Overview- Lecture 4 Research Methods
advertisement

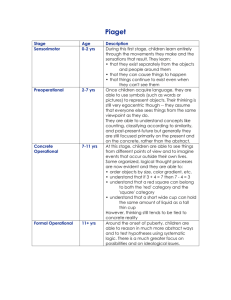
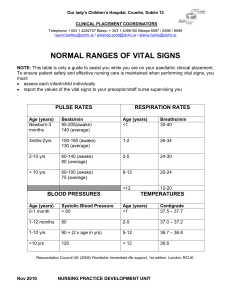
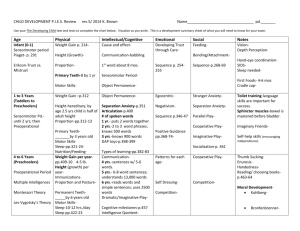
Overview- Lecture 4 Research Methods • • • • • Research Designs: Review of the Basics Developmental Research Designs Measurement Effects: Confounds Better Ways? Psychometrics Overview- Lecture 4 Research Methods • • • • • Research Designs: Review of the Basics Developmental Research Designs Measurement Effects: Confounds Better Ways? Psychometrics Simple Correlational Designs Basic Concepts •Two variables •Statistic can range from -1 to +1 •Cannot infer cause-effect relationships Basic Concepts Simple correlation- Positive . .. . . . .. . . . . . . .. . . . . . . Reaction time Age Basic Concepts Simple correlation- Negative Depression .. . .. . . .. . . . .. . . . . . . .. Age Experimental Designs Design Basics Independent •Variable that is manipulated Variable •Characteristic along which people differ Dependent •Variable that is observed Experimental Designs Experimental design •Manipulation of independent variable •Respondents randomly assigned to groups •Determine cause and effect Quasi-experimental design •Compare groups on predetermined characteristic •Cannot draw cause and effect conclusions •Used in most studies of aging Overview- Lecture 4 Research Methods • • • • • Research Designs: Review of the Basics Developmental Research Designs Measurement Effects: Confounds Better Ways? Psychometrics Developmental Research Designs Basic Designs Cross-Sectional Design Longitudinal Design Cross-sectional Design Year of test 1970 Year of birth 1980 1990 2000 1920 50 yrs. 60 yrs. 70 yrs. 80 yrs. 1930 40 yrs. 50 yrs. 60 yrs. 70 yrs. 1940 30 yrs. 40 yrs. 50 yrs. 60 yrs. Longitudinal Design Year of test 1970 Year of birth 1980 1990 2000 1920 50 yrs. 60 yrs. 70 yrs. 80 yrs. 1930 40 yrs. 50 yrs. 60 yrs. 70 yrs. 1940 30 yrs. 40 yrs. 50 yrs. 60 yrs. Overview- Lecture 4 Research Methods • • • • • Research Designs: Review of the Basics Developmental Research Designs Measurement Effects: Confounds Better Ways? Psychometrics Measurement Effects: Confounds Effects Term Definition Index of: Change within individual Age Chronological age, measured in years Cohort Year or period of birth Influences relevant to history Time of measurement Time of testing Current influences Measurement Effects: Confounds Basic problem: Cannot separate “age” from “time” Design Longitudinal Cross-Sectional Confound Seem to measure age “changes” but.. Age effects cannot be separated from historical change Age effects may be Measures age group differences due to cohort differences because… Overview- Lecture 4 Research Methods • • • • • Research Designs: Review of the Basics Developmental Research Designs Measurement Effects: Confounds Better Ways? Psychometrics Better Ways? Sequential Research Designs (Shaie’s Designs) • Involve a “sequence” of designs • Allow inferences to be made about age effects and historical influences (cohort effects and time of measurement/test year effects) Sequential Research Designs: Schaie’s “Most Efficient Design” Comparison of Designs Design Factor 1 Factor 2 Time sequential Age Test Year Cohort sequential Age Cohort Cross sequential Cohort Test year Alternative Sequential Designs (Baltes) Cross-Sectional Sequences Year of test 1970 Year of birth 1980 1990 2000 1920 50 yrs. 60 yrs. 70 yrs. 80 yrs. 1930 40 yrs. 50 yrs. 60 yrs. 70 yrs. 1940 30 yrs. 40 yrs. 50 yrs. 60 yrs. Alternative Sequential Designs (Baltes) Longitudinal Sequences Year of test 1970 Year of birth 1980 1990 2000 1920 50 yrs. 60 yrs. 70 yrs. 80 yrs. 1930 40 yrs. 50 yrs. 60 yrs. 70 yrs. 1940 30 yrs. 40 yrs. 50 yrs. 60 yrs. Correlational Approaches: Multivariate Correlational Designs • Multiple variables • Causal relationships estimated Correlational Approaches in Research on Aging: Multivariate Correlational Designs Types Multiple regression analysis •Predictor variables used to estimate dependent variable •Can suggest and test causal relationships Structural equations •Diagram a set of relationships •Test data against hypothesized model Correlational Approaches in Research on Aging: Multivariate Correlational Designs See text page 68 Overview- Lecture 4 Research Methods • • • • • Research Designs: Review of the Basics Developmental Research Designs Measurement Effects: Confounds Better Ways? Psychometrics Measurement Issues: Psychometrics Psychometrics Forms of reliability Test-retest Test gives consistent responses Give test on two occasions Internal consistency Test items yield similar answers Content Forms of validity Factual content Test measures what it measured correctly is supposed to Construct measure Scores fit with theory Criterion Scores predict actual performance Need to be established on all age groups tested