Carbohydrates Review

Carbohydrates Review
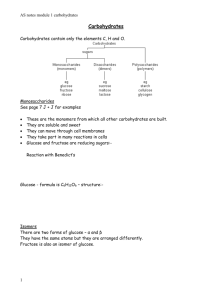
Carbohydrates
1 . What is a Carbohydrate ?
A carbohydrate is any of the group of organic compounds consisting carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1.
Examples include sugar, starch, cellulose, and gums.
Carbohydrates
This structure represents a polymer.
2. What are the individual units called?
They are called monomers
Carbohydrates
3. What does poly mean?
Poly means ‘many’ and polymer means ‘many pieces.’
4. What does mono mean?
Mono means ‘one’ and monomer means ‘one piece.’
Carbohydrates
5. Saccharide comes from the Greek word
‘sakkaron.’ What do you think the word means?
Saccharide means sugar.
6. What does monosaccharide mean?
Monosaccharide means one sugar.
Carbohydrates
7. Monosaccharides are also known as ‘simple sugars.’ Name at least three monosaccharides .
Glucose (also known as blood sugar) Gl
Fructose (also known as fruit sugar) Fr
Galactose (also known as brain sugar)
Ribose (a sugar found in RNA)
Deoxyribose (a sugar found in DNA)
Ga
R
D
Carbohydrates
8. What does disaccharide mean?
Disaccharide means two sugars.
9. Name three common disaccharides .
Sucrose (also known as table sugar)
Maltose (also known as malt sugar)
Lactose (also known as milk sugar)
Carbohydrates
10. Disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharides. What monosaccharides make up the following disaccharides?
Sucrose: Glucose + Fructose
Gl Fr
Maltose: Glucose + Glucose
Gl Gl
Lactose: Glucose + Galactose
Gl Ga
Carbohydrates
11. Name four common polysaccharides and the role each plays in living organisms.
Glycogen Made of glucose monomers; how animals store excess sugar.
Starch Made of glucose monomers; how plants store excess sugar.
Cellulose Made of glucose monomers; main component of cell walls in plants.
Chitin Made of modified glucose monomers; main component in cell walls of fungi and exoskeletons of arthropods
Carbohydrates
12. Where is glycogen found in animals?
Glycogen is mainly stored as granules in liver and muscle cells.
13. Where is starch found in plants?
Starch is mainly stored as starch grains inside plant cells.
Carbohydrates
14. List some ways that starch differs from cellulose?
a. The glucose monomers in starch are aligned in the same direction, while in cellulose every other glucose is inverted.
Starch Cellulose
Every other glucose is inverted (flip-flopped)
Carbohydrates
15. List some ways that starch differs from cellulose?
a. The glucose monomers in starch are aligned in the same direction, while in cellulose every other glucose is inverted.
Starch
Cellulose
Hydrogen bonds b. The flip-flopping of glucose monomers in cellulose allow hydrogen bonds to form between strands
Carbohydrates
16. Describe a simple test for detecting monosaccharides (simple sugars) in food.
a. Put blended samples of the food in a test tube filled with blue Benedict’s reagent.
b. Place the test tube in a hot water bath for
5 minutes.
If monosaccharides (like glucose) are present, the blue color will turn an orange/red color.
Carbohydrates
17. Describe a simple test for detecting starch in food.
a. Put blended samples of the food in a test tube.
b. Pour some yellow Lugol’s reagent (also known as iodine-potassium iodide solution or IKI) in the test tube.
If starches are present, the yellow color will turn a dark blue to black.
Carbohydrates
This structure represents starch.
18. What sugar makes up its monomers?
Glucose
Carbohydrates
This structure represents starch.
19. What are the bonds that link the glucose monomers called?
The bonds are glycosidic linkages
Carbohydrates
This structure represents starch.
20. What molecule is released when a glucose monomer is added to the starch polymer?
(Click once to see animation)
A water molecule is released
Carbohydrates
This structure represents starch.
21. What molecule must be added in order to remove a glucose monomer from the starch polymer?
(Click once to see animation)
A water molecule is added
Carbohydrates
22. Name a food or object that contains the following carbohydrates.
Sucrose:
Lactose:
Starch:
Cellulose:
Table sugar, syrup, honey, candy
Milk, ice cream, cheese
Bread, potatoes, pasta
Seeds, vegetables, fruit, wood, cotton