Chapter 9 notes
advertisement

Chapter 9
AP Calculus BC
9.1 Power Series
1 1 1 1 ... 1
2 4 8 16
1 1 1 1 1 ...
2 3 4 5
111111... ???
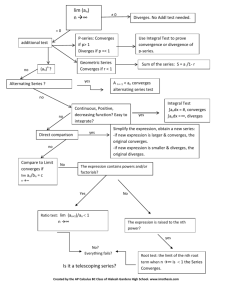
If the sequence of partial sums has a limit
S, as ninfinity, then we say the series
Converges to S. Otherwise it Diverges.
Infinite Series:
ak a1 a2 a3 ... an ...
k 1
a1, a2 are terms
an is the nth term
Partial Sums:
S1 a1
S2 a1 a2
S3 a1 a2 a3
n
Sn ak
k 1
Geometric Series:
a ar ar 2 ar3 ... ar n1 ...
converges if r 1 and
diverges if r 1
ar n1
n1
Interval of convergence : -1 < r < 1
Is the IOC for Geom. Series.
converges to sum
a
1 r
Representing functions by series:
If x 1, then the Geometric Series formula assures us that:
1 x x2 x3 x4 ... xn ... 1
1 x
xn is a Power Series centered at x=0 and it converges on the interval (-1,1)
n0
Definition of a Power Series: An expression of the form:
cn xn c0 c1x1 c2 x2 ... cn xn ... is a Power Series centered at x=0.
n0
cn (x a)n c0 c1(x a)1 c2(x a)2 ... cn(x a)n ...
n0
Given:
is a Power Series centered at x = a.
Find a Power Series for:
If x 1,
1 x x2 x3 x4 ... xn ... 1
1 x
1 on (1,1)
1 x
x
1 x
1
1 2x
Again,
Given:
If x 1,
1 x x2 x3 x4 ... xn ... 1
1 x
Find a Power Series for:
1
(1 x)2
Now, write down the series for:
and use it to write one for :
Answer:
nxn1
n1
1
1 x
ln(1 x)
(1)n xn1
Answer: n 1
n0
Copy down Theorem 1 p. 478 and Theorem 2 p. 479
9.2 Taylor Series
P( x) a0 a1x a2 x2 a3x3 a4 x4
Given:
P(0) 1
P '(0) 2
P ''(0) 3
P '''(0) 4
P IV (0) 5
Find the Taylor Polynomial…..
P( x) 1 2x 3 x2 2 x3 5 x4
2
3
24
Find the 4th order Taylor Polynomial of
ln(1 x)
Construct a Power Series for:
Taylor Series generated by f
at x=0:
Answer:
sin x
and
cos x
at x = 0
nth term answers:
2n1
sin x (1)n x
(2n 1)!
n0
2n
cos x (1)n x
(2n)!
n0
f k (0)
n (0)
f
''(0)
f
'''(0)
f
2
3
n
f (0) f '(0) x
x
x ...
x ...
xk
2!
3!
n!
k 0 k !
9.2 cont’d.
p. 489 Taylor Series centered at x = a.
Copy it down!!!!
p. 491 5 most important series: Copy them down, know them!!!
Occasionally you need 6, 7…….
9.3 Taylor’s Theorem
Adequate substitution: a Taylor series that
is off from the actual by less than 0.0001
Truncation Error:
NEXT TERM!!!!
If f has derivatives of all orders in an open interval, I, containing a,
then for each positive integer, n, and for each x in the interval:
n (a)
f
''(
a
)
f
2
f ( x) f (a) f '(a)( x a)
( x a) ...
( x a)n Rn( x)
2!
n!
n1(c)
f
Where: Rn ( x) (n 1)! ( x a)n1 Largest value of derivative..f part
If Rn ( x) 0 as n for all x in I, we say that the Taylor Series
generated by f at x = a converges to f on I.
Theorem 4 – Remainder Estimation Theorem. (do examples)
9.4 Radius of Convergence
A convergent series is a number and may be treated as such….
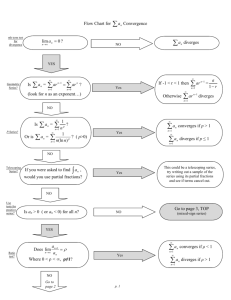
Theorem 5 - Convergence Theorem for Power Series -There are 3 possibilities for
cn( x a)n
n0
1. There is a R such that the series diverges for x a R but
converges for x a R. The series may or may not converge at the endpoints.
2. The series converges for every x. (R=)
3. The series converges at x = a, but diverges elsewhere. (R=0)
R = radius of convergence and the set of x-values for which the series
converges is called the Interval of Convergence.
Theorem 6 – nth term test
for divergence
a 0.
an diverges if nlim
n
n1
9.4 cont’d.
Direct Comparison Test (DCT) (non-negative terms)
Greatest Power Rules!!!!!
Let an be a series with no negative terms...
(a) an converges if there is a convergent series cn with an cn
(b) an diverges if there is a divergent series dn with an dn
Absolute Convergence - If the series an of absolute values converges,
then an converges absolutely.
Theorem 8…..
Ratio Test – (Powers and Factorials)
an1
Let an be a series with terms and with nlim
L
an
Then: (a) the series converges if L < 1.
(b) the series diverges if L > 1.
Telescoping series:
(c) the test is inconclusive if L = 1.
p. 510……
9.5 Testing Convergence at Endpoints
Theorem 10 - Integral Test - Let {an} be a sequence of terms.
Suppose that an f (n), where f is a cts., , decreasing function of x.
Then the series
an and the Integral N f ( x)dx either
n N
both converge or both diverge.
1
P-series test: n p converges if p > 1, diverges if p 1.
n1
Limit Comparison Test (LCT) Suppose that an 0, bn 0:
an c, 0 c , then a & b both converge or diverge
(1) If nlim
n
n
b
n
an 0, and b converges then a converges.
(2) If nlim
n
n
b
n
an , and b diverges then a diverges.
(3) If nlim
n
n
b
n
9.5 cont’d.
Alternating series Test (Liebniz’s Theorem)
The series
(1)n1un u1 u2 u3 u4 ...
n1
converges if all three of the following conditions are met:
(1) Each un is positive.
(2) un un1 for all n...
Error is next term sign
(3) nlim
u 0.
n
included…………
Look at examples 4 -6 pp. 518 - 520
Absolute and Conditional Convergence……