Ratifying the Constitution
advertisement

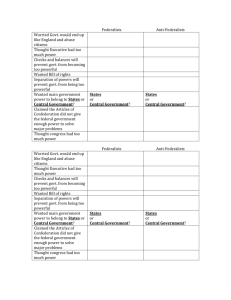
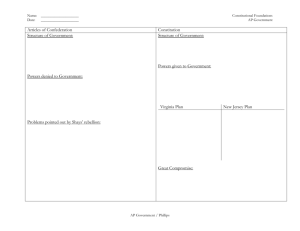
Ratifying the Constitution Federalists vs. Anti-federalists What does ratification mean? Ratification means to give formal consent or permission Although the Constitution was adopted by the framers on Sept. 17, 1787 – the states needed to formally consent to it = RATIFICATION Ratification Proves to be a Big Challenge 9 out of 13 states had to ratify for the new constitution to go into affect The ratification would be democratic: state citizens would elect conventions to decide whether or not to ratify Even with all the compromising, large and small states could still not agree Leaders split into two factions 1. the Federalists (pro-ratification) 2. the Anti-Federalists (anti-ratification) The Process • Each state hold special convention in order to vote on constitution • State delegates elected by people • Ratification of Constitution required the approval of 9 states. 3/5 Compromise • Written into the Constitution was the 3/5 Compromise • Not all of the delegates agreed with slavery, but they understood that the agricultural economy of the colonies in the south depended on slavery • Number of representatives in the House of Representatives depended on population • Slaves were counted as 3/5 of a person Federalists v. Anti-Federalists Federalists • Supported the Constitution Anti-Federalists • Supported the Articles of Confederation • Wanted a strong central government • Wanted a weak central government Federalists • Believed men with talents and experience should govern the nation • Believed the Constitution would protect the rights of the people “as is” Anti-Federalists • Believed the Constitution only supported wealthy men • Believed that the national gov’t would threaten the rights of the common people Federalists • Believed the Constitution and the state governments would protect the rights of the people Anti-Federalists • Did not trust gov’t • Even England had a Bill of Rights for the people Anti-Federalists • Samuel Adams Thomas Jefferson Patrick Henry The Federalist Papers • Written by James Madison, John Jay, and Alexander Hamilton • A collection of 85 articles written to convince New York state to approve the Constitution • James Madison’s papers #10 and #51 would prove to be the most influential and important Federalist #10 Main points of #10 Factions, defined as “any group of citizens who attempt to advance their beliefs or economic status at the expense of other citizens” are dangerous and real threat to liberty A well-formed, strong union can break and control the violence of any faction The US Constitution will provide protection against dangerous factions by uniting the nation’s citizens Federalist # 51 Main points of #51 Humans by nature form alliances around common shared beliefs Different interests must be represented in coalitions, aka alliances made by citizens coming together for the same cause Madison argues that the best and most successful coalitions can only be formed in a large republic united under one form of rule The bigger the republic, the greater the variety of interests, the greater the variety of interests, the larger and more successful the factions So… what did these “Papers” accomplish?? Probably only played a small role in securing ratification However…. They have a lasting value as an authoritative and inspiring explanation of the Constitution Showed citizens the importance of considering human nature when choosing a method of government Showed that both humans AND government can be corrupted – a form of government must protect against corruption and prevent both citizens and leaders from abusing their power STILL Not Ratified… What now?? Even with the efforts of men like James Madison, not all states were on the Constitution bandwagon People were still very afraid that all of the rights they fought for in the war were being threatened by the Constitutions open-ended structure The solution? The Framers realized that ratification would NEVER happen without at least the promise of a “bill of rights” Ratification • • • • Nine states were needed to ratify the Constitution Delaware was the first New Hampshire was the ninth on June 21, 1788 Five states ratified the Constitution with the understanding that a bill of rights would be added. The Bill of Rights • After ratification, James Madison proposed 12 amendments. • After two years of debate, state legislatures approved 10 of the 12. • Now called The Bill of Rights.