Seeds - Science with Spence
advertisement

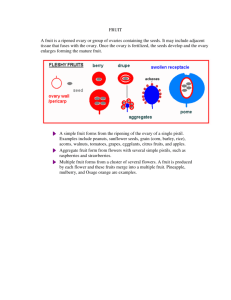
Plant Reproduction Plants can reproduce Sexually and Asexually. • Asexually- Plants can be regrown using a piece of an old plant. • Sexually- Most plants reproduce sexually using spores or seeds. 2 Types of Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction • New organism is produced • New organism is produced from 2 from 1 parent’s genetic parents’ genetic material material • Limits diversity -offspring and parent have the same • Genetic diversityoffspring and parents do DNA. not have the same DNA. • Mostly unicellular organisms. • Mostly multicellular organisms Sexual Reproduction involves two processes: • Meiosis • Fertilization A special form of cell division that produces sperm cells in males and eggs in females. Process that happens when one male and one female reproductive cell combine to make a new cell that can develop into a new organism Sexual Reproduction Sperm carries ½ the genetic material Egg carries ½ genetic material They meet to form one cell with a full set of genetic material Seeds vs. Spores Seed is a young plant that is enclosed in a protective coating Embryo Stored Food Protective Cover Spore is a single reproductive cell that can grow into a new organism. Seeds vs. Spores Spores and Seeds have common characteristics. • Have protective covering • Can survive harsh dry, harsh conditions • Contain parent plant’s genetic material • Grows into a new plant Seeds vs. Spores Seeds • Have multi-cellular embryo inside Spores • Made up of a single cell • Contain nutrient supply • Do not contain nutrient supply • Spread by wind, water, and animals • Limited spreading mostly by wind • Sperm do not need water to fertilize the egg. • Sperm need to swim through water to fertilize the egg “The Great Escape”: Germination When a seed or spore begins to grow. 4 Groups of Plants • Moss- Non-vascular plants that reproduce with spores • Ferns- Vascular plants that reproduce with spores • Gymnosperms- Vascular plants that reproduce with “naked” seeds that are in cones. • Angiosperms- Vascular plants that reproduce with seeds in flowers and fruit. Moss Fern Gymnosperms • Plants that reproduce using seeds but are not enclosed in fruit. • “Naked Seeds” Conifers Male Cone Female Cone Douglas Fir Angiosperm • A plant that has seeds that produce flowers and fruit. • Most species living now are angiosperms. Flower • Reproductive structure of an angiosperm • Egg cells develop in the ovary • Pollen containing sperm cells is located on the anther. • Pollen travels from anthers to fertilize the flower. Fruit • The ripened, enlarged ovary of a flower, which contains seeds. • When egg cells are fertilized by pollen in the ovary the ovary thickens and becomes a fruit. • Fruit can fall to the ground or be eaten by animals • If seeds inside the fruit land in a place where they can germinate they form a new plant. Flower Ovary Ovary Seeds Fruit 1 12 10 11 2 9 3 4 7 6 5 8 Life Cycle of a Cherry Tree Meiosis Fruit can be eaten, or can fall to the ground. Seeds and Fruit Pollination Fertilization Life Cycle of a Conifer 1. Meiosis – pollen and eggs are made in cones 2. Pollination- pollen is released from male cones and gets stuck to female cones 3. Fertilization- pollen “digs” a pollen tube that eventually reaches the egg and sperm unite with egg. 4. Seed- a fertilized egg becomes an embryo; seeds will disperse via wind, water, or animals. 5. Germination- seed lands and when conditions are right begins to grow a new plant. Gymnosperm Both Gymnosperms and Plant with “naked seed Angiosperms Both have 2-stage life cycle within a single plant Angiosperm Plant with seeds with flowers or fruit Separate male and female structures Reproduce sexually. Some flowering plants can reproduce asexually too. If Rick planted 7 pots with seeds and got the results below…. How many pots had seeds germinated? 4 What is so distinctive about gymnosperm seeds? Gymnosperms are “naked seeds”. They have contain no fruit. What do pollen grains and cone scales contain? Pollen grains contain sperm cells, and female cone scales contain egg cells. How does the shape of a pine seed affect how it travels? The shape of the seed allows the wind to carry the seed away instead of falling under the tree. What advantage(s) do gymnosperms have over mosses and ferns? Gymnosperms reproduce with seeds so their seeds can provide nutrients to the developing plant. Seeds can be spread easier (wind, water, and animals). Gymnosperms produce a lot of pollen, and most of it blows away, never fertilizing an egg. Why might this characteristic help a plant species survive? Lots of pollen increases the chances of a pollen grain reaching the female cone and the egg of another plant. Since there is less surface area on the needles of conifers for photosynthesis to take place, How do you think these plants get energy and materials they need? While they have smaller surface area to do photosynthesis… conifers keep their leaves all year round, so they can get energy and materials throughout the year. How do flowers relate to fruit? Ovary of a flower becomes fruit. How are animals involved in the life cycle of some angiosperms? Animals can be pollinators, carry pollen from flower to flower. Animals can disperse seeds through eating the fruit then depositing seeds in their waste. What part of a flower later becomes a fruit? An ovary becomes a fruit. What did the ovary contain in the flower, and what does it contain as it becomes a fruit? In a flower the ovary contains eggs which are fertilized by sperm in the pollen. As the ovary develops fertilized eggs become the seeds in the fruit.