Quiz 5 - Ch 6
advertisement

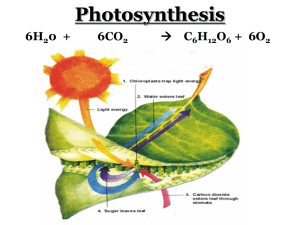
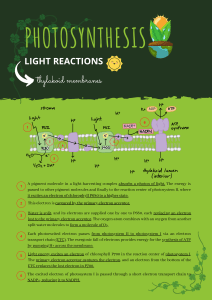
Name: _____________________Grader:___ Date: March 12, 2009 Class Section MC / SD Quiz 5: Chapter 7 1. What establishes the electrochemical gradient across a membrane to provide energy for ATP production? a. b. c. d. e. The chloroplast's electron transport system provides the ions. Hydrogen ions naturally collect on the outside of the organelle membrane. Hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane by carrier proteins. Photosystem II sends a high-energy electron down an energy gradient. All of the choices work to establish the electrochemical gradient. 2. If plants could only undergo the cyclic electron pathway during photosynthesis, which of the following would be FALSE? a. b. c. d. e. Plants would not produce oxygen. Carbohydrate could still be produced but in much smaller quantities. More NADPH would be produced. ATP production would decrease due to a smaller amount of H+ being available. Photosystem II obtains low-energy electrons from itself. 3. When an electron has been excited to a higher energy state, it can then drop back to the original level, reemitting the light as fluorescence. When chlorophyll is purified and placed in solution, and a bright red or blue light is shown on it, the chlorophyll fluoresces brightly. However, when the chlorophyll is packaged inside chloroplasts and the red or blue light is turned on, we do not see fluorescence. This most likely indicates that a. b. c. d. e. the red and blue light waves are reflected by the chlorophyll membrane. chlorophyll in solution is a different molecule than chlorophyll in a chloroplast. excited electrons are transferred to electron acceptors in the chloroplast. fluorescence does not work in living cells. green light must be used to make living cells fluoresce. 4. REDOX reactions within living cells could be considered to be concerned with… a. b. c. d. e. energy flow electron transfer the transfer of hydrogen the transfer of photons all of these choices are correct 5. If the Calvin cycle uses three molecules of CO2 to produce six molecules of G3P (glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate), but only one G3P molecule is kept as a carbohydrate molecule, what happens to the other carbons that were taken in? a. b. c. d. e. Any unused CO2 is released into the environment. The other five G3P molecules are used to regenerate more RuBP. Any unused G3P molecule is converted and stored as starch. The remaining five G3P molecules are used to reduce CO 2. They are used by the light reactions. 6. Which best describes the Calvin Cycle? a. CO2 is attached to a 5-carbon molecule, which becomes a 6-carbon molecule. This molecule is then given energy by ATP and NADPH, which we then call glucose. b. Stomates in the leaf allow O2 to enter, which is taken up by mesophyll cells. RuBP carboxylase then uses this oxygen and reacts with RuBP to form CO2. CO2 is then used to regenerate RuBP. c. CO2 is attached to RuBP by an enzyme, which then splits into 2 3-carbon molecules. These molecules are then given energy by ATP and NADPH to form a high energy 3-carbon carbohydrate. d. Photons are absorbed by Photosystem II, which are passed down an electron transport chain. This energy is used to drive protons into the thylakoid space, which are then used to produce ATP. e. Photons are absorbed by Photosystem I, which are passed to NADP reductase. NADP reductase uses these photons to reduce NADP to NADPH. 7. C4 plants… a. b. c. d. e. Contain an enzyme that fixes carbon dioxide in place that can utilize both oxygen and carbon dioxide. Perform photosynthesis much more efficiently thatn C3 plants. Contain bundle sheath cells that lack chloroplasts. Store and transport carbon dioxide in the form of malate. Two of the above choices are correct. PLEASE CLEARLY CIRCLE TRUE OR FALE. 8. The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the stroma of the chloroplast. T/ F 9. The enzyme complex called ATP synthetase is located in the thylakoid membranes. T/ F 10. The light independent reactions of the Calvin cycle occur in the thylakoids. T/ F