to the supernet. While RTC may be kept busy dealing with its own route flap, RTZ, and all upstream routers, are unaware of any downstream problem. Summarization effectively insulates the other routers from the problem of route flapping. Short Term Solutions: IPv4 Enhancements • • • • CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) – RFCs 1517, 1518, 1519, 1520 VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) – RFC 1009 Private Addressing - RFC 1918 NAT/PAT (Network Address Translation / Port Address Translation) – RFC VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) • • • Limitation of using only a single subnet mask across a given network-prefix (network address, the number of bits in the mask) was that an organization is locked into a fixed-number of of fixed-sized subnets. 1987, RFC 1009 specified how a subnetted network could use more than one subnet mask. VLSM = Subnetting a Subnet – “If you know how to subnet, you can do VLSM!” VLSM Example using /30 subnets 207.21.24.0/24 network subnetted into eight /27 (255.255.255.224) subnets 207.21.24.192/27 subnet, subnetted into eight /30 (255.255.255.252) subnets • • This network has seven /27 subnets with 30 hosts each AND eight /30 subnets with 2 hosts each. /30 subnets are very useful for serial networks. 207.21.24.192/27 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 207.21.24.192/30 207.21.24.196/30 207.21.24.200/30 207.21.24.204/30 207.21.24.208/30 207.21.24.212/30 207.21.24.216/30 207.21.24.220/30 207.21.24. 11000000 /30 207.21.24. 110 00000 207.21.24. 110 00100 207.21.24. 110 01000 207.21.24. 110 01100 207.21.24. 110 10000 207.21.24. 110 10100 207.21.24. 110 11000 207.21.24. 110 11100 Hosts Bcast 01 10 11 01 10 11 01 10 11 01 10 11 01 10 11 01 10 11 01 10 11 01 10 11 2 Hosts .193 & .194 .197 & .198 .201 & .202 .205 & .206 .209 & .210 .213 & .214 .217 & .218 .221 & .222 207.21.24.192/30 207.21.24.204/30 207.21.24.216/30 207.21.24.96/27 207.21.24.128/27 207.21.24.64/27 207.21.24.196/30 207.21.24.160/27 • • 207.21.24.208/30 207.21.24.200/30 207.21.24.224/27 207.21.24.32/27 207.21.24.212/30 207.21.24.0/27 This network has seven /27 subnets with 30 hosts each AND seven /30 subnets with 2 hosts each (one left over). /30 subnets with 2 hosts per subnet do not waste host addresses on serial networks . VLSM and the Routing Table Displays one subnet mask for all child routes. Classful mask is assumed for the parent route. Routing Table without VLSM RouterX#show ip route 207.21.24.0/27 is subnetted, C 207.21.24.192 is directly C 207.21.24.196 is directly C 207.21.24.200 is directly C 207.21.24.204 is directly 4 subnets connected, connected, connected, connected, Serial0 Serial1 Serial2 FastEthernet0 Each child routes displays its own subnet mask. Classful mask is included for the parent route. Routing Table with VLSM RouterX#show ip route 207.21.24.0/24 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 207.21.24.192 /30 is directly connected, Serial0 C 207.21.24.196 /30 is directly connected, Serial1 C 207.21.24.200 /30 is directly connected, Serial2 C 207.21.24.96 /27 is directly connected, FastEthernet0 • Parent Route shows classful mask instead of subnet mask of the child routes. • Each Child Routes includes its subnet mask. Final Notes on VLSM • Whenever possible it is best to group contiguous routes together so • • they can be summarized (aggregated) by upstream routers. (coming soon!) – Even if not all of the contiguous routes are together, routing tables use the longest-bit match which allows the router to choose the more specific route over a summarized route. – Coming soon! You can keep on sub-subnetting as many times and as “deep” as you want to go. You can have various sizes of subnets with VLSM. Discontiguous subnets • “Mixing private addresses with globally unique addresses can create • • discontiguous subnets.” – Not the main cause however… Discontiguous subnets, are subnets from the same major network that are separated by a completely different major network or subnet. Question: If a classful routing protocol like RIPv1 or IGRP is being used, what do the routing updates look like between Site A router and Site B router? Discontiguous subnets • • • • Classful routing protocols, notably RIPv1 and IGRP, can’t support discontiguous subnets, because the subnet mask is not included in routing updates. RIPv1 and IGRP automatically summarize on classful boundaries. Site A and Site B are all sending each other the classful address of 207.21.24.0/24. A classless routing protocol (RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPF) would be needed: – to not summarize the classful network address and – to include the subnet mask in the routing updates. Discontiguous subnets • • RIPv2 and EIGRP automatically summarize on classful boundaries. When using RIPv2 and EIGRP, to disable automatic