The Middle Colonies
advertisement

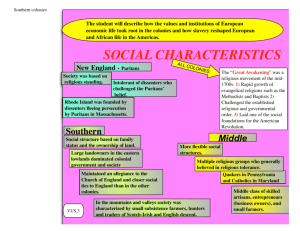
First Ten • Get out MBC homework/graphic organizer – Why was MBC settled? – Puritan view of church and state? • “The Puritans believed in a separation of church and state, but not a separation of the state from God.” – What influence did the MBC have on modern politics in the US? – One Short Answer/Unit One Test The New England Colonies pg. 50-54 How did the geography of the New England Colonies impact the development of its economy? (Trade v. Farming) The New England Colonies pg. 50-54 New England Colonies • Includes: – Massachusetts – Rhode Island – New Hampshire – Connecticut • Founded mainly for religious purposes – mainly from England – Puritans – Little religious tolerance • Short growing season with rocky soil = corn, shipping, fishing, timber INTRODUCTION, CHAPTER ONE, CHAPTER TWO Puritans and the Church of England • Residents of New England left England b/c they disagreed with the Church of England, also known as the Anglican Church (only legal church) – Known as Puritans (want to purify church, still affiliated) – Separatists: leave to begin their own church (PILGRIMS!) – Thought it was too similar to Catholic Church – Didn’t like hierarchy CHAPTER THREE Puritans arrive in Massachussetts: New England colony (Plymouth, Boston, Salem) 1. Motives = to escape religious persecution a. b. c. Governor John Winthrop: 1630 more Puritans come to make their colony, “A city upon the hill”… inspiration and example to the rest of the world of how one should be living Predestination: These people of the church were chosen by God to do this Non-puritans allowed to live here for economic purposes CHAPTER FOUR a. Puritans: Required all members to attend church (very strict, fined if missed, no sleeping, women important for child birth) b. Est. town meetings to make laws (democracy!) i. 1631, all male church members (THE CHOSEN ONES: had conversion experience of journey to the colony) had the right to vote ii. 1662, Half Way Covenant gives ½ church members (no conversion experience, children of original members) right to vote iii. 1691, all male landowners gain right to vote Half-way Covenant • Significance • This step increased the diminishing minority of church members in the colonies, extended church discipline over more people, and encouraged a greater number to seek conversion and work for the benefit of the church. CHAPTER FIVE Dissent in MBC a. Roger Williams: Founder of Rhode Island colony i. Banished for speaking out against Church regulation, ‘too strict!” ii. Est universal male suffrage (right to vote) and religious freedom in RI iii. Anne Hutchinson i. ii. female leadership in the church Personal relationship with God as opposed to church leaders CHAPTER SIX Connecticut • 1636 - Thomas Hooker • Hartford, CT • Significance: more gov’t representation and separation of church and state • Non-church members need voting rights • First constitution • Fundamental Orders of Connecticut CHAPTER SEVEN https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= JU8GvfeaOMo c. Salem Witch Trials • Blame witches for native attacks, disease, bad things, etc. • Target: women, non-puritans, poor http://www.history.com/shows/mankind -the-story-of-all-of-us/videos/mankind• “afflicted child” went into the-story-of-all-of-us-salem-witch-trials convulsions, ran around, hid under furniture • Around 20 put to death • IMPORTANCE = those accused were showing a loss of lose religious passion…making $ and freedoms become priority • (sex, drugs, & rock n’ roll!) CONFLICT WITH NATIVE AMERICANS Conflict with Natives in New England • Pequot War (1637) – NE colonist accuse Pequots of murdering English trader – NA deny – Significance: showed continued removal of native land at the expense of European expansion (over 700 dead) • Natives were not going to give up land without a fight • NE fought with enemies of the Pequot • Pequot nation was eliminated; few survivors went to live in the “praying towns” • Praying Towns: – – – – Puritans try to convert NA with missionaries Controlled location 1674: 14 praying towns with 1,600 inhabitants Assimilation clothing, religion, language, gender norms Let’s read about King Phillip’s War The Middle Colonies pg. 55-59 How did the geography of the Middle Colonies impact the development of its economy? (Trade