Physical Examination of the Upper Extremities

Physical Examination of the
Upper Extremities
Prof.Dr.Hidayet Sarı
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
Department
Shoulder Examination
ANATOMY
• Bones
• Joints
• Muscles
• Bursae
• Nerves
• Blood supply
Bony Anatomy
Anterior
Bony Anatomy
Posterior
SHOULDER JOINTS
1.
Glenohumeral
2.
Scapula thoracic
3.
Acromio-clavicular
4.
Sterno-clavicular
•
Bony Anatomy
Joints and Articulations
STATIC STABILIZERS
– Deltoid
– Rotator cuff
– Teres major
Clinical Anatomy
– Latissimus dorsi
– Biceps
– Pectoralis muscles
Clinical Anatomy
• Rotator Cuff
– S upraspinatus ABD
– I nfraspinatus ER
– T eres minor ER
– S upscapularis IR
Depress humeral head against glenoid to allow full abduction
Clinical Anatomy
• Bursae
– subacromial
– subdeltoid
– subscapular
Physical Examination
• Inspection
• Palpation –pression
• Range of motion examination
• Neurological examination
• Special tests for the shoulder problems
• Examination of the related areas
Shoulder Inspection
• Anterior side
• Posterior side
• Lateral side
• Medial side
Physical Exam
Inspection
• Front & back
• Height of shoulder and scapulae
• Muscle atrophy, asymmetry
SHOULDER PALPATION and
PRESSION
• Bones
• Joints
• Muscles
• Bursae
• Nerves
• Lymph nodes
SHOULDER Range Of Motion
• Flexion-180 degree
• Extension -45 degree
• Abduction -180 degree
• Adduction -30 degree
• Internal rotation -90 degree
• External rotation -90 degree
Physical Exam
Range of Motion
• Forward flexion:
– 0 o – 180 o
• Extension
– 0 o – 40 to 60 o
Physical Exam
Range of Motion
• Internal rotation
– 80-90 o
Physical Exam
Range of Motion
• External rotation
– 80-90 o
Speed shoulder tests
External rotation Internal rotation
Neurological Examination of the
Shoulder
Muscle tests :
• Flexion
• Extension
• Abduction
• Adduction
• Internal rotation
• External rotation
Muscle testing scoring
• 0 No contraction
• 1 Flicker or trace contraction
• 2 Active movement, with gravity eliminated
• 3 Active movement against gravity
• 4 Active movement against gravity and resistance
• 5 Normal power
Shoulder Abduction muscle test
Shoulder flexion and extension muscle test
Shoulder external and internal rotation muscle test
Shoulder abduction and adduction muscle test
Neurological Examination of the
Shoulder sensory tests :
• C4
• C5
• C6
• C7
• C8
• T1
• T2
Special Tests for the Shoulder
Problems
• Yergason test –biceps tendinitis
• Neer impingement test-acromioclavicular impingement
• Drop arm test –rotator cuff tear
• Resisted flexion (Speed)test –biceps tendinitis
• Resisted abduction(Supraspinatus) testsupraspinatus lesion
• Aprehension test –glenohumeral joint instability
Yergason test
• Yergason test for biceps tendon instability or tendonitis.
• The patient's elbow is flexed to 90 degrees, and the examiner resists the patient's active attempts to supinate the arm and flex the elbow.
Drop Arm Test
• Passive abduction to 90 °
• Instruct patient to slowly lower arm
• At 90 ° abducted arm will suddenly drop, may need to add slight pressure
• (+) drop = (+) test
SHOULDER PAIN
SPECIAL TESTS
• Neer
– PASSIVE
– Forced forward flexion of arm with internally rotated shoulder
– Test is positive if pain occurs at same point as with active forward flexion
Speed’s Maneuver
• Forward flex the shoulder against resistance while maintaining the elbow in extension and the forearm in supination. Pain or tenderness in the bicipital groove in dicates bicipital tendinitis.
Rotator Cuff Strength Testing
• Weakness on exam
• Grade strength on 0→5 scale
• Compare to other side
Supraspinatus testing
Apprehension Test/Relocation Test
Differantial Diagnosis for shoulder pain
• Subacromial impingement syndrome
• Adhesive capsulitis –frozen shoulder
• Biceps tendinopati
• Bursitis
• Rotator cuff pathology
• Glenohumeral joint pathology
• Acromioclavicular joint pathology
• Sternoclavicular joint pathology
• Myofascial pain syndrome
• Radiating or referred pain from cervical spine
Subacromial Impingement
• Neer proposed that 95% of rotator cuff tears are due to chronic impingement between the humeral head and the coracoacrominal arch.
Subacromial Impingement
• Stage 1 disease consists of edema and hemorrhage of the tendon due to occupational or athletic overuse, and is reversible under conservative treatment.
Subacromial Impingement
• Stage 2 disease shows progressive inflammatory changes of the rotator cuff tendons and the subacromial-subdeltoid bursa, and can be treated by removing the bursa and dividing the coracoacromial ligament after failed conservative management.
