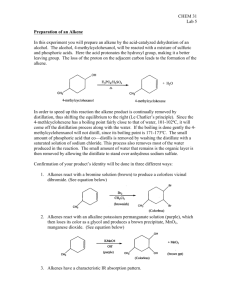
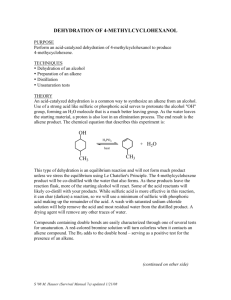
Experiment 13:
advertisement

Experiment 12: BASE PROMOTED ELIMINATION OF HBR FROM AN ALKYL HALIDE Br Base ROH + + Objectives To synthesize an isomeric mixture of alkenes from “E2” base promoted elimination of HBr from 2-bromoheptane under reflux. To purify the products through simple distillation. To study the effect of base size on product distribution using GC analysis. To identify characteristic absorptions in the IR spectra of reactants and products. CHEMICAL EQUATION Br 2-Bromoheptane MF: C7H15Br MW: 179.1 o bp: 180 C Base ROH + + MF: C7H14 MF: C7H14 MF: C7H14 MW: 98.2 MW: 98.2 MW: 98.2 bp: 94 oC bp: 98 oC bp: 98-99 oC d: 0.697 g/mL d: 0.701 g/mL d: 0.708 g/mL d: 1.14 g/mL Dehydrohalogenation of 2-bromoheptane. MECHANISM 1. Base oxygen attacks and removes a proton from carbon adjacent to bromine… Br Ha Ha Hb C H b + Hb b OH ALL STEPS OCCUR IN A CONCERTED FASHION! ROH + a + a b a 2. …C=C bond forms… 3. …bromine is eliminated from the opposite side of the molecule. MECHANISM (MOST SUBSTITUTED ALKENE ISOMER) Br C H H H H Base H + HBase + • Removal of more hindered proton, leading to more stable, more highly substituted alkene. • MAJOR product for small base, MINOR product for large base! Br MECHANISM (LEAST SUBSTITUTED ALKENE ISOMER) Br C H H H H Base H + HBase + Br • Removal of least hindered proton, leading to a less substituted alkene product. • MAJOR product for large base, MINOR product for small base. STERIC HINDRANCE The reason that the bulkier (larger) base gives more of the less substituted alkene is that steric hindrance prevents it from approaching a hydrogen on a more highly substituted carbon. OVERVIEW Heat alkyl bromide and assigned base in solvent under reflux to synthesize products. Purify products by simple distillation to remove unreacted starting materials. Prepare GC sample. Analyze and determine product ratio using GC results. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (SYNTHESIS) CaSO4 drying tube in thermometer adapter • Add 2-bromoheptane and alcohol solvent to 25 mL flask w/3 boiling chips. • Clamp flask to ring stand. • Add solid base to flask using powder funnel. water out •Place the condenser on the flask. •Using a thermometer adapter, place a CaSO4 drying tube in the top of the condenser. water in • Begin water flow, apply heat. heating mantle • Reflux the solution for 60 minutes. to voltage regulator iron ring • Cool flask using a beaker of tap water. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (PURIFICATION) • Once cooled, arrange a simple distillation apparatus. Keck clips here! • Apply water flow and heat. water out water in Heating Mantle iron ring to voltage regulator • Remember to clamp both flasks to ring stand! • When the first drop reaches the receiving flask, mark the temperature (Ti). • Collect ~5 mL in the receiving flask. • Read the temperature again (Tf). Remove the heat. • Prepare a GC sample. Table 12.1 GC Retention Times (min) and Adjusted Area Percent Compound Standard Rt SMALL BASE (methanol/sodium methoxide) Sample Rt Area Percent Adjusted Area Percent LARGE BASE (t-butanol/potassium t-butoxide) Sample Rt Area Percent Adjusted Area Percent methanol t-butanol --- 1-heptene trans-2heptene cis-2-heptene • Remember to get data from the opposite alcohol/base pair! EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (IR Analysis) Br IR spectra on page 103 of lab manual! Table 12.2 Functional Group C-Br stretch sp3 sp2 CH stretch CH stretch Alkene C=C stretch Base Values (cm-1) 500-700 2850-3000 3000-3100 1600-1680 2bromoheptane 1heptene cis-2heptene trans-2heptene Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) SAFETY CONCERNS Sodium methoxide and potassium tbutoxide are strong bases and corrosive! Use gloves when handling! Methanol and t-butanol are flammable! Wear safety goggles at all times and use extreme caution when heating! WASTE MANAGEMENT After adding water to the reaction flask, pour this and product solution into container labeled “LIQUID ORGANIC WASTE”. CLEANING… Clean round bottom flasks with soap/water/wash acetone. Clean all remaining reflux/distillation glassware with wash acetone ONLY while in your lab hood! DO NOT REMOVE THIS GLASSWARE FROM YOUR HOOD! Funnel and beaker can be cleaned with soap/water/wash acetone. LABORATORY NOTEBOOK (Pre-lab) • OBJECTIVE (Must clearly state…) •What compounds you will make and how • How you will purify the compound • How you will determine the purity of your compound • CHEMICAL EQUATION Include the general chemical equation from page 99. •TABLE OF PHYSICAL DATA (Complete the following table using MSDS sheets from a site on WWW Links ONLY. Wikipedia is unacceptable) Compound 2-bromoheptane cis-2-heptene trans-2-heptene 1-heptene methanol t-butanol sodium methoxide potassium t-butoxide MW (g/mol) • REFERENCE TO PROCEDURE bp (Co) 180 d (g/mL) 1.14 XXX XXX XXX XXX (Must include…) •full title, including edition and authors •page numbers where actual procedure can be found HAZARDS Flammable, irritant LABORATORY NOTEBOOK (In-lab) • DATA/CALCULATIONS • • • • • • • Initial weight of 2-bromoheptane used Initial weight and identity of base used Theoretical yield calculation (not just the value!) Physical state and color of product GC vial slot # GC sample solvent identity Give an example of an adjusted area % calculation • EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE • • In paragraph form, briefly describe the procedure that you actually followed during the lab. Paragraph must be written in PAST TENSE, PASSIVE VOICE. • Include ACTUAL volumes or weights of chemicals used during the experiment. • Include any mistakes, accidents, or observations if necessary.