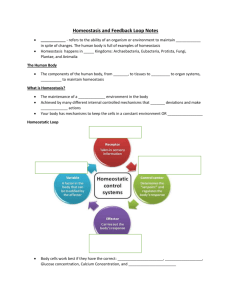
Homeostasis, Feedback mechanism and Enzymes
advertisement

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CLv3SkF_Eag refers to the ability of an organism or environment to maintain stability in spite of changes. The human body is full of examples of homeostasis. Homeostasis happens in all Kingdoms: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia The Human Body Humans require many systems for digestion, respiration, reproduction, circulation, excretion, movement, coordination, & immunity The components of the human body, from cells, to tissues to organs to organ systems, interact to maintain homeostasis. The maintenance of a constant environment in the body. Achieved by many different internal controlled mechanisms that detect deviations and make corrective actions. Your body has mechanisms to keep the cells in a constant environment OR Dynamic Equilibrium Homeostatic Loop: EXAMPLE Feedback Mechanisms In order to maintain homeostasis, the body uses feedback loops There are two types: 1. Negative Feedback 2. Positive Feedback Feedback Mechanism NEGATIVE FEEDBACK LOOP POSITIVE FEEDBACK LOOP (DECREASES EFFECTS) (INCREASES EFFECTS) Stimulus produces a response which reduces the original stimulus. (used for homeostasis) Most are in this category ◦ Examples: ◦ Sweating (reduces being hot) ◦ Shivering (reduces being cold) ◦ Blood Sugar (reduces sugar in blood) ◦ Stomata's and guard cells in plants (reduce water loss in transpiration) Stimulus produces a response which increases the stimulus. Examples: ◦ Drug addicts (needs more drugs) ◦ Apple ripening (ethylene is increased) ◦ Hormone produced to speed up contractions in childbirth (increases faster childbirth) Negative Feedback Mechanism Stimulus 1. Initial Hormone is Released 2. Stimulates 2nd Hormone to release 3. Inhibits further release of initial hormone Increase in Body Temperature Positive Feedback Mechanism Stimulus 1. Initial hormone is released 2. Stimulates 2nd hormone to release 3. Inhibits further release of initial hormone The release of oxytocin to intensify the contractions that take place during childbirth.[ Difference Between Negative and Positive Feedback Loops Negative feedback: the response is moved to the target set point Example: Thermostat turns on the A/C when the house get too hot. 1. Glucose (Blood sugar regulation) 2. Stomata in plants and guard cells in plants; regulates transpiration Positive feedback: the response is moved away from the target set point Example: Speakers, sound going into microphone is processed to produce a magnified response sound coming out of the speakers. 1. Childbirth (Labor) 2. Breastfeeding 3. Blood Pressure 3. Drug Addiction 4. Hunger 4. Fruit Ripening 5. Temperature Regulation 6. pH Balance Worksheet