summarization (on both routers): Router(config-router)#no auto-summary • • SiteB now receives 207.21.24.0/27 SiteB now receives 207.21.24.32/27 Short Term Solutions: IPv4 Enhancements • • • • CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) – RFCs 1517, 1518, 1519, 1520 VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) – RFC 1009 Private Addressing - RFC 1918 NAT/PAT (Network Address Translation / Port Address Translation) – RFC Private IP addresses (RFC 1918) If addressing any of the following, these private addresses can be used instead of globally unique addresses: • A non-public intranet • A test lab • A home network Global addresses must be obtained from a provider or a registry at some expense. Short Term Solutions: IPv4 Enhancements • • • • CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) – RFCs 1517, 1518, 1519, 1520 VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) – RFC 1009 Private Addressing - RFC 1918 NAT/PAT (Network Address Translation / Port Address Translation) – RFC Network Address Translation (NAT) NAT: Network Address Translatation • NAT, as defined by RFC 1631, is the process of swapping one address for another in the IP packet header. • In practice, NAT is used to allow hosts that are privately addressed to access the Internet. Network Address Translation (NAT) • • • • • TCP Source Port 1026 2.2.2.2 TCP Source Port 1923 TCP Source Port 1026 2.2.2.2 TCP Source Port 1924 NAT translations can occur dynamically or statically. The most powerful feature of NAT routers is their capability to use port address translation (PAT), which allows multiple inside addresses to map to the same global address. This is sometimes called a many-to-one NAT. With PAT, or address overloading, literally hundreds of privately addressed nodes can access the Internet using only one global address. The NAT router keeps track of the different conversations by mapping TCP and UDP port numbers. Classless Routing Protocols RIPv2 Classless routing protocols • The true defining characteristic of classless routing protocols is the • capability to carry subnet masks in their route advertisements. “One benefit of having a mask associated with each route is that the all-zeros and all-ones subnets are now available for use.” – Cisco allows the all-zeros and all-ones subnets to be used with classful routing protocols. Classless Routing Protocols “The true characteristic of a classless routing protocol is the ability to carry subnet masks in their route advertisements.” Jeff Doyle, Routing TCP/IP Benefits: • All-zeros and all-ones subnets – - Although some vendors, like Cisco, can also handle this with classful routing protocols. • VLSM – Can have discontiguous subnets – Better IP addressing allocation • CIDR – More control over route summarization Classless Routing Protocols Classless Routing Protocols: • RIPv2 • EIGRP • OSPF • IS-IS • BGPv4 Note: Remember classful/classless routing protocols is different than classful/classless routing behavior. Classlful/classless routing protocols (RIPv1, RIPv2, IGRP, EIGRP, OSPF, etc.) has to do with how routes get into the routing table; how the routing table gets built. Classful/classless routing behavior (no ip classless or ip classless) has to do with the lookup process of routes in the routing table (after the routing table has been built). It is possible to have a classful routing protocol and classless routing behavior or visa versa. It is also possible to have both a classful routing protocol and classful routing behavior; or both a classless routing protocol and classless routing behavior. RIP version 1 • • • • Classful Routing Protocol, sent over UDP port 520 Does not include the subnet mask in the routing updates. Automatic summarization done at major network boundaries. Updates sent as broadcasts unless the neighbor command is used which sends them as unicasts. 0 1 2 3 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | command (1) | version (1) | must be zero (2) | +---------------+---------------+-------------------------------+ | address family identifier (2) | must be zero (2) | +-------------------------------+-------------------------------+ | IP address (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | must be zero (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | must be zero (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | metric (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ RIP version 2 • • • • Classless Routing Protocol, sent over UDP port 520 Includes the subnet mask in the routing updates. Automatic summarization at major network boundaries can be disabled. Updates sent as multicasts (224.0.0.9) unless the neighbor command is used which sends them as unicasts. 