MEASUREMENT Power Point
advertisement

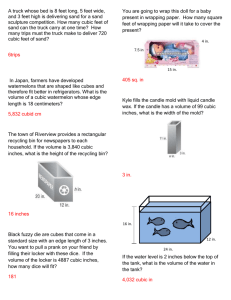
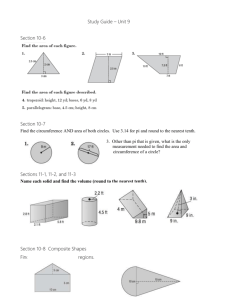
In the U S A the system of weights and measured first adopted was that of the English, though a few differences came in when decisions were made at the time of standardization in 1836. For instance, the wine-gallon of 231 cubic inches was used instead of the English one (as defined in 1824) of about 277 cubic inches. The U S A also took as their standard of dry measure the old Winchester bushel of 2150.42 cubic inches, which gave a dry gallon of nearly 269 cubic inches. Even as late as the middle of the 20th century there were some differences in UK and US measures which were nominally the same. The UK inch measured 2.53998 cm while the US inch was 2.540005 cm. Both were standardized at 2.54 cm in July 1959, though the U S continued to use 'their' value for several years in land surveying work - this too is slowly being metricated. 4 inches= 1 hand 1.98 hands= 1 link 1.5151 links= 1 foot 3 feet= 1 yard 2yards= 1 fathom 2.75 fathoms= 1 rod, pole, or perch 4 rods= 1 chain 10 chains= 1 furlong 1.0909 furlongs= 1 cable’s length 7.333 cable’s length’s = 1 mile 1.1508= 1 international nautical mile Make the following conversions: 1 yard= ____ links 1 fathom= ____ poles 1 international nautical mile= ____ furlongs 1 mile= ____ inches 144 square inches= 1 square foot (ft2) 9 square feet= 1 square yard (yd2) 272 1/4 square feet= 1 square rod 9 (sq rd) 160 square rods= 1 acre 640 acres= 1 square mile (mi2) 1 mile square= 1 section of land 36 sections= 1 township 1 square yard= ____ square inches 1 township= ____ acres How many square feet is the Pekin township? 33.6003 cubic inches= 1 pint (pt) 2 pints= 1 quart 8 quarts= 1 peck 3.2143 pecks= 1 cubic foot (ft3) 1.2444 cubic feet= 1 bushel (bu) 21.6972 bushels= 1 cubic yard 9 (yd3) 1 quart= ____ cubic inches 32 pints= ____ cubic feet 1 bushel= ____ quarts 20 minims (min)= 1 fluid scruple 3 scruples= 1 fluid dram (fl dr) 1 1/3 fluid drams= 1 teaspoon 3 teaspoons= 1 tablespoon 2 tablespoons= 1 fluid ounce (fl oz) 4 fluid ounces= 1 gill 4 gills= 1 pint 2 pints= 1 quart 4 quarts= 1 gallon 2 gallons= 1 peck 4 pecks= 1 bushel 8 bushels= 1 quarter 1 gill= ____ scruples 500 minims= ____ tablespoons 80 tablespoons= ____ pints 1 bushel= ____ gills 20 grains= 1 scruple 1.2 scruples= 1 pennyweight 1.393 pennyweights= 1 dram 16 drams= 1 ounce (oz) 1.0971 ounces= 1 ounce troy (oz t) 12 ounces troy= 1 pound troy (lb t) 1.2153 pounds troy= 1 pound (lb) 100 pounds= 1 hundredweight 1.12 hundredweight's= 1 long hundredweight 17.8571 long hundredweight's= 1 ton 1.24 ton= 1 long ton 40 grains= ____ drams 1 pound= ____ ounces troy 2000 pounds= ____ ton(s) 1 ounce= ____ pennyweights Le Systeme international d’Unites was adopted by nearly every country in the world in October 1960. It is based upon 7 fundamental units. We will look at 3 of them, 2 of which are metric units. They are: the meter (the distance light travels, in a vacuum, in 1/299792458 of a second), the kilogram (the mass of an international prototype in the form of a platinum-iridium cylinder kept at Sevres in France), and the Kelvin (1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water). Here are some common prefixes used in the metric