v. Farming) • Hudson River (navigation), many seaports • Soil suitable for farming, mild climate • Big food producing region that included corn and wheat and livestock including beef and pork. Other industries included the production of iron ore, lumber, textiles, and furs, which they exported to England The Middle Colonies • The Dutch settled New Amsterdam in1625 • Religious tolerance and diverse European groups – Didn’t pressure natives to convert – Mainly focused on mercantilism • 1644 The English take over the colony from the Dutch($$$), name changed to New York Pennsylvania pg. 58 • Founded by William Penn 1680 – Quaker: a radical form of Protestantism that believed in equality between men and women, pacifists, and tolerated other faiths – Philadelphia: City of Brotherly love (cause everybody got along!) – Got along with natives 7. What religious groups settled in New England? Where did they settle? What were their reasons for settlement? 12. What was the Half-way Covenant? Why was it necessary? 14. Why did Massachusetts lose its charter? How does this change the relationship between the colonies and England? Becomes a royal colony because of its reluctance to recognize the British crown’s authority >>> this limits the freedoms of the colonists 15. What country settled in New York first? How did New Amsterdam become New York? 16. Who settled Pennsylvania? Why? How did the settlers of Pennsylvania treat Native Indians? 17. Why were the Middle Colonies more diverse than either the Southern or New England colonies? (pg. 59!!!!!) #MCM #kingphillip #metacomet who are these guys? #powhatan #NathanielBacon • What is mercantilism? • What are the benefits of mercantilism? • Who benefits of mercantilism? • What is the negative impact of mercantilism? The Triangle Trade Draw this chart and fill in as we discuss XXX XXX • How did trans-Atlantic trade develop? • What raw materials were shipped from North America to Europe? • What about Europe to America? • • • • • • Roots of Slavery (How did it begin?) http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/africa/features/storyofafrica/9chapter1.shtml Timeline of Slavery http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/africa/features/storyofafrica/9generic3.shtml The Journey http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/africa/features/storyofafrica/9chapter5.shtml Middle Passage 1-3 month journey Separated from family and villages Did not share a language Branded with hot irons Jammed into a dark and crowded ship hold (3feet 3 inches high) Urine, fesses, birth, and death were everywhere 10% of captures did not survive Slaves in the Northern colonies Small minority Why? Farmhands, dockworkers, sailors, house servants Some success stories – Phillis Wheatley -Slave from west Africa -Worked for a Boston tailor, wrote a book of poems that her owner helped to get published -And was freed Slaves in the southern colonies Sometimes outnumbered White settlers Ability to develop culture: • separated from whites •Able to practice African traditions And blend it with their new Found Christianity •Created music with banjos, Rattles and drums Raised labor intensive crops: Tobacco, rice, Indigo, sugar 30. Give two examples of African-American culture in the colonies. • http://www.pbs.org/wnet/slavery/experienc e/education/history.html Africans in the colonies • Started = indentured servants, being freed after a few years of service • Later = permanently enslaved Africans – due to Bacon’s Rebellion Crash Course “The Atlantic Slave Trade” • “I was soon put down under the decks, and there I received such a salutation in my nostrils as I had never experienced in my life: so that, with the loathsomeness of the stench, and crying together, I became so sick and low that I was not able to eat, nor had I the least desire to taste anything. I now wished for the last friend, death, in to relieve me…” - Olaudah Equiano https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dnV_MTFEGIY 27. Describe conditions on ships for enslaved Africans being shipped to North America. 28. How did labor practices change from early settlement in the 1600s to later colonies in the 1700s? 29. How did slavery in the New England and Middle colonies differ from slavery in the Southern colonies? 30. Give two examples of African-American culture in the colonies.