Exam 1d - University of Missouri
advertisement

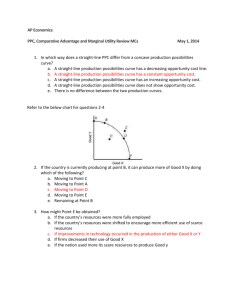
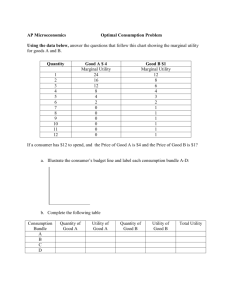
Ag Econ 1041 First Exam, 130 points September 23, 2010 Name _____KEY_____________________ 11 a.m. Section True/False – one point each T 1. T 2. T 3. T T T 4. 5. 6. T T 7. 8. F T 9. 10. T T 11. 12. F T 13. 14. T F F T F T 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. The production possibilities curve shows the greatest amount of two goods that can be produced. The opportunity cost of a choice or decision is the highest valued alternative foregone. Any production levels below the production possibilities curve are not as efficient as possible. Scarcity forces individuals to make choices that have opportunity cost(s). “Ceteris paribus” is a Latin term that means “other things being equal.” As we consume more French fries our marginal utility will eventually decline. which at least partially explains a downward sloping demand curve. Trade is how we acquire goods including income and food. The law of demand specifies an inverse relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and its price. If the demand curve for a product moves to the left, the demand has increased. The opportunity cost of producing a good tends to increase as more of it is produced because resources less suitable to its production must be employed. Markets require laws to clarify the rules of exchange. Hamburgers and hot dogs are substitutes but hamburgers and French fries would be considered complements. Gasoline and motor oil would be considered substitute products. If two goods are complements, a decline in the price of one will cause an increase in the demand for the other. Incentives are created to motivate people and/or institutions. Prices do not help us allocate resources. Utility has no relationship to demand. Marginal utility can decline even as total utility increases. An increase in the price of cotton increases the supply of t-shirts. If the demand for Levis increases, their price will rise. 1 Multiple choice are two points each __A___ 21. Assuming Pepsi and Coke are substitutes and the price of Pepsi goes down, one would expect a) A decrease in demand for Coke b) An increase in the supply of Coke c) A decrease in the supply of Coke d) An increase in the demand for Coke __B___ 22. The supply curve for a product would probably shift to the right if a) Resources used in production became more costly b) The technology of production improved c) The price of the good decreased d) Some sellers left the market __C___ 23. If both demand and supply were to increase, then a) Quantity exchanged would fall and price would rise b) Quantity exchanged and price would both fall c) Quantity exchanged would rise and price might rise or fall d) Quantity exchanged and price would both rise __B___ 24. The demand curve for most products is downward sloping which indicates the relationship between price of a product and the quantity demanded of that product is a) Positive b) Inverse c) Direct d) Constant __D___ 25. Which of the following is likely to cause an increase in market efficiency? a) No price information b) Restrictions on trade c) A lack of information d) Clear standards and measurements __B___ 26. If the supply curve for a product shifts to the right there has been a) An increase in demand b) An increase in supply c) A decrease in demand d) A decrease in supply 2 __A___ 27. If incomes of consumers increase, one would expect a) The demand for theater tickets to shift to the right b) The quantity demanded of theater tickets to increase c) The price of theater tickets to decrease d) The supply of theater tickets to decrease __B___ 28. Which of the following causes the demand for hot dogs to increase? a) A decline in the price of hot dogs b) An increase in the price of hamburgers c) An increase in the price of hot dog buns d) A decrease in the wages of hot dog makers __D___ 29. Which of the following is most likely to cause an increase in the supply of kiwi fruit? a) An increase in consumer disposable income b) An increase in the price of kiwi fruit c) The development of an improved variety of apples that tastes like kiwi fruit d) The development of improved varieties of kiwi fruit which result in higher yields per acre __B___ 30. The resulting effect on equilibrium price will be indeterminate if a) Supply decreases and demand increases b) Both supply and demand increase c) Demand decreases and supply increases d) Supply increases while demand remains the same 3 Matching – one point each L N M O K T J S I R H Q G D F E P C B A 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. Margin Opportunity cost Utility Scarce good Demand Production possibilities Ceteris paribus Market Inelastic demand Quantity supplied Price Equilibrium Supply Input cost Comparative advantage Consumer goal Marginal utility Substitute Revenue Inefficient A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. Q. R. S. T. Below PPC Price x quantity sold A replacement Determinant of supply MU/MCa = MU/MCb… Lowest opportunity cost Direct or positive relationship of P & Q Universal measure of value P increase causes revenue increase Other variables unchanged Willingness and ability to buy Edge, where change occurs Value to individual(s) Foregone alternative(s) Has a price or cost Incremental change in utility Qs = Qd Increases as price rises Where exchange is arranged What could be produced Short answers – five points each 51. Diagram the change in the ethanol market from corn price increases. $/Q or P S1 S P1 P0 D 0 Q1 Q0 Q 4 52. Diagram what happens in the market for snow skiing equipment as winter approaches. $/Q or P S P1 P0 D 0 Q0 Q D1 Q 53. Diagram the situation for the prescription drug market knowing only that income is increasing substantially. P S P1 P0 D 0 Q0 Q1 D1 Q 5 54. The supply of computers is increasing and prices are falling. Diagram completely, showing price and quantity outcomes. P S S1 P0 P1 D 0 Q0 Q1 Q 55. What are marginal costs? ∆ in costs or incremental costs 56. Specifically state how a person makes an efficient decision. MU a > MU any other choice MC MC 57. Draw a PPC or PPF and show the opportunity cost of increasing tomato production when lettuce is the only other good produced. lettuce AL PPC BL 0 At Bt tomato 6 58. What is the true cost of any decision we make? Opportunity cost 59. What happens to revenue if the price of a good rises and the good has inelastic demand? Revenue increases 60. Diagram the impact and what caused the impact of increased lumber prices on the market for furniture. $/Q or P S1 S P1 P0 D 0 Q1 Q0 Q 7 61. Draw a PPC for Jeromie’s Collectibles and Cakes. Now show what happens if Jeromie enlarges his kitchen and buys more cake decorating equipment. collectibles PPC0 0 PPC1 cake 62. If Jeromie gives up less value to be a TA than his older brother, Jeromie possesses a ____comparative _______ ____advantage_________________ for being a TA. The following question is valued at 10 points 63. Finish the equation or statement a) % ∆ Qd ÷ % ∆ P = ___Ep own price elasticity of demand_______________________ b) If the % change in quantity demanded is greater than the relative change in price, demand is __elastic____________________________ c) Demand reflects the _buyer or consumer__________ side of the market. d) Marginal utility will eventually ____diminish______________________________ e) Lowest opportunity cost = ___comparative advantage________________________ 8