system. yotta, zetta, exa, peta, tera, giga, mega, kilo, hecto, deka, (Y), (Z), (E), (P), (T), (G), (M), (k), (h), (da), 10 24 10 21 10 18 10 15 10 12 10 9 10 6 10 3 10 2 10 1 deci, centi, milli, micro, nano, pico, femto, atto, zepto, yocto, (d), (c), (m), (u), (n), (p), (f), (a), (z), (y), 10 –1 10 –2 10 –3 10 –6 10 –9 10 –12 10 –15 10 –18 10 –21 10 –24 Units of length 10 millimeters (mm) = 1 centimeter (cm) 10 centimeters = 1 decimeter (dm) 10 decimeters = 1 meter (m) 10 meters = 1 dekameter (dam) 10 dekameters = 1 hectometer (hm) 10 hectometers = 1 kilometer (km) 46 hm = ____ cm 11 m = ____ km 1 m 2 = ____ cm 2 Units of area 100 square millimeters (mm 2 ) = 1 square centimeter (cm 2 ) 100 square centimeters = 1 square decimeter (dm 2 ) 100 square decimeters = 1 square meter (m 2 ) 100 square meters = 1 square dekameter ( dam 2 ) 100 square dekameters = 1 square hectometer ( hm 2 ) 100 square hectometers = 1 square kilometer ( km 2 ) Units of liquid volume 10 milliliters ( mL ) = 1 centiliter ( cL ) 10 centiliters = 1 deciliters ( dL ) 10 deciliters = 1 liter ( L ) 10 liters = 1 dekaliter ( daL ) 10 dekaliters = 1 hectoliter ( hL ) 10 hectoliters = 1 kiloliter ( kL ) CONVERT 30 mL = ____ L 1400 mg = ____ g 3m 3 = ____ mm 3 Units of dry volume 1000 cubic millimeters ( mm 3 ) = 1 cubic centimeter ( cm 3 ) 1000 cubic centimeters = 1 cubic decimeter ( dm 3 ) 1000 cubic decimeters = 1 cubic meter ( m 3 ) Units of mass 10 milligrams ( mg ) = 1 centigram ( cg ) 10 centigrams = 1 decigram ( dg ) 10 decigrams = 1 gram ( g ) 10 grams = 1 dekagram ( dag ) 10 dekagrams = 1 hectogram ( hg ) 10 hectograms = 1 kilogram ( kg ) 1000 kilograms = 1 megagram ( Mg ) or metric ton 32 degrees Fahrenheit is the freezing point of water at sea level 212 degrees Fahrenheit is boiling point of water at sea level 0 degrees Celsius is the freezing point of water 1oo degrees Celsius is the boiling point of water 273 Kelvin is the freezing point of water 373 Kelvin is the boiling point of water 86 degrees F = ____ degrees C 29 degrees Celsius = ____ Kelvin 60 seconds= 1 minute 60 minutes= 1 hour 24 hours= 1 day 28, 29, 30, or 31 days= 1 month 12 months= 1 year 10 years= 1 decade 10 decades= 1 century 10 centuries= 1 millennium How many seconds in a year? First: Answer a couple of questions! Which measurement system do you think is more reliable? Justify your answer! What are some reasons for the international community of scientists development of SI? Second:Create your own units of measurement for length and mass! Provide a standard you would base the measurements on. Name the unit! Show at least five examples of how you would use the measurements in everyday life. STATE GOAL 11: Understand the processes of scientific inquiry and technological design to investigate questions, conduct experiments and solve problems. STATE GOAL 13: Understand the relationships among science, technology and society in historical and contemporary contexts. Any pictures, sounds, or movies used in this presentation were taken from a link off of the credits listed below and are to be used for educational purposes only. • • • • • • • • • • http://www.frogstar.com http://www.wavplace.com http://www.wavcentral.com http://www.ask.com http://www.soundamerica.com http://www.clipartconnection.com http://www.movietunes.com http://www.cbul.com/tileindex.com http://www.clicksahoy.com http://www.ditto.com