0 1 2 3 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | command (1) | version (1) | must be zero (2) | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Address Family Identifier (2) | Route Tag (2) | +-------------------------------+-------------------------------+ | IP Address (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | Subnet Mask (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | Next Hop (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | Metric (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ Issues addressed by RIP v2 The following four features are the most significant new features added to RIP v2: • Authentication of the transmitting RIP v2 node to other RIP v2 nodes • Subnet Masks – RIP v2 allocates a 4-octet field to associate a subnet mask to a destination IP address. • Next Hop IP addresses – A better next-hop address, than the advertising router, if one exists. – It indicates a next-hop address, on the same subnet, that is metrically closer to the destination than the advertising router. – If this router’s interface is closest, then it is set to 0.0.0.0 • Multicasting RIP v2 messages – Multicasting is a technique for simultaneously advertising routing information to multiple RIP or RIP v2 devices. RIP v2 message format • All the extensions to the original protocol are carried in the unused • fields. The Address Family Identifier (AFI) field is set to two for IP. The only exception is a request for a full routing table of a router or host, in which case it will be set to zero. Authentication • • RFC 1723 describes only simple password authentication Cisco IOS provides the option of using MD5 authentication instead of simple password authentication. Same limitations of RIPv2 as with RIPv1 • Slow convergence and the need of holddown timers to reduce the possibility of routing loops. Note: See CCNA 2 for review if needed. Same limitations of RIPv2 as with RIPv1 • • • RIP v2 continues to rely on counting to infinity as a means of resolving certain error conditions within the network. Dependent upon holddown timers. Triggered updates are also helpful. Note: See CCNA 2 for review if needed. Same limitations of RIPv2 as with RIPv1 • Perhaps the single greatest limitation that RIP v2 inherited from RIP is that its interpretation of infinity remained at 16. Basic RIPv2 configuration Other: For RIP and IGRP, the passive interface command stops the router from sending updates to a particular neighbor, but the router continues to listen and use routing updates from that neighbor. (More later.) Router(config-router)# passive-interface interface Default behavior of version 1 restored: Router(config-router)# no version Compatibility with RIP v1 NewYork interface fastethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.50.129 255.255.255.192 ip rip send version 1 ip rip receive version 1 RIPv2 interface fastethernet0/1 ip address 172.25.150.193 255.255.255.240 ip rip send version 1 2 • • • Interface FastEthernet0/0 is configured to send and receive RIP v1 updates. FastEthernet0/1 is configured to send both version 1 and 2 updates. FastEthernet0/2 has no special configuration and therefore sends and receives version 2 by default. interface fastethernet0/2 ip address 172.25.150.225 225.255.255.240 router rip version 2 network 172.25.0.0 network 192.168.50.0 Discontiguous subnets and classless routing router rip version 2 no auto-summary • RIP v1 always uses automatic summarization. • The default behavior of RIP v2 is to summarize at network boundaries the same as RIP v1. Configuring authentication (EXTRA) Router(config)#key chain Romeo Router(config-keychain)#key 1 Router(config-keychain-key)#key-string Juliet The password must be the same on both routers (Juliet), but the name of the key (Romeo) can be different. Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)#ip rip authentication key-chain Romeo Router(config-if)#ip rip authentication mode md5 • If the command ip rip authentication mode md5 is not added, the interface will use the default clear text authentication. Although clear text authentication may be necessary to communicate with some RIP v2 implementations, for security concerns use the more secure MD5 authentication whenever possible. Show commands show ip rip database Router# show ip rip database 172.19.0.0/16 auto-summary 172.19.64.0/24 directly connected, Ethernet0 172.19.65.0/24 [1] via 172.19.70.36, 00:00:17, Serial1 [2] via 172.19.67.38, 00:00:25, Serial0 172.19.67.0/24 directly connected, Serial0 172.19.67.38/32 directly connected, Serial0 172.19.70.0/24 directly connected, Serial1 172.19.86.0/24[1] via 172.19.67.38, 00:00:25, Serial0 [1] via 172.19.70.36, 00:00:17, Serial1 • The show ip rip database command to check summary address • • entries in the RIP database. These entries will appear in the database if there are only relevant child or specific routes being summarized. When the last child route for a summary address