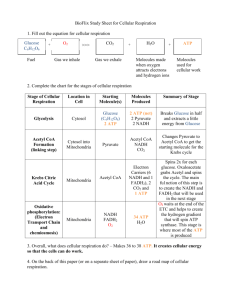
Biology 120 Ch. 4 Cellular Respiration
advertisement
Photosynthesis Quiz 1. The protons/hydrogen ions go from ________ to ________ when the electron goes through the electron transport chain. 2. Name the protein in the thylakoid membrane that makes ATP when protons go through it. 3. Why do protons go through the above protein during the light reactions? 4. Where do ATP and NADPH go after the light reactions? 5. What molecules enter the Calvin cycle? Photosynthesis Quiz 6. What molecules are produced in the Calvin cycle? 7. What do CAM plants do to conserve water, but still be able to go through photosynthesis? 8. What in the thylakoid membrane contains the electrons that get excited? (really important molecule) 9. What drives H+ into the thylakoid? 10. Do organisms other than plants go through photosynthesis? Cellular Respiration Glycolysis converts 1 glucose into 2 pyruvate Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration 2 ATP/ glucose 36 ATP/ glucose Fig. 8-2b, p. 124 Aerobic Respiration Cytoplasm glucose 2 ATP ATP Glycolysis 2 NADH 1 4 ATP (2 net) ATP 2 pyruvate Mitochondrion 2 Krebs Cycle 6 CO2 2 ATP ATP 8 NADH, 2 FADH2 ATP 3 oxygen Electron Transfer Chain 32 ATP Stepped Art Fig. 8-3a, p. 125 Glycolysis Summary A An enzyme splits a pyruvate molecule into a two-carbon acetyl group and CO2. Coenzyme A binds the acetyl group (forming acetyl–CoA). NAD+ combines with released hydrogen ions and electrons, forming NADH. Acetyl–CoA Formation pyruvate NAD+ coenzyme A NADH CO2 B The Krebs cycle starts as one carbon atom is transferred from acetyl– CoA to oxaloacetate. Citrate forms, and coenzyme A is regenerated. acetyl–CoA coenzyme A H The final steps of the Krebs cycle regenerate oxaloacetate. citrate C A carbon atom is removed from an intermediate and leaves the cell as CO2. NAD+ combines with released hydrogen ions and electrons, forming NADH. D A carbon atom is removed from another intermediate and leaves the cell as CO2, and another NADH forms. CO2 oxaloacetate Krebs Cycle NAD+ G NAD+ combines with hydrogen ions and electrons, forming NADH. NADH NADH NAD+ CO2 NAD+ FADH2 FAD NADH Pyruvate’s three carbon atoms have now exited the cell, in CO2. ADP + Pi ATP F The coenzyme FAD combines with hydrogen ions and electrons, forming FADH2. E One ATP forms by substrate-level phosphorylation. Stepped Art Fig. 8-6, p. 129 Electron Transfer Phosphorylation Summary: Aerobic Respiration Sprinters and Lactate Fermentation The Fate of Glucose at Mealtime and Between Meals When blood glucose concentration rises, the pancreas increases insulin secretion • Cells take up glucose faster, more ATP is formed, glycogen and fatty-acid production increases When blood glucose concentration falls, the pancreas increases glucagon secretion • Stored glycogen is converted to glucose Links Between Photosynthesis and Aerobic Respiration