Ch. 7 Cellular Respiration
advertisement
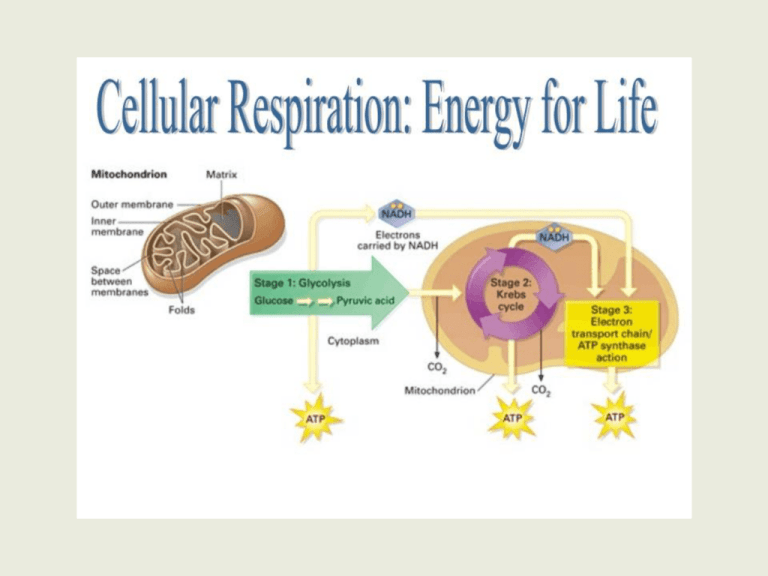
The Equations: Cell Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP) Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 BIG PICTURE OF CELL RESPIRATION: -process by which the mitochondria produce ATP by breaking down organic compounds (food we eat). -cells need “usable” forms of energy to function and maintain homeostasis. ATP is the usable form. Flowchart of Cell Respiration Step 1: Glycolysis Function: -food we eat is converted to pyruvic acid (2 molecules pyruvate). -anaerobic (no oxygen) Location: cytosol of the eukaryotic cell Reactants: organic compounds (food), NAD+ & ADP Products: 2 pyruvic acid (pyruvate) 2 NADH (energy) 2 ATP’s (energy) Energy Yield: 2 ATP’s Step 2 (if oxygen is present): Aerobic Respiration -pyruvic acid is converted to Acetyl Coa prior to entering the Kreb’s Cycle. Function: 1. Krebs cycle- produce NADH & FADH2 2. ETC & Chemiosmosis- produce ATP Location: eukaryotes- Krebs in the mitochondrial matrix & the ETC is in the inner mitochondrial membrane. prokaryotes- cytoplasm & cell membrane Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) Reactants: Acetyl CoA, NAD+ & FAD+ Products: CO2 (given off as a waste product) NADH FADH ATP (2 molecules) Electron Transport Chain & Chemiosmosis (uses enzyme: ATP synthase) Reactants: NADH, FADH2 Products: NAD+ & FAD+ get recycled water (given off as a waste product) ATP (34 molecules) Fermentation: (if no oxygen is present) Two common fermentation pathways: 1. Lactic Acid Fermentation 2. Alcoholic Fermentation Function: -always start with glycolysis -no oxygen is present -NADH NAD+ (recycled back to glycolysis) -produce either lactic acid or alcohol. Location: cytosol *No oxygen = no ATP production. Lactic Acid Fermentation Reactants: pyruvic acid NADH Product: NAD+ lactic acid -Lactic Acid Fermentation is important in the manufacturing of various foods. (yogurt, cheese) -Athletes also experience Lactic Acid buildup…cramping and fatigue. Alcoholic Fermentation Reactants: pyruvic acid NADH Product: NAD+ alcohol -Process occurs in plants and yeast. -This process is important in making bread and alcohol products. Final Analysis: Net production of ATP through aerobic respiration…38 ATP (2 from glycolysis 2 from Kreb’s and 34 from ETC/Chemiosmosis) Aerobic Respiration is much more efficient in producing ATP! Why…oxygen is present.





