FOUNDATION BUSINESS SIMULATION
advertisement

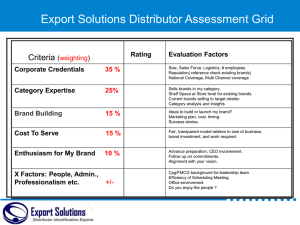
CHAPTER 12: PRODUCT STRATEGY Delivering More Value PRODUCT DEFINITION: IT’S PROBABLY MORE THAN YOU THINK Car Wash ~ Cooking Lesson ~ Computer ~ Soap ~ Car Product – anything a company offers to satisfy customer needs and wants. Brand ~ Image ~ Packaging ~ Reputation ~ Guarantee SERVICES: A PRODUCT BY ANY OTHER NAME Most services embody these qualities: Intangibility Inseparability Variability Perishability GOODS V. SERVICES: A MIXED BAG PRODUCT LAYERS: PEELING THE ONION PRODUCT CLASSIFICATION: IT’S A BIRD, IT’S A PLANE…. Consumer Products • Convenience Products • Shopping Products • Specialty Products • Unsought Products PRODUCT CLASSIFICATION: IT’S A BIRD, IT’S A PLANE: • Installations Business Products • Accessory Equipment • Maintenance, Repair, and Operating Products • Raw Materials • Component Parts & Processed Materials • Business Services PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION AND PLANNING A Meaningful Difference: Product Quality Features Product & Benefits Lines & Product Mixes Branding Packaging PRODUCT QUALITY Quality Level – how well a product performs its core functions. Product Consistency – how reliably a product delivers it promised level of quality. QUALITY INDICATORS Internet Search Engine: Fast, relevant, far-reaching results Stylish Blue Jeans: High-profile designer, high price, celebrity customers TV Editing Equipment: Reliability, flexibility, and customer services Roller Coasters: Thrill factor, design and setting Chain Saws: Effectiveness, safety, and reliability FEATURES AND BENEFITS Product Features – specific characteristics of a product. Customer Benefit – the advantage that a customer gains from specific product features. PRODUCT FEATURES AND BENEFITS Subway Sandwiches Lower fat Looser pants Contact Lenses Different colors A new-looking you High-definition TV 46-inch screen The party’s at your house Hybrid Car Lower gas mileage More cash for other needs Triple Latte Caffeine, caffeine… More time to, uh, study PRODUCT LINE AND PRODUCT MIX Product Line – products that are closely related, either in terms of how they work, or the customers they serve. Product Mix – the total number of product lines by a single firm. Cannibalization – a producer offers a new product that takes sales away from its existing product. BRANDING Brand - a product’s identity that sets it apart from other players in the same category. Brand Equity – the extra money that consumers will spend to buy that brand. Brand Name – a catchy, memorable name is a powerful part of strong brand. LINE EXTENSIONS AND BRAND EXTENSIONS Line Extensions Brand Extensions Similar products offered under the same brand name A product in a new category under an existing brand name GOOD AND BAD BRAND EXTENSIONS GOOD Snoop Dog Pet Accessories Tide To Go stain removal pen BAD Budweiser Barbeque Sauce Starbucks Coffee Liqueur w/ Jim Beam Cheetos Lip Balm Smackers Starburst Bath and Body Collection Hooters Air Harley Davidson Cake Making Kit Maxim Hair Color For Men COBRANDING Cobranding - established brands from different companies join forces to market the same product. Examples: • Ford markets the Eddie Bauer Explorer • Frito-Lay markets KC Masterpiece BBQ chips • Betty Crocker markets brownies with Hershey’s syrup NATIONAL BRANDS VS. STORE BRANDS National Brands/ Manufacturer Brands – Brands owned and marketed by the producer. Store Brands/ Private Label Brands – brands produced and marketed by the retailer. BECOME CEO OF ME, INC. Create a meaningful brand for yourself Become CEO of Me, Inc. What makes you different from others? Better than your competition? Once you define your brand Be sure to deliver Pump up your visibility A BRAND NEW YOU Millions recognize Donald Trump’s trademark blond hair Trump stands for autocratic power and selfindulgent luxury There is a 25% premium for any property that carries his name He told BusinessWeek that he is “a bigger brand now than Pepsi Cola or Coca-Cola.” PACKAGING Protect the Product Provide Information Facilitate Storage Suggest Product Uses Promote the Brand Attract Buyer Attention PRODUCT LIABILITY AN ISSUE? Toilet brush: “Do not use for personal hygiene.” Scooter: “This product moves when used.” Thermometer: “Once used rectally, the thermometer should not be used orally.” Electric blender: “Never remove food or other items from the blades while the product is operating.” Bag of packing air: “Do not use this product as a toy, pillow, or flotation device.” NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT Nuts, Bolts, And A Spark Of Brilliance NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS PRODUCT ADOPTION CATEGORIES How willing are consumers to buy/try new products? First Adopters – 2.5% Adventurous Risk Takers Laggards – 16% Everybody else falls in between PRODUCT DIFFUSION RATES Observability How visible is the product to other potential consumers? Trialability How easily can potential consumers sample the new product? Complexity Can potential consumers easily understand what your product is and how it works? Compatibility How consistent is your product with the existing way of doing things? Relative Advantage How much better are the benefits of your new product compared to existing products? THE PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE: RESULTS OVER TIME PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE AND MARKETING STRATEGIES Phase Examples