Final Lesson Plan
advertisement

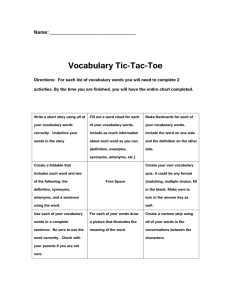
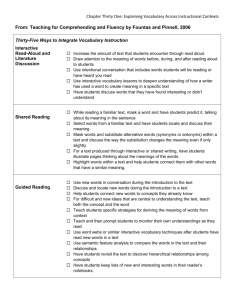
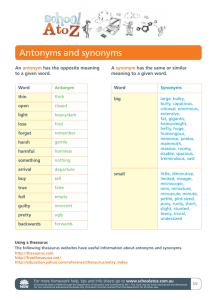
Synonyms and Antonyms Teacher: Lauren Murphy Grade Level: 5th Grade Course Unit: Analogies with Synonyms, Antonyms, and Homophones Lesson Title: Synonyms and Antonyms Length of Lesson: 45 minutes Focus Question/Big Idea/Learning Goals: What do you Learning Objectives: What do you want students to be able want students to be able to know as a result of this lesson? What questions or big ideas drive the instruction? to do as a result of this lesson? Include academic language and vocabulary objectives too. Objectives must be measureable. What are synonyms? How can synonyms be used to enhance writing? What is a resource I can use to find synonyms of a word? What are antonyms? The learner will use synonyms and antonyms correctly within his or her own writing. The learner will be able to write his or her own definition of synonyms and antonyms. The learner will be able to locate synonyms using a thesaurus. STANDARDS: Reference State (Social Studies and Science) Common Core (Math and ELA only) SL.5.1 Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacherled) with diverse partners on grade 5 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. L.5.4c Consult reference materials (e.g., dictionaries, glossaries, thesauruses), both print and digital, to find the pronunciation and determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases. L.5.5c Use the relationship between particular words (e.g., synonyms, antonyms, homographs) to better understand each of the words. Academic Language (discipline specific) – list terms Academic Vocabulary (lesson specific) Synonym- A word or phrase that means exactly Opposite- A person or thing that is totally or nearly the same as another word or phrase. different from or the reverse of someone or something else. Antonym- A word having a meaning opposite to that of another word. Synonymous- the same Adjective- An adjective is the part of speech that Antonymous- different, opposite modifies a noun or a pronoun. Gargantuan-huge Noun- The part of speech that is used to name a Miniscule- small person, place, or thing. Famished- hungry Pronoun- A word that takes the place of a noun, Daring- brave noun phrase, or noun clause. Pre-Assessment: How Hook: How will you catch the Real World Connection: Student Reflection: will you determine prior knowledge? attention of your students and focus their minds on today’s learning goals? How are learning goals relevant to students’ lives? How will you provide for student reflection? Quiz Brain Pop Video: Synonyms, Antonyms, Homophones Students will learn the importance of synonyms to the authors of the books they are reading. They will be able to see how using synonyms makes a work more interesting. Students will be asked to write down why synonyms and antonyms are important in their lives. ASSESSMENT What evidence will you collect that students have mastered the learning objectives? Formative Assessment of Lesson Objectives: How will you monitor and give feedback during the lesson? Be specific. Pre-Assessment Quiz (used to gauge initial level of understanding of the topics) Answers during the Smart Board lesson (matching correct items on the board, using thumbs up/down) Using popsicle sticks with students’ names on them to randomly call on students throughout the lesson in order to get a generalized understanding of what the students in the class know. Summative: How will performance be measured? What evidence will you collect? Check all that apply How will you define mastery? Attach relevant rubrics and grading criteria as needed. 75% or better defines mastery. Project Essay Experiment Short Answer Presentation Multiple Choice Other Assessment requires students to: Check all that apply Organize Writing: Draw Conclusions Connection to: prior learning Interpret Make Generalizations life experiences Analyze Produce arguments Synthesize Evaluate information Academic Feedback: How will you provide feedback to students based upon the data you collected in assessments? Students will be given individual written feedback on each “Opposite Day” assignment. The entire class will be given overall feedback after returning the data that is collected in order to review any common misunderstandings that the class may be having. How do learning segments align with objectives and allow for higher order thinking? What questions do you ask that promote higher order thinking? Learning Segments and Pacing: What strategies, procedures, and transitions, will you use? What essential questions will you address in each segment? How will you begin? Students will begin by taking a preassessment quiz in order to evaluate the level of prior understanding that they have about the topic. synonyms and antonyms are? 5 min. Beginning Essential Questions: What are synonyms? What are antonyms? What are homophones? Can you explain what Time Materials Pre-assessment quiz Middle th e d o c Transition? Synonyms and Antonyms Brain Pop Video (Hook) (5 min.) u m e nt What will you do during the lesson Time 1. Students will actively participate in a 25or Smart Board lesson that teaches the th min. concepts of synonyms and antonyms. e The students will also be introduced to su how to use a thesaurus in the Smart m Board lesson. While being introduced to the thesaurus and how it is similar m and different to a dictionary, the ar students will be given the “Using a y Thesaurus” activity sheets. Each of group of students will be asked to find a several synonyms listed on their sheets. This will serve as a brief n introduction, using collaborative in groups, on how to use a thesaurus. te During the Smart Board lesson, the re students will also be presented with a graphic organizer on the screen that st the teacher will fill in about the in students’ knowledge of synonyms and g antonyms. p oi Essential Questions: What are synonyms? nt How can synonyms be used to . enhance writing? Y What is a