ELBOW EXAMINATION
• Anatomy
• Evaluation
• Inspection-Observation
• Palpation-Pression
• Range of motion
• Neurological examination
• Special tests
• Examination of related areas
ELBOW ANATOMY
• Bones
• Joints
• Ligaments
• Muscles
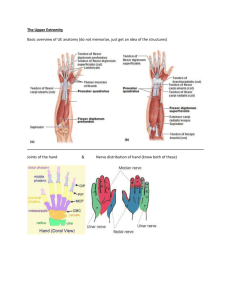
Elbow Anatomy
Medial Elbow
Elbow Anatomy
Lateral Elbow
ELBOW Anatomy
EVALUATION
INSPECTION
• Anterior –posterior side
• Medial-lateral side
• Carrying angle
• Swelling
PALPATION and PRESSION
Bone palpation :
• Lateral epicondyle
• Radial head
• Medial epicondyle
• Olecranon
SOFT TISSUE PALPATION
Medial aspect
• Ulnar nerve
• Wrist flexor –pronator group
• Medial collateral ligament
Lateral aspect
• Wrist extensors (ECRL-ECRB)
• Lateral collateral ligament
• Annular ligament
SOFT TISSUE PALPATION
Anterior aspect
• Cubital fossa
• Brachial artery
• Median nerve
• Musculo-cutaneus nerve
Posterior aspect
• Olecranon bursa
• Triceps tendon
ELBOW ROM
• Flexion -135 degree
• Extension -0 degree
• Pronation -90 degree
• Supination -90 degree
NEUROLOGICAL
EXAMINATION
Muscle tests:
• Flexion - Extension
• Pronation - Supination
Sensation tests
• C5-C6-C7-C8-T1
Reflex test:
• Biceps reflex –C6
• Brachioradial reflex –C6
• Triceps reflex-C7
Elbow Reflex testing
• Biceps reflex –C6
• Brachioradial reflex –C6
• Triceps reflex-C7
SPECIAL TESTS
• Ligament tests (varus-valgus stres test)
• Tennis elbow test
• Golfers elbow test
• Tinels sign for ulnar nerve
Ligament tests (varus-valgus stres test)
Tennis elbow test
Golfers elbow test
Tinels sign for ulnar nerve
COMMON ELBOW PROBLEMS
• Lateral epicondylitis
• Medial epicondylitis
• Olecranon bursitis
• Fractures
• Triceps tendinitis
• Post immbolization capsular tightness
(contracture)
EXAMINATION of the WRIST and HAND
Anatomy
• Surface anatomy
• Skeletal anatomy
• Fibrous anatomy
• Muscles
• Nerves
• Blood supply
Bony
Anatomy
• Phalanges: 14
• Sesamoids: 2
• Metacarpals: 5
• Carpals
– Proximal row: 4
– Distal row: 4
• Radius and Ulna
Lister’s tubercle
ANATOMY
• Surface anatomy
• Palmar surface
• Radial border
• Thenar surface
• Thumb –index-middle-ring-small fingers
• Hypothenar surface
• Dorsal surface
• İnterosseus muscle
JOINTS
• Radio-carpal
• Ulna-carpal
• İnter-carpal
• Metacarpo-phalangial (MCP)
• Proximal inter-phalangial (PIP)
• Distal inter-phalangial (DIP)
Muscles
EVALUATION
• History
• Inspection-Observation (dorsum of the hand-palm of the hand )
• Palpation-Pression
• Range of motion
• Functional assessment
• Neurological examination
• Special tests
• Examination of related areas
INSPECTION
Palmar Surface
• Creases
• Thenar and Hypothenar
Eminence
• Arched Framework
• Hills and Valleys
• Web Spaces
Palpation-Pression
ROM EXAMINATION
• Forearm pronation-90 degree
• Forearm supination -90 degree
• Wrist flexion (palmar flexion)-90 degree
• Wrist extension (dorsal flexion )-90 degree
• Wrist radial deviation -30 degree
• Wrist ulnar deviation -20 degree
RANGE OF MOTION
Wrist
• Flexion
• Extension
• Radial deviation
• Ulnar deviation
– Ulnar deviation is greater than radial
FINGERS ROM
MCP joint :
• Flexion -90 degree
• Extension -20 degree
PIP joint :
• Flexion -90 degree
• Extension -0 degree
DIP joint :
• Flexion -80 degree
• Extension -0 degree
• Flexion
• Extension
• Abduction
• Adduction
• Opposition
THUMB ROM
NERVES and BLOOD SUPPLY
• Radial nerve
• Median nerve
• Ulnar nerve
• Radial artery
• Ulnar artery
COMMON PROBLEMS
• Fractures
• Tenosynovitis :
1.
Thumb extensors –De Querveins disease
2.
Finger flexors tenosynovitis
3.
Finger extensors tenosynovitis
• Arthritis
1.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
2.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
–bouchards nodes
-heberdans nodes
- First MCP OA-Rhizarthrosis
DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis
• Inflammation of EXT
Pollicis Brevis and ABD
Pollicis Longus tendons
• Tenderness 1st
Dorsal Compartment
• Finkelstein’s Test
Rheumatoid Arthritis
• MCP swelling
• Swan neck deformities
• Ulnar deviation at
MCP joints
• Nodules along tendon sheaths
Osteoarthritis
• Heberden’s nodes:
DIP
• Bouchard’s nodes:
PIP
COMPRESSION
NEUROPATHIES
• Median nerve compression syndrome carpal tunel syndrome (tinel and phalen test )
• Pronator syndrome
• Ulnar nerve compression syndromes compression at the elbow ulnar tunel syndrome
Compresssion at the wrist Guyon canal syndrome
• Radial nerve compression syndromes
Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome
Superficial radial nerve entrapment
SPECIAL TESTS
• Finkelsteins test –De Quervein tenosynovitis
• Tinel test –CTS, UTS
• Phalens test –CTS
Carpal Tunnel Tests
• Neurologic exam
– Median nerve sensation and motor
• Phalen’s Test: both wrists maximally flexed for 1 minute
• Tinel’s Test
EXAMINATION of the RELATED
AREAS
• Cervical spine
• Shoulder
• Elbow
• Arteries ,veins ,lymph
• gallbladder stone
• Heart