Sales/Profits Marketing Strategies Introduction Plasma TV, fuel cell technology Low sales, low profits Build awareness, trial, and distribution Growth Hybrid cars, video cell phones, Increasing sales and profits Reinforce brand positioning, often through heavy advertising Maturity Airlines, DVD players Flat sales and declining profits Target competitors, new product features, competitive advertising, promotion, and price cuts Decline Pagers, videocassettes Declining sales and profits Reduce spending and consider terminating the product FOUNDATION BUSINESS SIMULATION Objectives Demonstrate effectiveness of multi-discipline teams working together. Use strategic thinking to an advantage. Develop your business expertise. Understand overall interaction and impact of various parts of a business on one another. Grow an awareness of competition. Take away practical know-how to improve the effectiveness of your business. SENSOR INDUSTRY OVERVIEW The Marketplace • Customers (OEMs) need sensors for their products Large • Initially one segment, now breaking into two Size • Very different customer demands between the two segments Low Tech High Tech • Diversification in the use and utility of the sensors Small Slow Performance Fast The Marketplace In our industry we track the changing customer demand on a perceptual map Low Tech High Tech Over 8 years the customers will demand much faster and smaller sensors Market Segments will continue to diverge Each Segment has an Ideal Spot Large Perceptual Map Low Tech Size High Tech Spot Where Customer Demand Is Highest Small Slow Performance Fast Low Tech Customers “I want these sensors to be cheap” “I want them to have been around for a while – no Beta Testing!” “They have to be moderately reliable.” “The technology doesn’t have to be cutting edge.” You’re not giving me what I want High Tech Customers “These sensors have to be small, like micro, and fast” “I need them to be right out of R&D, I’m talking ZERO years on the market” “I’ll pay more to get what I want.” “I like a pretty high reliability, but it’s not that important.” And I’m not getting what I want! SENSOR INDUSTRY ANALYST PROJECT ONGOING GROWTH Sees the next 5 years as consistent growth. Both market segments increase at a nice “clip,” according to market analyst. “I see the entire market growing at around 14% or 15% per year. The High Tech market will be growing at a whopping 20%.” 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 I hope those companies out there are ready for that kind of expansion!” 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Low Tech Year 4 High Tech Year 5 COMPANY OVERVIEW The Competition ANDREWS BALDWIN 6 Companies $40 Million in Sales DIGBY ERIE 1 Product Line CHESTER Closed Marketplace FERRIS SHAKE UP IN SENSOR INDUSTRY Company Fires Management Team After poor results, lackluster sales and angry customer reports, the Chairman of the Board of Directors has announced the immediate termination of the Management Team. “This is a black day for our company,” said Chairman Patrick Nuss, “We need to hire a dynamic leadership group who will be able to take this company into the future!” “Due to this immediate need I have hired the “Dream Team” to start on January 1st. I expect to see great things from this Executive Team! WELCOME TO YOUR NEW COMPANY! Functional Areas R&D Production Finance Marketing Research & Development Establish the specification of the products to meet customer demand Build the quality and reliability (MTBF) into the products Ensure the perceived age of the product meets customer demands “Our product straddles both market segments. Create new products to meet the changing marketplace It isn’t a great low tech product, or a great high tech one.” Marketing “Our product isn’t priced optimally for either market. And many of our customers don’t even know our product exists.” Set the price of our products in the marketplace Build customer awareness through promotion Establish a sales force and distribution channels Set the sales forecast for our products Set Credit Policies AR/AP Production “We are paying too much for labor costs. Very soon we will run out of capacity to meet demand.” Purchase machinery to automate our facilities Buy or sell capacity of product lines Schedule production for each line Manage the majority of the companies fixed assets Establish workforce compliment Finance Acquire capital to fund capital expansions Issue Stock Short Term Debt Issue Long Term Bonds Issue dividend to our shareholders Balance our debt portfolio Manage our Proforma “We have poor cash flow and substandard financial ratios. We have no financial policy statement.” Proformas A great management tool driven by forecasts and projections. Allows “What if” Scenarios by the company. Balance Sheet Profit & Loss Cash Flow Financial Ratios Scoring the Simulation 1. 2. 3. Analyst Report Round Analysis Success Measures Select a minimum of three criteria to be measured by: ROE ROS ROA CUM Profit Stock Price Market Capitalization Asset Turnover Market Share Weight each selection. Running Your Company To Do List Establish business strategy for your company Analyze Foundation FastTrack to see industry results Make tactical decisions across each functional area (aligned to strategy!) Upload official results and confirm on the website Await results Rejoice in your superior capitalistic acumen Begin the process again by confirming alignment of your results with your company’s strategic goal Good Luck and Enjoy!