Link to Vocab. list #1 Rhetorical Features
advertisement

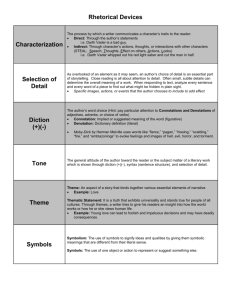
AP Vocabulary list 1 Rhetorical Tools—words to help analyze rhetoric Tone • The writer’s or speaker’s attitude toward the subject. Do not confuse with mood, which is the feeling that a text is intended to produce in the audience. Diction A writer’s or speaker’s word choice. Not the same thing as syntax. Generally, the important words in a passage are the verbs, nouns, adjectives, and adverbs. More on diction at last slide. Syntax The arrangement of words in a sentence; sentence structure. This affects pacing. How and why does a writer change the pacing? Look for parallelism, Compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences Periodic vs. cumulative sentences Denotation The literal meaning of a word; the dictionary definition of a word. Connotation That which is implied by a word, as opposed to the word’s directly expressed, literal “dictionary definition.” The added psychological and emotional associations that certain words carry in addition to their simple meaning. We often speak in terms of positive and negative connotations. Metaphor A figure of speech in which one thing is spoken of as though it were something else, thus making an implicit comparison. From the Greek word meaning “To ferry over.” “The moon was a ghostly galleon, tossed upon cloudy seas” “The fruit-bat swings on its branch, a tongueless bell.” Submerged or implied metaphor: “I like to see it [the train] lap up the miles.” The train is an animal, but “animal” is never said. Simile A type of comparison between two unlike things that uses “like,” “as,” “thus,” or “so”. “But hark, my pulse, like a soft drum / beats my approach, tells thee I come.” More on Diction • Diction is thought about in terms of several “scales”: • • • • • Formal words vs. informal words, colloquialism, or slang. Latinate-derived words vs. anglo-saxon-derived words Specific and Concrete nouns vs. general and abstract nouns Denotative value vs. CONNOTATIVE VALUE Literal vs. figurative meaning