File
advertisement

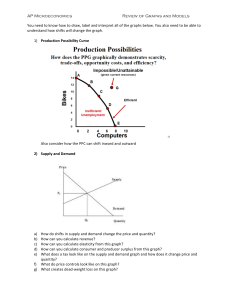
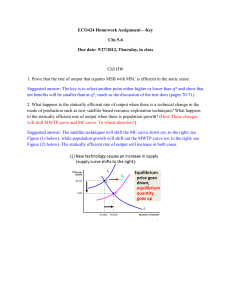
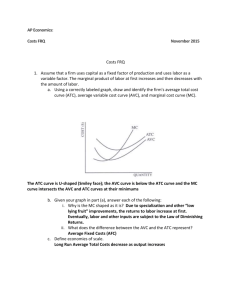
AP Economics Microeconomics Terms Economics Microeconomics Macroeconomics Scarcity Opportunity cost Cost benefit analysis Marginal Efficiency Equity Positive Normative Market economy Traditional economy Command economy Circular-flow diagram Market for Goods & Services Production possibilities Specialization Comparative advantage Absolute advantage Imports Exports Demand Law of Demand Demand curve Quantity demanded Shift determinants Diminishing marginal utility Shift in demand vs. movement along curve Normal good Inferior good Substitutes Complements Ceteris paribus Supply Law of Supply Quantity supplied Supply curve Inputs Equilibrium price/quantity Surplus Shortage Shift in supply vs. movement along curve Indeterminate change Elasticity Inelastic/perfectly inelastic Elastic/perfectly elastic Price elasticity of demand Cross-price elasticity of demand Elasticity of supply Income elasticity Price ceiling Price floor Tax incidence Total surplus Consumer surplus Producer surplus Marginal buyer Tax revenue Deadweight loss Laffer curve Domestic price World price Tariff Quota Externality Negative externality Positive externality Internalizing costs Private solutions Coase theorem Command and control policies Pigovian tax Tradable permits Public good Private good Excludable Rival Natural monopoly Common resource Costs Implicit Explicit Accounting profit Economic profit Total revenue Total costs Fixed costs Sunk costs Variable costs Average costs Marginal costs Production function Marginal product Diminishing marginal product Efficient scale Allocative efficiency Productive efficiency Economies of scale Diseconomies of scale Constant returns to scale Short-run average total costs Long-run average total costs Perfect competition Imperfect competition Monopoly Oligopoly Monopolistic competition Barriers to entry Homogenous good Free entry Perfect substitutes Price taker Zero economic profits Positive profits Negative profits Average revenue Marginal revenue Profit maximization (MR = MC) Shut down rule (P < AVC) Exit rule (P < ATC) Long-run equilibrium Market power Price maker Patent Copyright Socially efficient quantity Price effect Output effect Antitrust laws Price discrimination Perfect price discrimination Oligopoly Duopoly Collusion Cartel Game theory Prisoner’s dilemma Dominant strategy Nash equilibrium Compete vs. cooperate Predatory pricing Advertising Excess capacity Markup Factors market Derived demand Marginal product of labor (MPL) Diminishing marginal productivity Marginal factor cost (MFC) Marginal revenue product (MRP) Least Cost Rule Profit Maximization Rule (factors market) Monopsonist labor market Draw the following graphs using axes below. Remember to clearly label each graph. A. Microeconomics 1. Supply and demand for a market, showing an increase in supply and an increase in demand 2. Market with demand inelasticity and supply elasticity 3. Cost curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive market in long-term equilibrium, with market graph on right 4. Curve showing a negative externality and the increased social cost and decreased benefit 5. Curve showing a positive externality. Show deadweight loss, MPC, MSB, MPB. 6. Consumer surplus / producer surplus 7. International supply and demand, showing world price lower than domestic price and the effect on consumer / producer surplus 8. Binding price ceiling; binding price floor 9. Deadweight loss from tax 10. Cost curve for an individual firm—unregulated monopoly making economic profits. 11. Cost curves for monopolistically competitive firm—short-run and long-run profits 12. Supply and demand showing a leftward shift in demand and a rightward shift in supply, long with new equilibrium P and Q 13. Perfectly Competitive market for labor, showing where MRP = MFC at the equilibrium wage 14. Monopsony market for labor, showing the number of workers at profit maximizing capacity, and the wage. Also show deadweight loss and amount of economic welfare transferred. Most Important Rules to Know for the Micro AP 1. The profit maximizing output for all firms is the point at which MR = MC. 2. The allocatively efficient output is the point at which P = MC. 3. All firms PRICE their goods on the demand curve. If a firm is a price-taker, their demand curve is flat (completely elastic). If the firm is a price-maker, it means their demand curve is downward sloping. Monopolies and monopolistic competition are price makers. 4. Marginal cost is the cost to produce the next unit. The MC curve passes through ATC at the minimum of ATC. When the curve is still below ATC, average costs are falling. When the curve is above ATC, the average costs are rising. 5. For perfect competition, the short-run supply curve for the individual firm is the MC curve starting at average variable costs. The long run supply curve is the MC curve starting a ATC. 6. The shut down rule happens when P < AVC. If the low price continues in the market, eventually the firm faces an exit decision, which happens when P < ATC. 7. Perfect competition is perfect because both the allocatively efficient and productively efficient points are also the profit maximizing point for the firm. 8. In perfect competition, the market drives the firm. Remember to draw side-by-side graphs. 9. Know the difference between the unregulated output (profit-max) for a monopolist and the regulated allocatively efficient output. 10. All firms will hire labor until the value of the goods produced by the last worker is equal to the cost of that worker. The rule is MRP = MFC. (marginal revenue product = marginal factor cost) 11. Monopolistic competition will have short-run profits but in the long run, profits are zero, just like perfect competition. If the monopolistic competitor is willing to advertise, it can differentiate its good, which helps retain pricing power. 12. Firms will use the combination of labor and capital that yields the most utility at the least cost. MU labor/P of labor = MU capital / P of capital. Ten Important Things to Understand About Cost Curves 1. What is the relationship between fixed costs and production? 2. Why do variable costs go up? 3. Why & how are marginal costs related to variable costs? 4. Why do fixed costs become sunk costs? Why is that important to learn outside the field of economics? 5. How does the relationship between ATC and MC work? 6. Why do firms really only care about MC in the short run? 7. Why are MP and MC mirror images of each other? 8. What are economies of scale, constant returns to scale, and diseconomies of scale? How are they related to plant size? 9. Why does ATC fall at first and then rise? 10. When do diminishing marginal returns set in? Why is that an important thing to understand in my life?