unit 5 matt x
advertisement

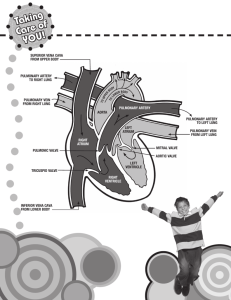
Maria Iqbal Unit 5 Matt Hopton Unit 5 Anatomy & Physiology for Health & Social Care Body Systems In this task I am going to explain what the heart structure and the circulation system is and I am also going to explain what each function does. The Circulation System The circulatory system is made up of vessels and the muscles this helps and also controls the flow of the blood around the body. This process is known as a circulation. The heart, arteries, capillaries and vein are the main parts of the system. Capillaries Capillaries are tiny blood vessels which pass blood from the arteries into the veins. The capillary walls are thin this is so that it allows materials to pass into the capillaries. There are different types of them that exist and perform different functions for the body. They are also able to profuse the tissues of the body with oxygen needed and also important nutrients that are supplied by blood. http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-capillaries.htm 14/10/2010 14:12 pm Red Blood Cells Red blood cells carry oxygen, these cells travel in the blood and start their journey in the lungs, where they pick up oxygen from the air you breathe. It is then travelled to the heart, which pumps out the blood delivering oxygen to all body parts. http://kidshealth.org/kid/word/r/word_red_blood_cells.html 14/10/201015:10pm White Blood Cells White blood cells this defenses the system in the body. These also fight infections and protect our body from other particles; this is because it includes harmful germs and bacteria. White blood cells and the red blood cells this is formed from the stem Maria Iqbal Unit 5 Matt Hopton cell of the bone marrow. They also have a life-span of a couple of days, so when they are destroyed by the other white blood cells and are then replaced with new ones. http://library.thinkquest.org/C0115080/?c=wbc 14/10/2010 15:26pm Blood Blood is a fluid of life, it transports oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues and carbon dioxide from body tissue to the lungs. The average blood that adults have living inside their bodies are about five liters, the function of blood is that it delivers essential elements, courses through the vessels and also removes harmful wastes. So therefore without blood, the human body would stop functioning. The blood is also the fluid of growth, this transport nourishment from digestion and hormones from glands throughout the body. It is also the fluid for health this transport disease from fighting substances to the tissue and the waste to the kidneys. http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/blood.html 14/10/2010 17:09pm Platelets Platelets are tiny cells that are found in the blood. Their function is to help it to clot; they are made in large numbers by the bone marrow which is the spongy material inside the bones. The platelets develop in the bone marrow, it is then released in the bloodstream where it circulates around the body. They usually survive for 7–10 days before either being destroyed by the liver or spleen, or being used to clot the blood. http://www.macmillan.org.uk/Cancerinformation/Cancertreatment/Treatmenttypes/Su pportivetherapies/Platelettransfusions.aspx 14/10/2010 14/10/2010 17:45pm Arteries An artery is an elastic blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart. Pulmonary and systemic these are the two main arteries. The pulmonary artery carries blood from the heart to the lungs where the blood picks up oxygen. The oxygen rich blood is then returned to the heart through the pulmonary veins. Systemic arteries deliver blood to the rest of the body. The aorta is the main systemic artery and the largest artery of the body. It comes from the heart and Maria Iqbal Unit 5 Matt Hopton branches out into smaller arteries which supply blood to the head area this is known as brachiocephalic artery. http://biology.about.com/od/anatomy/ss/artery.htm 14/10/2010 18:00pm Heart The heart is the organ that supplies blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. The heart is located in the upper body which is the chest area between lungs. Blood is pumped away from the heart through arteries and returns to the heart through veins. The heart has four chambers, the upper two chambers of the heart is the right atrium and left atrium, and the lower two chambers is the right ventricle and left ventricle. The right hand side sends blood to the lungs, and the left hand side sends blood to the rest of the body. The valves allow the blood to flow in one direction between the chambers of heart. http://biology.about.com/od/anatomy/a/theheart.htm 14/10/2010 18:42pm Veins A vein is an elastic blood vessel that carries blood from a range of parts of the body to the heart. Veins can be considered into four main types which are: pulmonary, systemic, superficial, and deep veins. The pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart, the systemic veins return deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body to the right atrium of the heart, the superficial veins are to be found close to the surface of the skin and are