becomes invalid, the summary address is also removed from the routing table. Router#show ip rip database Show commands Debug commands RIPv2 Example Scenario: • • • • Internet Discontiguous subnets VLSM static route to 207.0.0.0/8 10.0.0.0/8 CIDR .1 .1 e0 ISP Supernet to 207.0.0.0/8 With the default auto-summary on ISP, it will load balance for all packets destined for 172.30.0.0/16 .25 s0 s1 .21 192.168.4.24/30 192.168.4.20/30 172.30.200.32/28 Lo2 .26 172.30.2.0/24 207.0.0.0/16 207.1.0.0/16 207.2.0.0/16 207.3.0.0/16 etc. s0 Lo0 .1 SantaCruz1 .1 e0 172.30.1.0/24 s0 .22 Lo1 ` 172.30.200.16/28 SantaCruz2 Lo0 .1 e0 .1 172.30.100.0/24 172.30.110.0/24 SantaCruz1 router rip network 172.30.0.0 network 192.168.4.0 version 2 no auto-summary RIPv2 Example Internet static route to 207.0.0.0/8 10.0.0.0/8 .1 SantaCruz2 router rip network 172.30.0.0 network 192.168.4.0 version 2 no auto-summary 207.0.0.0/16 207.1.0.0/16 207.2.0.0/16 207.3.0.0/16 etc. .1 e0 ISP .25 s0 s1 .21 192.168.4.24/30 192.168.4.20/30 172.30.200.32/28 ISP router rip redistribute static network 10.0.0.0 network 192.168.4.0 version 2 no auto-summary Lo2 .26 172.30.2.0/24 ip route 207.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 null0 s0 Lo0 .1 SantaCruz1 .1 e0 172.30.1.0/24 s0 .22 Lo1 ` 172.30.200.16/28 SantaCruz2 Lo0 .1 e0 .1 172.30.100.0/24 172.30.110.0/24 SantaCruz2#show ip route C C R R C C R C R R Examining a Routing Table 172.30.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks 172.30.200.32/28 is directly connected, Loopback2 172.30.200.16/28 is directly connected, Loopback1 172.30.2.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.4.21, 00:00:21, Serial0 172.30.1.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.4.21, 00:00:21, Serial0 172.30.100.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0 172.30.110.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0 192.168.4.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets 192.168.4.24 [120/1] via 192.168.4.21, 00:00:21, Serial0 192.168.4.20 is directly connected, Serial0 Internet 10.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 192.168.4.21, 00:00:21, Serial0 static route to 207.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 192.168.4.21, 00:00:21, 10.0.0.0/8 Serial0 207.0.0.0/8 .1 207.0.0.0/16 207.1.0.0/16 207.2.0.0/16 207.3.0.0/16 etc. .1 e0 ISP .25 Supernet, classless routing protcols will route supernets (CIDR) s0 s1 .21 192.168.4.24/30 192.168.4.20/30 172.30.200.32/28 Lo2 .26 172.30.2.0/24 s0 Lo0 .1 SantaCruz1 .1 e0 172.30.1.0/24 s0 .22 Lo1 ` 172.30.200.16/28 SantaCruz2 Lo0 .1 e0 .1 172.30.100.0/24 172.30.110.0/24 RIPv2: Sending and Receiving Updates ISP(config)# line console 0 ISP(config-line)# logging synchronous ISP#debug ip rip RIP protocol debugging is on ISP#01:23:34: RIP: received v2 update from 192.168.4.22 on Serial1 01:23:34: 172.30.100.0/24 -> 0.0.0.0 in 1 hops 01:23:34: 172.30.110.0/24 -> 0.0.0.0 in 1 hops Includes mask ISP# 01:23:38: RIP: received v2 update from 192.168.4.26 on Serial0 01:23:38: 172.30.2.0/24 -> 0.0.0.0 in 1 hops 01:23:38: 172.30.1.0/24 -> 0.0.0.0 in 1 hops multicast ISP# 01:24:31: RIP: sending v2 update to 224.0.0.9 via Ethernet0 (10.0.0.1) 01:24:31: 172.30.2.0/24 -> 0.0.0.0, metric 2, tag 0 01:24:31: 172.30.1.0/24 -> 0.0.0.0, metric 2, tag 0 01:24:31: 172.30.100.0/24 -> 0.0.0.0, metric 2, tag 0 01:24:31: 172.30.110.0/24 -> 0.0.0.0, metric 2, tag 0 01:24:31: 192.168.4.24/30 -> 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0 01:24:31: 192.168.4.20/30 -> 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0 <text omitted> Adding a default Routes to RIPv2 ISP 207.0.0.0/16 207.1.0.0/16 207.2.0.0/16 207.3.0.0/16 etc. Internet router rip redistribute static static route to 207.0.0.0/8 10.0.0.0/8 network 10.0.0.0 .1 .1 e0 ISP network 192.168.4.0 .25 s0 s1 .21 version 2 no auto-summary 192.168.4.24/30 192.168.4.20/30 default-information originate 172.30.200.32/28 Lo2 ip route 207.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 null0 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.2 etherenet0 .26 172.30.2.0/24 s0 Lo0 .1 SantaCruz1 .1 e0 172.30.1.0/24 s0 .22 Lo1 ` 172.30.200.16/28 SantaCruz2 Lo0 .1 e0 .1 172.30.100.0/24 172.30.110.0/24 Other RIPv2 Commands (EXTRA) Router(config-router)# neighbor ip-address Defines a neighboring router with which to exchange unicast routing information. (RIPv1 or RIPv2) Router(config-if)# ip rip send|receive version 1 | 2 | 1 2 Configures an interface to send/receive RIP Version 1 and/or Version 2 packets Router(config-if)# ip summary-address rip ip_address ip_network_mask Specifies the IP address and network mask that identify the routes to be summarized. Authentication and other nice configuration commands and examples: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps1831/products_configurati on_guide_chapter09186a00800d97f7.html