File
advertisement

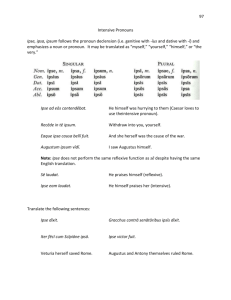
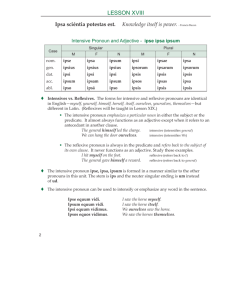
Chapter 13 Review: Personal Pronouns • What is a personal pronoun? – Word taking the place of a noun which refers to a person or thing • Marcus and Iulia love Iason. – They love him. • Vōs omnēs sunt amīcī. • What is a possessive adjective? – Word that describes a noun to show who possess it – The walls of your city are high. – Moenia urbis vestrae sunt alta. Reflexive Pronouns • Pronoun that reflects back to the subject – Narcissus looks at himself in the pond. – I cut myself with my sword. • They all end in –self • Reflexive pronouns refer to the subject. • Thus, reflexive pronouns cannot be the nominative. • Therefore, what case are they missing? Reflexive Pronouns Declension • SAME as the personal pronouns we learned last week but no nominatives! • Example sentences: – Ego laudo me. – Nos laudamus nos. – Laudas te. – Laudatis vos. New reflexive pronoun • The third person reflexive pronoun is NEW! (this takes the place of the is, ea, id chart) • SAME for singular and plural G: suī D: sibi AC: sē AB: sē • Ea laudat sē • Eae laudant sē. Usage • Just like the personal pronouns the genitive does NOT indicate possession • To show possession use the REFLEXIVE, POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVE suus, sua, suum/ meus/ tuus/ noster/ vester – Cicero amicum suum laudat. • Cicero praised his (own) friend – Cicero amicus eius laudat. • Cicero praised his (some other guy’s) friend – Latin is much more specific than English in this regard! The Intensive Pronoun • Emphasizes a noun or pronoun • Translate “…self” or “the very” • I MYSELF went to the store • Declension is just like ‘ille’ and the ‘naughty nine’ INTENSIVE PRONOUN: ipse, ipsa, ipsum m. f. n. SINGULAR Nom. ipse ipsa ipsum Gen. ipsīus ipsīus ipsīus Dat. ipsī ipsī ipsī Acc. ipsum ipsam ipsum Abl. ipsō ipsā ipsō Nom. ipsi ipsae ipsa etc. etc. etc. etc. PLURAL (see Wheelock pg. 497) Examples • Brutus ipse mē nēcāvit. = Brutus himself killed me. • Brutus ipsōs agricolās nēcāvit. = Brutus killed the farmers themselves. • Ipse Brutum nēcāvī. = I myself killed Brutus.