resource I can use to find o synonyms of a word? u What are antonyms? ca n 2. The teacher will already have words written on the whiteboard. The p teacher will draw popsicle sticks with os the students names on them. Two iti students will come up to the board at o a time and the teacher will call out a word that the students either have to n find the correct synonym or antonym th of. The student will look on the e whiteboard and try to swat the correct te answer before his or her peer is does. xt 3. Students will be paired up with a b classmate and asked to interview their o partners about 6 adjectives that x describe themselves. The partner will a write down the adjectives, come up with antonyms of the adjectives that n y w Brain Pop video http://www.brain pop.com/english/ grammar/antony mssynonymsand homonyms/ Can you provide a definition for synonyms and antonyms? Evaluate the importance of using a thesaurus for your own writing. Smart Board Lesson http://exchange.s marttech.com/se arch?q=jodie+pri ce&subject=All+s ubjects&grade=A ll+grades&region =en_US& Smart Board Projector Thesauruses “Using a Thesaurus” Activity Sheets Fly Swatters Dry Erase Markers Whiteboard Popsicle Sticks with Names “Opposite Day” sheets his or her partner said, and then create a story using the antonyms about that person and also a synonym for a special word that will be listed on the student’s writing sheet. Before starting, the students will be asked to create and write a definition for synonyms and antonyms at the top of the “Opposite Day” writing sheet. Words for Chant jcschools.net/dyna mic/la/activities/A ntonymRap0101.1 .2.doc Transition? Chant about Synonyms and Antonyms (5 min.) Time 5 min. End How will you close the lesson? Students will be asked to reflect by writing on a piece of paper why and how using synonyms is so important to their writing. The student will then crumble up his or her own piece of paper, toss the paper in a game of snowball, and several students will be asked to read the paper that they received from a peer. What are some problems with an author not knowing many synonyms? Paper Pencils Essential Question: How can synonyms be used to enhance writing? Technology Integration Teacher Strategies – Best Practices Highlight desired bullets; check all that apply Word Processing Power Point Internet Resources Graphics/Charts Internet Research Web 2.0 Tool(s) Interactive whiteboard Other: Highlight desired bullets; check all that apply Student choice Modeling Cooperative learning Independent learning Implementing pre, post, and during lesson activities Teaching metacognitive strategies Hands-on learning/manipulatives utilized Higher-ordering thinking skills Real-world connections Grouping Options: How will your groups be organized? What roles will students fulfill? Check all that apply. Individual Pairs Cooperative Whole Group Criteria charts created (student-driven; supports learning by defining and clarifying a task ) Rubrics created (student-centered) Mentor texts Anchor charts (a reference tool that “anchors” new and ongoing learning to key concepts previously introduced) Research/research materials Evidence of assessment for learning (teacher modifies instruction based on students’ understanding) Academic language used in context Conferencing Other (please explain) Differentiation: How will you differentiate instruction to accommodate individual students’ anticipated learning difficulties, interests, and/or cultural heritage? Students’ individual learning needs will be accommodated by giving lower level vocabulary terms to students during the Smart Board lesson and the fly swat activity. Furthermore, cooperative groups will be used in the thesaurus activity so that students who may be on a lower level are grouped with higher level students in order to advance the lower level students knowledge. The teacher will monitor students with learning difficulties and provide scaffolding during the various activities when needed. Gifted students in the classroom will serve as leaders in their cooperatives groups. The teacher will assign harder vocabulary terms to these students. Intervention: How will you use the results of the Special Situations in the Classroom? Are there any assessment(s) to inform future instruction? management and/or safety issues that need to be considered? The teacher will use the assessments to be able to One student with ADHD should be monitored and redirected understand whether synonyms and antonyms should be in order to ensure that the maximum amount of information reviewed again. Furthermore, the concept of adjectives can be obtained during the lesson. and using them in context will also be a critical area of interest in the student’s writing assignment. The teacher will be able to see from the class’ “Opposite Day” writing samples whether or not the prior objective of adjectives was mastered. Rationale/Theoretical Reasoning: What sources support your pedagogy and methodology? Why have you chosen the strategies you have elected to use? Many different areas of Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences are utilized throughout my lesson. Children will be exposed to bodily-kinesthetic, musical, linguistic, intrapersonal, and interpersonal skills. By using several different types of intelligences, I hope to enhance the learning of students who might not be able to learn as well through only a single type of intelligence such as linguistic. I chose this strategy in order to promote the learning of all individuals in my classroom, as well as bring a higher level of engagement through a wide variety of activities. Furthermore, I used Benjamin Bloom’s Taxonomy of higher order questions in order to elicit a more advanced level of understanding of why synonyms are needed for writers. Finally, Jean Piaget’s theory that knowledge is best created by social and physical interaction is used throughout the span of this lesson. I think that social and physical interactions allow students to retain the information for a longer period of time.