Chemistry BTEC revision
advertisement

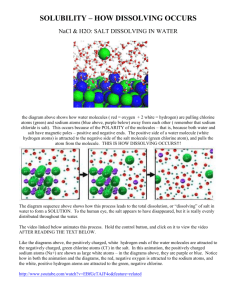
Subatomic particle Mass Charge +1 -1 0 On the Periodic table on the left • Circle where the non-metals are With different coloured pencils colour in: • The group where the unreactive gases are found. • The group where the alkali metals are found (very reactive) Atoms in the same group have similar properties because they have the same number of _____________ in the outer shell. The mass number is the total number of ________ and _______. The atomic number is the number of __________. Match the pictures above with the words below and define the words Element Compound Mixture Complete the sentences with the following words. (some are red herrings!) Ionic element Isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with sodium electron covalent chlorine chlorine sodium Na+ the same/different numbers of protons. NaCl+ compoundClIsotopes are atoms of the same element with Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the _____________ atom. This results in 2 ions : _______ the same/ different numbers of neutrons. and _______. Complete the electron arrangement of a boron atom Complete the electron arrangement of a boron ion ion Lost/ gained? Number of electrons Mg 2+ lost 2 Cl Li + O 2Fe 3+ Working out Relative Atomic Mass You need to know 2 things • The relative mass of each isotope. • The relative abundance of each isotope. Then: 1. Times the mass of each isotope by its relative abundance. 2. Add together your answers. 3. Divide by the sum of the relative abundances Try this example: A sample of copper (Cu) contains 70-% Cu-63 and 30% Cu-65 Calculate the relative atomic mass of copper Zinc reacts with oxygen. Zinc oxide is made. What are the reactants?________ ________ What is the product?_____________ Complete the word equation for this reaction ___________+ ____________ __________ ________ 2Zn + O2 2ZnO How many Zinc and Oxygen atoms are on the left-hand side? Zn ______ 0_______ How many Zinc and Oxygen atoms are on the right-hand side? Zn ______ O______ Is this equation balanced? Yes/No pH 2 What do you do? What happens? Gives a squeaky pop Bubble through limewater Acid Alkali, neutral? Purple Strong Alkali 7 Red 8 Blue 14 Reactions with Acids. Complete the equations Acid+ metal salt + hydrogen Hydrochloric acid + _________ magnesium chloride + hydrogen _________ acid + zinc zinc sulfate + Hydrogen Acid + metal oxide salt + water Acid + metal hydroxide salt + water Nitric acid + copper oxide- ___________ ___________ + water Sulphuric acid + ________ _______ zinc sulfate + water ___________acid + sodium hydroxide sodium chloride + ______ Acid+ metal carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide Hydrochloric acid + sodium carbonate ______ ________ + water + ___________ ____________ Which gas Colour with Universal indicator Write down the meaning of these symbols. Green Acids have pHs of _____ to _____ Bases (soluble alkalis) have pHs of _______ to ______. Neutral is pH _______ Indicators are used to…. Complete the equation for a neutralisation reaction: Acid+ Alkali ________ + _________ Tick which of the following are real uses of neutralisation reactions. Indigestion tablets (neutralising stomach acid) In cars (neutralising battery acid) On fish and chips (vinegar is an acid) In Gardening (Neutralising acidic soils) In Lakes (Neutralising lakes which have become acidic due to acid rain