not located near a related artery and also the deep veins are located deep within muscle tissue and are typically located near a corresponding artery. The venules these are the smallest veins in the body, they receive blood from the arteries passing through the arterioles and also the capillaries. Heart Structure The heart is a muscular cone-shaped organ; it is about the same size of the same person’s clenched fist. It is located in the upper body which is the chest area between the lungs. The apex is pointed downwards, forwards and also pointing towards the left. The hearts main purpose is to pump blood around t he body, it is divided into left and right sections by the septum, the sections for the upper chamber Maria Iqbal Unit 5 Matt Hopton is the left and right atrium and lower chamber is the left and right ventricles. The deoxygenated blood from the body is pumped through the right atrium and the right ventricle to the lungs. While the oxygenated blood from the lungs is pumped through the left atrium and the left ventricle to the body deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the superior vena cava. It is important that blood flows in the right direction through the heart so the structure of the heart has a series of valves include these are the tricuspid. Pulmonary, mitral and aortic valve. http://www.ivy-rose.co.uk/HumanBody/Blood/Heart_Structure.php 15/10/2010 12:03pm Aorta The aorta is the largest artery in the body, it arises from the left ventricle of the heart which then forms an arch and extends down to the abdomen, where it branches of into two smaller arteries. The aorta also carries and distributes oxygen rich blood to all arteries. Pulmonary artery The pulmonary artery carries blood away from the heart and carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. It extends from the right ventricle and the branches into the left and right pulmonary arteries, the left and right pulmonary arteries also extend to the left and right lung. Pulmonary vein Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium. There are four pulmonary veins which extend from the left atrium to the lungs, these are the right superior, right inferior, left superior and also the left inferior. Left atrium The left atrium is located in the upper chamber of the heart. It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it down into the left ventricle which delivers it to the body. Maria Iqbal Unit 5 Matt Hopton Right Atrium The right atrium is the upper chamber of the heart. It receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the vena cava and is pumped into the right ventricle, it is then sent to the lungs to be oxygenated. Inferior vena cava The inferior vena cava is a large vein that receives blood from the legs, the back and the walls and contents of the abdomen and pelvis; it then delivers it to the right atrium of the heart. . Mitral Valve The mitral valve controls the flow of blood between the two chamber son the left side of the heart. This is the left atrium and the left ventricle. It allows blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, but not back the other way. Tricuspid valve The tricuspid valve controls the opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle. As the right atrium contracts, the tricuspid valve opens, it allows the blood to eject into the right ventricle. When the atrium stops contracting, the tricuspid valve closes, in that way it prevents a backwash of blood into the right atrium this is also known as regurgitation. Left Ventricle The left ventricle is the lower chamber of the heart, which receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium and pumps it to the aorta and through the body. Right ventricle The right ventricle is the lower chamber of the heart, which receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the main pulmonary artery. Maria Iqbal Unit 5 Matt Hopton Aortic Valve The aortic valve is one of the four valves in the heart, it is located at the exit of the left ventricle of the heart where the aorta begins. The aortic valve also lets blood from the left ventricle be pumped up and ejected into the aorta but prevents blood once it is in the aorta from returning to the heart. Pulmonary Valve The pulmonary valve is one of the four valves in the heart, it stands at the opening from the right ventricle in the pulmonary artery trunk. It lets blood flow in the right direction towards the lungs, it also keeps it from splattering back from the pulmonary artery into the heart. Maria Iqbal Unit 5 Matt Hopton References http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=5129 http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-capillaries.htm . http://kidshealth.org/kid/word/r/word_red_blood_cells.html http://library.thinkquest.org/C0115080/?c=wbc http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/blood.html http://www.macmillan.org.uk/Cancerinformation/Cancertreatment/Treatmentty pes/Supportivetherapies/Platelettransfusions.aspx brachiocephalic artery. http://biology.about.com/od/anatomy/ss/artery.htm http://biology.about.com/od/anatomy/a/theheart.htm http://www.ivy-rose.co.uk/HumanBody/Blood/Heart_Structure.php