File
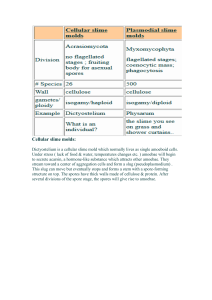
advertisement

11 C Fungus like protists ► Fungus like protists Heterotrophic, need moist environments Cell walls of cellulose (not chitin) Motile Example: water molds & slime molds 1. Water molds- Phylum Oomycota ► Aquatic members live on dead or decaying organic matter (like dead fish) ► Land members parasitize plants blights (crop loss) ► Ex. Irish Potato famine (1845-1847) Ireland’s population 8mil to 4 mil go to USA Asexual reproduction: sporangia produce zoospores that swim away ► Sexual reproduction: sperm and ova with fertilization tubes ► 2. Slime molds – (DECOMPOSERS!) ► 2 phased life cycle feeding phase – mold looks like amoeba, eats bacteria & organic matter (slimy white/yellow/red mass) Reproductive phase - fruiting bodies produce spores 2. Slime molds- cont’d ► A. Phylum Acrasiomycota – cellular slime molds Amoeba like, unicellular, crawl in moist areas decomposing When food scarce – gather together into colony (called pseudoplasmodium) looks like slimy slug forms fruiting bodies 2. Slime molds- cont’d ► B. Phylum Myxomycota – cellular plasmodial slime molds Plasmodium is multinucleate – cells all come together and cell walls dissolve, creeps like a blob & phagocytizes organic matter When food is scarse fruiting body form sspores haploid cells emerge fuse do mitosis without cytokinesis new plasmodium