WM52_S_MN_R1
advertisement

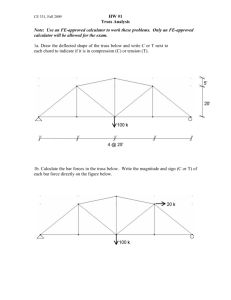
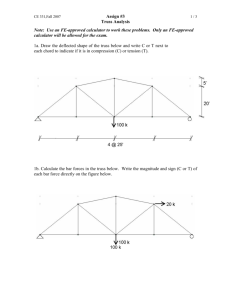
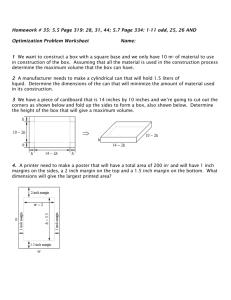
NASA-Threads Work and Mechanics Lesson 52: Truss Design Truss Member Materials and Dimensions Watch truss fabrication movie, review the truss dimensions below, and provide truss building materials to teams. compressive members tensile members Specimen Dimensions: member length = distance between holes member width = ½ inch cut strips 1 inch longer than “member length” punch 7⁄32 inch diameter holes ½ inch from ends glue stiffeners to sides of member; cut stiffeners about 2 inches shorter than the “member length” Paper Mat Board Provided to Each Team: mat board strips pre-cut to ½ inch wide length provided should be about 6 times the span Specimen Dimensions: member length = distance between holes cut strips 1 inch longer than “member length” member width = ½ inch at ends member width narrows to ¼ inch at center make narrow region at least 1 inch long glue 1 inch mat board pieces to each end punch 7⁄32 inch diameter holes ½ inch from ends File Folder Material Provided to Each Team: one file folder uncut OR precut strips ½ inch wide if precut strips are provided, then provide each team with a length about 5 times the span Aluminum Screw Posts Provided to Each Team: a total of 12 screw posts, with the option of getting more as needed 2 screw posts 1/8 inch long 5 screw posts 3/16 inch long 5 screw posts ¼ inch long Tools Supplied by Students: scissors flat head screw driver ruler Tools Supplied by Instructor: hot glue gun (low temp) with glue sticks 7/32 inch heavy-duty hole punch Paper cutter (if folder strips are not pre-cut) NASA-Threads Work and Mechanics Lesson 52: Truss Design Design Tips You choose your favorite truss design and think about the number of members that you would like to use. A truss with more members is harder to build, but it looks really cool! 1. Howe truss with 21 members 2. Howe truss with 13 members and 45 degree angles 3. Howe truss with 13 members and low angles 4. Howe truss with 13 members and high angles 5. Center member removed; truss with 12 members and high angles 6. Simplest possible truss with 3 members (this is a Kingpost truss with the vertical center member missing) Zero Force Members: The center vertical members in trusses 1 through 4 above are zeroforce members. That is, they theoretically carry zero load. They are included to make the truss more stable. Since you don’t have to worry about stability very much (due to the transparent side plates on the truss testing apparatus), zero force members may not increase the strength of your truss very much. Your truss analysis will tell you whether or not a member is a two force member, but a general rule is provided below. Spotting Two Force Members: When three members intersect at a joint and two of the members are co-linear (they are in line with one another), then the third member is a zero-force member if no external load or reaction is applied at the joint. Design Work Spend the rest of class working on your design (you may start on fabrication if you are ready).