BS100 Self Test Week 7 Short Run and Long Run Costs
advertisement

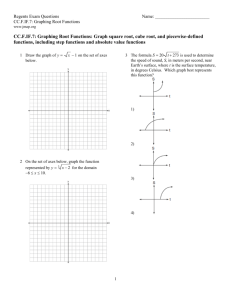
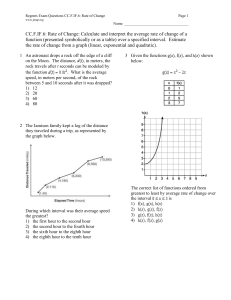
BS100 Economics Multiple Choice self test Week 7 – Short Run and Long Run Costs 1. The amount of money that a firm receives from the sale of its output is called: a. total revenue b. total gross profit c. total net profit d. net revenue 2. The amount of money that a firm pays to buy inputs is called: a. variable cost b. marginal cos c. fixed cost d. total cost 3. A firm’s profit is equivalent to: a. its total sales b. average revenue minus average total cost c. marginal revenue minus marginal cost d. total revenue minus total cost 4. Total revenue equals: a. total output multiplied by the unit price of output b. total output multiplied by profit c. total output multiplied by the unit cost of output d. total output divided by profit 5. Those things that must be forgone to acquire a good are called: a. competitors b. substitutes c. opportunity costs d. explicit costs 6. Suppose a firm produced 500 units of output but sold only 400 of the units it produced. The average cost of production for each unit of output produced was $100. Each of the 400 units sold were sold for a price of $80. The total revenue of this firm would be: a. $50 000 b. $40 000 c. $32 000 d. -$8 000 7. Opportunity costs are comprised of: a. explicit costs b. implicit costs c. forgone income d. all of the above 8. Which of the following would be categorised as an opportunity cost? (i) wages of workers (ii) raw material costs (iii) forgone investment opportunities a. (i) and (iii) b. (iii) only c. (ii) and (iii) d. (i), (ii) and (iii) 9. An a. b. c. example of an explicit cost of production would be: having to give up wages to become an entrepreneur the cost of glass for a lens manufacturer an entrepreneur using their own savings for finance and giving up on the interest payments they were previously getting d. none of the above 10. A production function is a relationship between inputs and: a. revenue b. costs c. profit d. quantity of output 11. Which of the following describes the marginal product of labour? a. the increase in labour necessary to generate a one-unit increase in output b. the increase in output obtained from a one-unit increase in labour c. the additional profit created with a one-unit increase in labour d. the additional cost created with a one-unit increase in labour 12. The a. b. c. d. marginal product of labour can be defined as (where output/ labour labour/ output profit/ labour labour/ total cost denotes ‘change’): 13. Diminishing marginal product of labour occurs when adding another unit of labour: a. increases output but not by as large a margin as previous units of labour b. decreases output c. increases output by more than the margin of previously employed labour d. none of the above are true 14. Which of the following costs do not vary with the amount of output a firm produces? a. marginal costs and average fixed costs b. total fixed costs c. average fixed costs d. total fixed costs and average fixed costs 15. The cost to produce the typical unit of output is the firm’s: a. average total cost b. variable cost c. fixed cost d. marginal cost 16. Average total cost is equal to: a. average fixed cost plus average variable cost b. total cost less total output c. average variable cost plus marginal cost d. average variable cost divided by total output 17. Marginal cost equals which of the following? (i) the average fixed cost of the current unit (ii) the change in total costs divided by change in quantity produced (iii) the change in variable costs divided by change in quantity produced a. (i) and (ii) b. (ii) and (iii) c. (ii) only d. (i), (ii) and (iii) 18. The average fixed cost curve: a. declines as long as it is above marginal cost b. declines as long as it is below marginal cost c. always declines with increased levels of output d. always rises with increased levels of output 19. Diminishing marginal product causes the average variable cost curve to: a. rise b. fall c. rise until it equals the total cost curve d. level out Graph 1 The set of curves above reflect information about the cost structure of a firm. Use this graph to answer the following question(s). 20. Refer to Graph 1. Which of the curves is most likely to represent average total cost? a. A b. B c. C d. D 21. Refer to Graph 1. Which of the curves is most likely to represent average fixed cost? a. A b. B c. C d. D 22. Refer to Graph 1. Which of the curves is most likely to represent average variable cost? a. A b. B c. C d. D 23. Refer to Graph 1. Which of the curves is most likely to represent marginal cost? a. A b. B c. C d. D 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. ANS: A ANS: D ANS: D ANS: A ANS: C ANS: C ANS: D ANS: D ANS: B ANS: D ANS: B ANS: A ANS: A ANS: B ANS: A ANS: A ANS: B ANS: C ANS: A ANS: B ANS: D ANS: C ANS: A Easy Easy Easy Easy Easy Moderate Easy Moderate Easy Easy Easy Easy Easy Easy Easy Easy Moderate Moderate Moderate Moderate Moderate Moderate Moderate REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p 271 271 271 271 272 271 272 272 272 275 275 275 276 278 280 280 280 281 281 281 281 281 281