Biomolecules: You are what you eat
advertisement
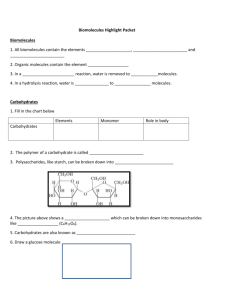
Biomolecules: You are what you eat Obj.: B.9A: Students will be able to compare the structure and function of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Carbon Carbon: it is called the building block life because carbon atoms are the basis of most molecules that make up living things. Carbon is found nearly everywhere! What happens to the food you eat? mitochondri a • Food (made of biomolecules) gets broken down into its basic building blocks or monomers. • Then, it is absorbed into the blood from the small intestines. • Lastly, it is taken up by the trillions of cells in your body to be converted into energy (ATP) or building materials. Definitions: Biomolecules: any molecule that is found in living things. Monomer: a molecule that binds to other molecules to make polymers. Polymer: A large molecule that is made up of smaller molecules called monomers. Element Essential Elements of Life: Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Phosphorus Which is known as the building block of life? Biomolecules 4 Types of Biomolecules or Macromolecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids We eat to produce ATP and building materials! Carbohydrates Made up of C,H,O Function: source of energy Examples: sugar, rice, apples, bread Polymer: polysaccharide (carbohydrates) Monomer: monosaccharide Monosaccharide Lipids Made of C,H,O Function: Store energy Examples: wax, oil, butter, cholesterol Structure: 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids Proteins Made of C,H,O,N Function: Building and repairing cells, speeds up or slows down chemical reactions Examples: meat/muscle, hair, nails, enzymes Polymer: Polypeptide (proteins) Monomer: amino acid Enzymes Proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the cell (catalysts). Catabolism - breaking molecules Anabolism – making molecules Nucleic Acids Made of C,H,O,N,P Function: Store genetic information, determines physical appearance Example: DNA, RNA, ATP (energy) Polymer: nucleic acids Monomer: nucleotides What biomolecule is the following? What biomolecule is the following? What biomolecule is the following? What biomolecule is the following? What biomolecule is the following? What biomolecule is the following? What biomolecule is the following? What biomolecule is the following? Biomolecules Foldable Outside: Label 4 flaps: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids and draw your favorite biomolecule for each (add color) Inside: Label each section: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids and Include the function, elements, structure, and 2 of your own examples for each biomolecule.